- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
May 25, 2024 Current Affairs
IIT Madras-incubated ePlane Company is expected to launch electric Vertical Take-Off and Landing (eVTOL) aircraft in Bengaluru.
electric Vertical Take-Off and Landing Aircraft (eVTOL):
- eVTOLs are designed to take off and land vertically, which allows them to operate effectively in congested urban areas.
- These aircraft utilize electric propulsion to achieve lift and controlled flight, significantly reducing noise and air pollution compared to traditional aircraft.
- eVTOLs are equipped with electric motors that drive rotors or propellers. These are arranged in various configurations to provide lift and enable movement in all directions.
- The power for these aircraft is supplied by energy storage systems, commonly lithium-ion batteries, which store the necessary energy for both lift-off and flight.
- They employ distributed electric propulsion technology, integrating multiple motors with the airframe to enhance efficiency and ensure safety. This technology has developed from advancements in motor, battery, fuel cell, and electronic controller technologies.
- The typical seating capacity of eVTOLs can include configurations like six-seaters and eight-seaters, highlighting their role in low-altitude urban air mobility for a small number of passengers.
- eVTOLs have a wide range of applications including air taxis, cargo transport, emergency medical services (EMS), and recreational purposes.
- They promise to significantly enhance on-demand urban air mobility (UAM), improving connections between city centers and airports, and addressing issues like traffic congestion and accessibility.
Applications and Benefits:
- Air taxis and delivery services can utilize eVTOLs to bypass road traffic, offering faster and more efficient transportation options.
- Medical assistance and emergency services can greatly benefit from the quick response capabilities of eVTOLs.
Birth anniversary of Kartar Singh Sarabha was recently celebrated.
Kartar Singh Sarabha:
- An Indian revolutionary, born on 24 May 1896 in Village Sarabha, Ludhiana.
- Nicknamed ''General'' by Sohan Singh Bhakna, President of the Ghadar Party.
Key Contributions:
- Became a member of the Ghadar Party (founded in Oregon in 1913) and edited the Urdu version of Ghadar into Gurmukhi script.
- Delivered pistols and ammunition to the Ghadar Party President for attacking the British, involved in the Komagata Maru incident.
- Charged in the First Lahore Conspiracy Case and executed in 1915 along with compatriot Vishnu Ganesh Pingle.
Honour:
- In 2020, the Punjab Government renamed Ludhiana-Pakhowal Road to Shaheed Kartar Singh Sarabha Marg.
Ministry Of Renewable Energy Issued A Warning To Farmers On PM-KUSUM Website Against Fake Websites And Mobile Applications.
- The Ministry of Renewable Energy recently issued a warning to farmers on PM-KUSUM website against fake websites and mobile applications that provide fake online application forms and demand registration fees for installing solar water pumps under PM Kusum scheme.
PM-KUSUM Scheme:
- The PM-KUSUM Scheme was launched in 2019 for de-dieselisation of the farm sector and enhancing the income of farmers.
- It is aimed at ensuring energy security for farmers in India, along with honouring India’s commitment to increase the share of installed capacity of electric power from non-fossil-fuel sources to 40% by 2030 as part of Intended Nationally Determined Contributions (INDCs).
- The scheme aims to add Solar capacity of about 34,800 MW by March 2026 with the total Central Financial support of Rs 34,422 crore.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE)
- Under the Scheme, a central government subsidy upto 30% or 50% of the total cost is given for the installation of standalone solar pumps and also for the solarization of existing grid-connected agricultural pumps.
- Further, farmers can also install grid-connected solar power plants up to 2MW, under the Scheme on their barren/fallow land.
- This scheme is being implemented by the designated departments of the State Government.
The Scheme consists of three components:
Component A:
- 10,000 MW of solar capacity through the installation of small Solar Power Plants of individual plants of capacity up to 2 MW.
- The solar power plants will be preferably installed within five-kilometre radius of the notified sub-stations in order to avoid high cost of transmission lines and losses.
- The power generated will be purchased by the local DISCOM at a pre-fixed tariff determined by the respective State Electricity Regulatory Commission (SERC).
Component B:
- Installation of 20 lakhs of standalone Solar Powered Agriculture Pumps.
- Individual farmers will be supported to install standalone solar Agriculture pumps of capacity up to 7.5 HP for the replacement of existing diesel Agriculture pumps / irrigation systems in off-grid areas, where grid supply is not available.
- The State Government will give at-least subsidy of 30% and the remaining will be provided by the farmer.
Component C:
- For Solarisation of 15 Lakh Grid Connected Agriculture Pumps.
- Under this Component, individual farmers having grid connected agriculture pump will be supported to solarise pumps.
- The farmer will be able to use the generated solar power to meet the irrigation needs and the excess solar power will be sold to DISCOMs at pre-fixed tariff.

Eligible categories for KUSUM Scheme are:
- An individual farmer.
- A group of farmers.
- FPO or Farmer producer organization.
- Panchayat.
- Co-operatives.
- Water User Associations.
A recent study challenges the perceived heart health benefits of fish oil supplements rich in omega-3 fatty acids, raising concerns about their impact on cardiovascular health.
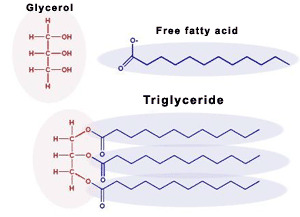
Fatty Acids:
- Fatty acids are the building blocks of the fat in our bodies and in the food we eat.
- During digestion, the body breaks down fats into fatty acids, which can then be absorbed into the blood.
- Fatty acid molecules are usually joined together in groups of three, forming a molecule called a triglyceride.
- Triglycerides are also made in our bodies from the carbohydrates that we eat.
- The two main types of fatty acids are saturated fat and unsaturated fat.
- Saturated fats are sometimes known as “bad” or “unhealthy” fats because they increase your risk of certain diseases like heart disease and stroke.
- Unsaturated fats (polyunsaturated and monounsaturated) are considered “good” or “healthy” fats because they support your heart health when used in moderation.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids:
- Omega-3 fatty acids (omega-3s) are polyunsaturated fats that perform important functions in your body.
- Your body can’t produce the amount of omega-3s you need to survive.
- So, omega-3 fatty acids are essential nutrients, meaning you need to get them from the foods you eat.
- They are found in foods, such as fish and flaxseed, and in dietary supplements, such as fish oil.
- The three main omega-3 fatty acids are alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
- ALA is found mainly in plant oils such as flaxseed, soybean, and canola oils. DHA and EPA are found in fish and other seafood.
- Omega-3s are important components of the membranes that surround each cell in your body.
- DHA levels are especially high in retina (eye), brain, and sperm cells.
- Omega-3s also provide calories to give your body energy and have many functions in your heart, blood vessels, lungs, immune system, and endocrine system (the network of hormone-producing glands).
- Omega-3s in fish and fish oil supplements may help with symptoms of several autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and Crohn''s disease.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies