- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
Mid-Oceanic Ridges
The study of ocean floor has been made through various underwater expeditions and explorations. These underwater explorations have shown very contrasting and spectacular features inside the seas and oceans. When there is a Tsunami, everyone will say that it is due to the origin of earthquake below the sea floors. It is also a fact that the Earth’s tectonic processes are happening along the plate boundaries. These boundaries are very distinct lithological portions existing below the seas and oceans. The modern ocean floor maps have provided enormous opportunities to understand these underwater features. They also helped us to know the theories behind the earth’s ongoing tectonic processes.
Ocean’s morphological features vary with reference to their site, location, origin, morphology, lithology and dynamics of the water masses.
- The general profile of oceans include the Continental Shelf, Continental Slope and the Deep Ocean basins. Each one of these have their own variations in spread, depth, slope and hydrodynamics.
- The life in the marine waters depend on the depth, air-sea interactions, radiation, hydrodynamics, morphology and the physico-chemical conditions of the oceans.
- The Circulation of ocean waters, as waves and currents, and the interaction of oceans with the atmosphere, have very significant effects on the weather and climate of the entire globe.
- There are several kinds of distinct and most striking features observed on the ocean bottoms.
- These underwater relief features are very essential to our human understanding about the earth, oceans, oceanic crusts, tectonic processes and their impacts.
Among them, the Mid Ocean ridges are very unique structures.
The Mid Ocean Ridges, as the name implies, exist mostly in the middle of the ocean basins, where the divergent plate boundaries are located. The theory of Plate Tectonics has indicated many major tectonic processes which also include:
- the release of convection currents along Divergent Plate Boundaries,
- the origin of Mid Ocean ridges and
- the spreading of the sea floor.
All these processes are everlasting phenomena on the Planet Earth.
Major Oceanic Relief features
The painstaking ocean floor mapping Project of Bruce Heezen and Marie Tharp after the Second World War has shown the distinguishing underwater features of the world’s oceans. It is really a thought provoking highly heterogeneous relief system seen below the seas and oceans.
The profile of the oceans has shown innumerable curves, dips, ridges, valleys, mountains, plateaus, trenches, fractures and canyons.
The following major kinds of features have been observed based on the ocean floor expeditions and explorations made during the last 100 years.
They are: – Oceanic abyssal plains, Oceanic trenches, Oceanic plateaus, Oceanic fracture zones, Seamounts and Mid ocean ridges
- An Abyssal Plainis an underwater plain located on the deep ocean floor. It is usually found at depths between 3000 m and 6000 m. These are the flattest, smoothest and least explored regions on the planet earth. Abyssal plains lie generally between the foot of a continental rise and a mid-ocean ridge.
- Oceanic Trenchesare long, narrow topographic depressions of the sea bed. They are the boundary zones of lithospheric plates. An oceanic trench is a type of convergent boundary at which two lithospheric slabs meet. Trenches are generally parallel to the volcanic arcs. Oceanic Trenches extend 3 to 4 km deeper below the level of the surrounding ocean floor. The greatest depth is seen at the Challenger Deep of the Marianas Trench in the northwest Pacific Ocean. It extends upto a depth of 10911 m below the sea level. There are about 30 notable trenches existing in different oceans of the globe.
- AnOceanic Plateau is a large relatively flat region under the marine waters. They rise well above the average level of the seabed. There are about 16 oceanic plateaus existing in different regions of the oceans.
- A seamountis an underwater mountain rising from the ocean floor. It does not reach the water surface. Hence, it is not an island. Some of them are formed from extinct volcanoes. A seamount rises from 1000 m to 4000 m depth of water. There are about 100,000 seamounts existing across the globe.
- Submarine Canyonsare long narrow and deep valleys cutting across the continental shelves and slopes. The depth of these Canyons may range from 600m to 3000m.
Among these, the Mid Oceanic Ridges are the most remarkable features existing along the Divergent plate boundaries. These are underwater mountain chains. They are not similar to the mountains of continents. The Mid Oceanic ridges cover about 23% of the earth’s surface. Their origin, extent and distribution are essential aspects to be studied in oceanography and physical geography.
Mid-ocean ridge
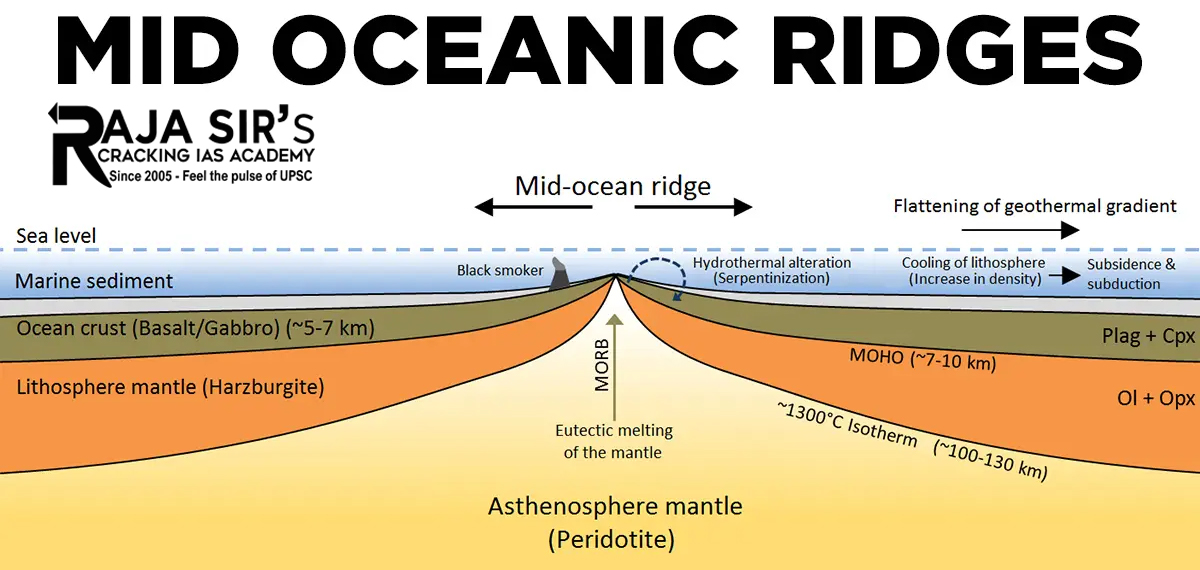
One of the most striking features of the ocean floor is the distribution of mid oceanic ridges. These ridges are mountain-like structures standing well above the deep ocean floors. The mid oceanic ridges are, in total, 65,000 km long and cover almost 23% of the earth’s surface. These are considered as the world’s largest mountain ranges existing below marine waters. They exist as chains, in the centre of the oceanic basins. These are rugged features. They stand 1 to 3 km above the deep ocean floors. The most prominent feature of a ridge is its steep-sided central valley called rift valley. A rift valley may be 25 to 50 km wide and 1 to 2 km deep in its profile. The rift valley of a mid oceanic ridge is bordered by rugged mountains with the tallest peaks. These peaks may rise upto 2 km above the sea surface also as seen in some locations. Upwelling of molten mantle rock has created these rift zones.
The mid oceanic ridges are formed along the boundary between two divergent tectonic plates. These zones are tectonically active regions. Hence, small earthquakes occur frequently on crests of mid ocean ridges. These earthquakes coincide with the location of the central rift valleys. They are the most active volcanic regions on the earth.
At the mid oceanic ridges, two plates move away from each other. This process is called as sea-floor spreading and it creates a new seafloor. Ocean basins were formed through such breakup of continents and movement of plates. Thick continental crust was subjected to heat flow from earth’s interior. When the warm mantle expands, the continental crust is domed and stretched away from each other thereby forming the rift valleys. Some form of thermal convection within the asthenosphere appears to create
- New lithosphere at the oceanic ridges and rises. This simultaneously made the old lithosphere back into the mantle to be subducted beneath oceanic trench systems.
- The spreading rates of mid ocean ridges may be 2-3 cm per year. A mid ocean ridge has a steeper and more irregular topography as a result of a low spreading rate. The ridge consists of a high central axial zone, with a narrow crest.
- The mid ocean ridges and rises are offset by rugged fault scars called fracture zones. These linear bands of mountains and troughs intersect all oceanic ridges at intervals in right angles.
- The system of mid-ocean ridges ranks with the continents and ocean basins as one of the three main units exposed at the earth’s surface. They are – the topography, structure, areal extent and geological importance.
- The Mid-Atlantic ridge is the best known example in the world.
- It is 40,000 miles long encircling the whole world.
- The mid-Atlantic Ridge is centrally located between the eastern and western margins of the Atlantic Ocean. It is also about 2000 km wide.
- It is elongated in a general North-South direction and follows a sinuous course roughly parallel to the present coastlines. With reference to areal extent, it is one-third of the entire Atlantic ocean.
Formation of Oceanic ridges
Mid ocean ridges are characteristic of sea floor spreading processes. These are very active zones wherein a new magma is expected to emerge on the ocean floor regularly. There are two processes responsible for the ocean floor spreading
- Mechanism –One is ridge-push and slab-pull process. Ridge-push occurs when the ridge pushes the tectonic plate away from the ridge, often towards the subduction zone. At the subduction zone, slab -pull come into effect. The other process is the mantle conveyor mechanism.
Mid oceanic ridges form new oceanic crusts.
- Convection currents from the mantle moves up as magma and leaves through weak zones as volcanic eruptions creating new crust upon cooling. These are called as mid ocean ridge basalts. The rocks making up the crust below the seafloor are youngest at the axis of the ridge. Most oceanic crust in the ocean basins is less than 200 million years old. The crust is in a state of constant renewal at the ocean ridges .
- Moving away from the ridges, the depth of the ocean increases progressively. The greatest depths are in the ocean trenches.
- Alfred Wegener while proposing the old theory of continental drift in 1912, specified that mid oceanic ridges are continuously tearing open the ocean floors and make the magma to erupt from the deep interior. Later the theory of Plate Tectonics provided a better understanding of the movements of plates, spreading of ocean floors, underwater volcanic eruptions and formation of mid oceanic ridges.
- It is also found that 20 volcanic eruptions occur every year along the se mid oceanic ridges. It is also seen that every year about 2.5 sq.km of new sea floor is formed by this process. With a crustal thickness of 1 to 2 km, this amounts to about 4 Cu .Km of new oceanic crust formed every year.
- Distribution of Mid-Ocean Ridges in the World
Mid oceanic Ridges are distributed in almost all major oceans of the world. They range from the longest mid Atlantic Ridge of one ocean floor to a small ridge of another ocean.
The Atlantic Ocean has the following notable ridges.
- The Mid Atlantic Ridgeis a world famous ridge. It is the longest one in the world. It divides the Atlantic in the middle along the plate boundary. Its alignment is broken near the equator. It starts from Iceland in the north and ends near the Rouvet Island near the Antarctica. The Mid Atlantic Ridge is exactly following the boundary of coastlines and continental margins on both sides of the ocean. It is flanked by many ocean basins.
- The Reykjanes Ridge –The Reykjanes Ridge exists in the Reykjanes Basin near Iceland as the starting point of Mid Atlantic Ridge. Its continuity has been broken by a fracture zone.
- The Madeira Ridgeis a small oceanic ridge located near Madeira, west of Morocco.
- The Atlantic Indian Ridge –The Atlantic Indian Ridge is existing at the Southern end of Mid Atlantic Ridge. It is about 2000 km long. It is located along the northern boundary of the Atlantic – Indian Basin.
- The South Scotia Ridge –The South Scotia Ridge is located near the southern tip of south America in the Scotia Sea.
- The Zapiola Ridge– The Zapiola Ridge is a small ridge in the Argentine Basin east of Argentina.
- The America –Antarctica Ridge. The America – Antarctica Ridge is located in the Southern Ocean, North of Antarctica. It has a North East – South West alignment. It is 1500 km long.
- The Astrid Ridge –The Astrid Ridge is a small ridge located in the Lazarev sea of Antarctica. It is at the southern part of Atlantic-Indian Basin.
- The Parnaiba Ridge –The Parnaiba Ridge is a minor ridge located near the equator in the west Atlantic and east of Amazon delta.
- Belem Ridgeis yet another one in the Atlantic Ocean.
- The Ceard Ridge –The Ceard Ridge is located in the western end of Atlantic Ocean near the equator.
- The Barracuda Ridge-The Barracuda Ridge is located North of Barbados.
- The Blake Bahama Ridge –The Blake Bahama Ridge is located closer to Bahamas in the West Atlantic.
- The Eirik Ridge –The Eirik Ridge is a minor oceanic ridge located in the North Atlantic existing near the south of Greenland.
- The West Scotia Ridge –The West Scotia Ridge is located in the western parts of Scotia Sea.
- The Newfoundland Ridge –The Newfoundland Ridge is located in the north west Atlantic ocean near
- The Walvis Ridge –The Walvis Ridge is located in the Southern Atlantic west of Namibia of South Africa.
- The Hatton Ridge –The Hatton Ridge is parallel to Reykjanes Ridge in the Iceland Basin.
The Pacific ocean has the following notable ridges:
- Gorda Ridgesare located west of north America near Cascade mountain ranges.
- Kyushu– Palau Ridge is located in the middle of Philippine Sea.
- South Honshu Ridge
- West Norfolk Ridgeand Norfolk Ridge are located near the Norfolk Island of Australia.
- Kermadec Ridgeis located along the western parts of Southwest Pacific basin.
- Robbie Ridgeis located to the southwest of Phoenix islands. It is a north-south trending ridge. It is parallel to the Kermadec trench.
- Hawaiian Ridgeis located Northwest of Hawaii.
- Christmas Ridgeand Necker Ridge are in the Central Pacific basin southwest of Hawaii.
- Tehuantepec Ridgeis located in the Guatemala Basin South of Salina Cruz.
- Colon Ridgeexists in southern parts of Guatemala Basin between north and south America in the east pacific.
- Pacific Antarctic Ridgeis in the middle of the Southern ocean. It is an east-west trending ridge.
- NazcaRidge is located west of South America near Peru-Chile trench.
- Society Ridge and Tuamotu Ridgeare in the middle of the Pacific ocean near Society islands. It is in the southern Hemisphere.
- Macquarie Ridgeis along the boundary between Southern Ocean and the Tasman Sea and South of New Zealand.
- Caroline Ridgeis located near the Challenger Deep of Marianas Trench.
- Galapagos Ridgeis located west of South America near Andes.
The Ridges of Indian Ocean are the following:
- Ninety East Ridge. It is a north-south trending ridge located in the middle of Cocos Basin and Mid-Indian Basin. It starts from the Andaman Sea in the North and extends upto the Broken Ridge in the South. It runs parallel to the longitude 90 degrees E.
- Investigator Ridgeis located in the southeastern parts of Cocos basin and east of Cocos islands.
- Chain Ridge is located northeast of Somali Basin and North of Seychelles.
- Amirantle Ridgeis near the Seychelles, south of Somali basin.
- Davie Ridgeis located in the Mozambique Channel between Mozambique and Madagascar.
- Murray Ridgeis in the Arabian Sea, east of Oman.
- Carlsberg Ridgeis located south of Arabian Sea and northeast of Somali basin.
- Sheba Ridgeis located in the Gulf of Aden extending from the red Sea.
- Atlantic Indian Ridgeis in the south of Africa in the Atlantic-Indian basin.
- Southwest Indian Ridgeis located in the southwest parts of Indian ocean. It is trending along NE-SW direction.
- Mid Indian Ridgeis a Northwest to Southeast trending ridge in the middle of Indian Ocean.
- Broken Ridgeis an east-west trending ridge located to the west of Perth basin.
- Southeast Indian Ridgeis an east-west trending ridge located in the southeast parts of Indian Ocean.
- Hartog Ridgeis in the western parts of Perth basin west of Australia.
- East Indiaman Ridgeis near the Broken Ridge west of the Perth Basin.
Significance of Oceanic Ridge | UPSC – IAS
The alignments of the ridges have some common trends. The ridges are structurally displaced due to transform faults. Their alignments are cut across by a series of transform faults. The horizontal displacement along these zones bring more opportunities to expose the crustal weaknesses. The length of volcanic vents or pipes may be shortened and due to this more convection currents may emanate rapidly. Due to this, the rising of magma could be more easy.
- When there is subduction along the convergent boundaries, we get ocean trenches. Below the zones of subduction, the materials get crushed and may be melted. This zone of crushing is known as benioff zone. The scientists believe that the volcanic island arcs are formed from magmas produced by the partial melting of the descending and/or the overriding plate. Considerable volcanic activity worldwide is the result of subduction.
- Benioff is the zone which normally creates the focus for earthquakes and subsequently generate tsunamis from the oceans. Ocean ridges are the spreading centers. The ocean floor is mountainous and uneven, much like Earth’s surface.
- Sea-floor spreading is driven by the crust formation along these mid-ocean ridges. They are like meandering undersea mountain ranges. They span on the Earth like the seams of a baseball. Oceanic crust is continually produced by magma welling up along the centerlines of the mid-ocean ridges. This new crust flows away from the ridgeline in two symmetric sheets, one on each side. The rate of sea-floor spreading resulting from this process is from 1–20 cm/yr, depending on the particular mid-ocean ridge.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies