- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
What is organoid intelligence?
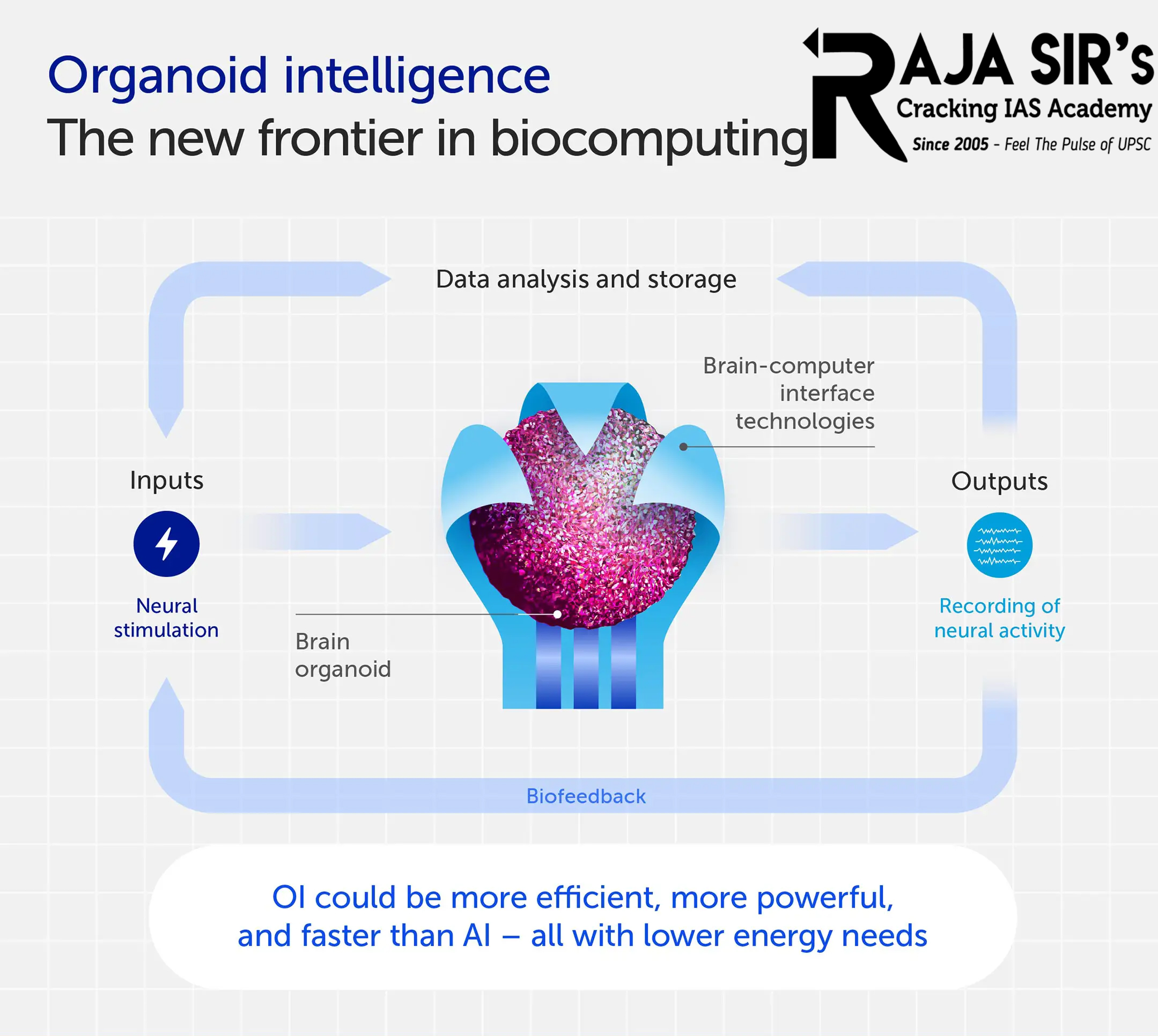
Recently, Scientists have outlined a plan for a potentially revolutionary new area of research called “organoid intelligence”, which aims to create “biocomputers”, where 3D brain cultures grown in the lab are coupled to real-world sensors and input/output devices.
- Technology is expected to harness the processing power of the brainand understand the biological basis of human cognition, learning, and various neurological disorders.
- These “mini-brains”(with a size of up to 4 mm) are built using human stem cells and capture many structural and functional features of a developing human brain. It is used to study human brain development and test drugs to see how they respond.
- However, Brain organoids developed in the lab are not advanced enoughas they lack the required sensory inputs and blood circulation that are necessary for the development of a complex organ like the human brain.
- Moreover, Scientists transplanted human brain organoid cultures into rat brainsand observed that they formed connections with the rat brain and showed functional activity.
- This system could provide a way to study brain diseasesin a human context.
- However, the organoids are still in the rat-brain microenvironment, which may not be representative of the human brain.
New ‘Bio-computer’
- Researchers plan to combine brain organoids with modern computing methods using machine learningto create “bio-computers”.
- They willgrow organoids inside structures with multiple electrodes that can record the firing patterns of neurons and mimic sensory stimuli.
- Machine-learning techniques will then be used to analyse the effect of neuron response patterns on human behavioror biology.
- Scientists have already grown human neurons on a microelectrode array and trained them to generate electrical activity similar to what electrons would generate while playing table tennis.
Opportunities for ‘Bio-Computers’
- Brain organoids developed using stem cells from individualswith diseases like Parkinson''s disease and microcephaly can aid drug development for these conditions.
- These organoidscan provide insights into the biological basis of human cognition, learning, and memory by comparing the data on brain structure, connections, and signaling between healthy and patient-derived organoids.
- While human brainsare slower than computers at simple arithmetic, they outshine machines at processing complex information.
Looking ahead
- Currently, brain organoids have a diameter of less than 1 mm, roughly three-millionth the size of an actual human brain.So, scaling up the brain organoid is key to improving its computing capacity.
- Neural recordings from each neuron and connection will be needed to store and analyse using ‘Big Data’ infrastructure.
- Researchers will alsohave to develop microfluidic systems to transport oxygen and nutrients, and remove waste products.
- There is also a need to identify, discuss, and analyse ethical issuesas they arise in the course of this work.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies