- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
What does an UV Index mean and how it’s calculated?
The UV index tells you how much ultraviolet radiation is around at ground level on a given day, and its potential to harm your skin. UV radiation is a component of sunlight that can cause tanning and sunburn in the short term. In the longer term, too much exposure to UV can cause cataracts and skin cancer.
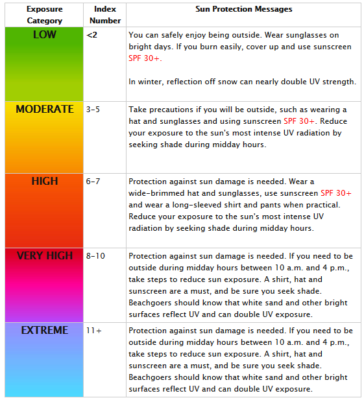
In 2002, the World Health Organisation devised the UV index in an effort to make people around the world more aware of the risks. The index boils down several factors into a single number that gives you an idea of how careful you need to be in the sun. A score of 1 or 2 is low, 3 to 5 is moderate, 6 or 7 is high, 8 to 10 is very high, and 11 and above is extreme.
The Sun showers Earth with light at a huge spectrum of different wavelengths, and each wavelength can have a slightly different effect on human skin. An important part of the spectrum is ultraviolet or UV radiation: light with wavelengths too short for our eyes to see, from around 400 nanometres to 10 nanometres.
There are two important kinds of UV radiation: UV-A, with wavelengths from 400 to 315 nanometres, and UV-B with wavelengths from 315 to 280 nanometres. (Shorter wavelengths are called UV-C, but are mainly blocked by the atmosphere so we don’t need to worry about it.)
UV-A and UV-B both contribute to skin damage, ageing and skin cancer. But UV-B is the more dangerous: it is the major cause of sunburn, cataracts and skin cancer.
The UV index takes into account how much UV radiation of different wavelengths is around and how each of those wavelengths affects our skin.
ARPANSA has a network of sensors around Australia measuring sunlight at different wavelengths to determine the UV index, with the information available online in real time. This data is combined with other information about location, cloud cover and atmospheric conditions to produce maps and forecasts of the UV index for the whole country.
How are UV levels different around the world?
The UV index you see reported is usually the daily maximum — that’s the highest it will be all day. How high it gets depends on lots of factors, including your location, the time of year, the amount of cloud cover, and ozone and pollution in the atmosphere.
The index tends to be higher closer to the Equator and at high altitudes, as the sunlight has to pass through less air before it reaches the ground. People often experience the sun in Australia as particularly harsh, compared with places in North America or Europe.
In a British summer, for example, the maximum UV index might be between 6 and 8. In an Australian summer it can range from 10 to 14.
There are a few reasons for this. One is that Australia’s cities are closer to the Equator than many big cities in Europe and North America. Another is that Earth is very slightly closer to the Sun in the southern hemisphere’s summer than the northern summer, meaning the sunlight is a few percent brighter. A third reason is the ‘hole’ in the ozone layer. The layer of ozone in the upper atmosphere, which absorbs some UV-B, is thinner towards the South Pole. This was caused by the use of chemicals called chlorofluorocarbons or CFCs, and it has been improving since they were banned by an international agreement in 1987. And finally, the air in Australia generally has less smoke, dust and other small particle pollution than many places in the northern hemisphere. While this makes the air nicer to breathe, pollution does absorb or block some UV radiation.
Is UV changing over time?
We know UV levels have increased in recent decades. In Australia, a study in 2011 found the average UV index had increased by 2 to 6 per cent between the 1970s and the period 1990 to 2009, due to depletion of the ozone layer. A NASA study found similar results for 1979 to 2008. It’s harder to say what will happen in the future, as there are several uncertain factors.
We expect the ozone layer to slowly recover from the impact of CFCs, which is likely to reduce UV levels. However, we also expect less fossil fuel will be burned, which would mean less air pollution and higher UV levels.
On the flip side, we may also have more bushfires due to climate change, which would mean more air pollution and lower UV. Clouds are also likely to behave differently due to climate change, but we’re not sure exactly how. Researchers in Japan found reductions in clouds and tiny particles in the air are expected to have a bigger impact than the recovery of the ozone layer, which would mean UV levels are likely to go up overall.










 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies