- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
Hit List Questions 34 - PPP 100 PRELIMS 2024 - 52
Questions & Explanations:
|
1. |
I. They play a crucial role in the feeding and defence strategies of cnidarians. II. Jelly Fish has Nematocysts. Which of the above statements is/are true w.r.t. Nematocysts? (a) Only I (b) Only II (c) Both I & II (d) Neither I nor II
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2. |
1. It is in Antarctica. 2. It is a meromictic Lake. Which of the statements given above is/are correct w.r.t. the Crawford Lake? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
3. |
Which of the following rocks is not likely to contain fossils?. 1. Conglomerate 2. Granite 3. Shale 4. Sandstone (a) 2 only (b) 2 and 4 only (c) 1 and 2 only (d) 1, 2 and 4 only
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
4. |
The Solar Eclipse achieves totality only in limited geographical regions because (a) The size of the shadow of the Moon on the Earth is small as compared to cross-section of Earth (b) The Earth is not a smooth flat surface, but has elevations and depressions (c) The trajectories of the Earth around the Sun and Moon around the Earth are not perfect circles (d) Sun rays can reach most of the peripheral regions of the shadow of the Moon due to atmosphere refraction
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
5. |
1. Article 112 of Indian Constitution provides for an interim budget. 2. Article 116 of Indian Constitution provides for vote on account. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
6. |
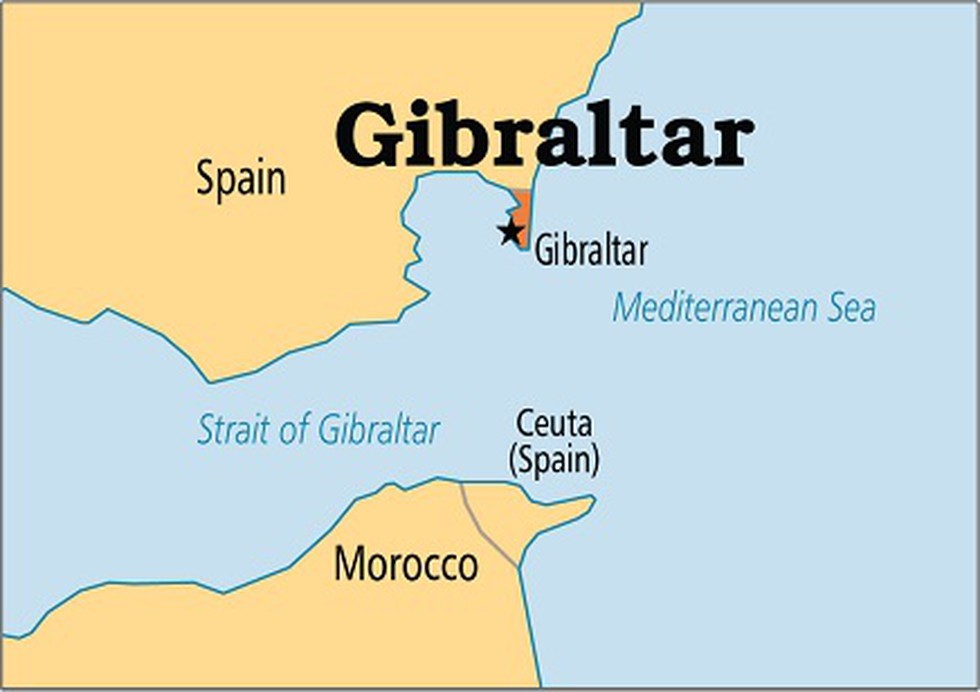
Strait of Gibraltar I. separates Europe from Africa II. Connects Mediterranean Sea with Atlantic Ocean Which of the above statements is/are true? (a) Only I (b) Only II (c) Both I & II (d) Neither I nor II
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
7. |
Consider the following statements w.r.t. Raphuscucullatus. I. It is an extinct flightless bird. II. Its closest living relative is the Nicobar pigeon. Which of the above statements is/are true?. (a) Only I (b) Only II (c) Both I & II (d) Neither I nor II
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
8. |
The reasons why Kashmir and Ladakh are without snow in this winter is/are 1. Decline in Western Disturbance events. 2. El Nino event in the eastern Pacific Ocean. (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
9. |
“CRISPR-based therapies for sickle-cell disease and β-thalassaemia” in headline news in recent times. Consider the following statements in this context. I. The Cas9 enzyme is derived from the Streptococcus pyogenes bacteria. II. CRISPR relies on the ability of gRNAs. Which of the above statements is/are true? (a) Only I (b) Only II (c) Both I & II (d) Neither I nor II
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
10. |
Match the following
Codes
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
11. |
‘Death Valley’ in the U.S.A. is a/an (a) Anticlinal Valley (b) Geosynclinal Valley (c) Desert Valley (d) Rift Valley
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
12. |
Which of the following originates from a deep spring at Vernag at Anantnag, situated at the base of the Pir Panjal range in the Kashmir Valley?. (a) Jhelum (b) Chenab (c) Sutlej (d) Beas
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
13. |
1. Ethanol production in India is mainly based on ‘B-heavy’ molasses. 2. Ethanol yields from grains are higher compared to molasses. 3. B-heavy molasses has no sugar content left in it for sugar production. (a) 3 only (b) 2 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
14. |
The Santiago Network seen in news frequently refer to the context of (a) Seismic Proof buildings (b) Climate Change fund (c) Afforesattion efforts (d) Averting Monoculture
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
15. |
Consider the following statements. I. Temperate cyclones rise in the belt of trade winds. II. Temperate cyclones move from west to east. Which of the above statements is/are true? (a) Only I (b) Only II (c) Both I & II (d) Neither I nor II
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
16. |
Israel has common borders with (a) Lebanon, Syria, Jordan and Egypt (b) Lebanon, Syria, Turkey and Jordan (c) Cyprus, Turkey, Jordan and Egypt (d) Turkey, Syria, Iraq and Yemen
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
17. |
1. In a La Niña year, the tropical Pacific Ocean soaks up heat like a sponge and builds up its volume of warm water. 2. ENSO phenomenon was discovered by Sir Gilbert Walker. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
18. |
1. An El Niño year creates a global-warming crisis in miniature. 2. Pre-monsoon and monsoon circulations tend to be weaker in an El Niño year. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
19. |
Planets are (a) non-luminous bodies and don’t shine (b) non-luminous bodies and shine (c) luminous bodies and do not shine (d) luminous body and shine
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
20. |
Consider the following. 1. SBI 2. HDFC 3. ICICI 4. IOB How many of the above is/are Domestic Systemically Important Banks (D-SIBs).? (a) Only one (b) Only two (c) Only three (d) All the four |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
21. |
Based on the ascending order of gravity, the correct order is (b) Jupiter, Neptune, Uranus, Saturn, Earth, Venus (c) Jupiter, Uranus, Earth, Venus, Saturn, Neptune (d) Venus, Earth, Uranus, Saturn, Neptune, Jupiter
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
22. |
Match the following
Codes
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
23. |
Consider the following statements in the context of India’s public debt-to-GDP ratio. I. The 2018 amendment to the Union government’s FRBMA specified debt-GDP targets for the Centre, States and their combined accounts at 40%, 20% and 60%, respectively. II. Dip in tax collections post covid pandemic have increased the debt-to-GDP ratio. Which of the above statements is/are true?. (a) Only I (b) Only II (c) Both I & II (d) Neither I nor II
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
24. |
With reference to ‘Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD)’ sometimes mentioned in the news while forecasting Indian monsoon, which of the following statements is/are correct?. 1. IOD phenomenon is characterised by a difference in sea surface temperature between tropical Western Indian Ocean and tropical Eastern Pacific Ocean. 2. An IOD phenomenon can influence an El Nino’s impact on the monsoon. (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
25. |
Which of the following is/are unique characteristic/ characteristics of equatorial forests?. 1. Presence of tall, closely set trees with crowns forming a continuous canopy 2. Coexistence of a large number of species 3. Presence of numerous varieties of epiphytes Select the correct answer using the codes given below: (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
1. |
https://www.thehindu.com/todays-paper/2023-12-25/th_chennai/articleGTAC6HPVB-5298540.ece |
C |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2. |
Crawford Lake Crawford Lake is a small, deep lake within a protected conservation area in Southern Ontario, Canada as part of a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve. Topography - The lake is situated in a karstic limestone landscape and fills a sinkhole created by the dissolution of underground rock. Meromictic Lake - Because of the lake’s great depth (24 meters) relative to its surface area it is known as a meromictic lake. It refers to a permanently stratified body of water where the bottom layer of water does not mix with the upper layers because of differences in chemical composition. Crawford Lake and its layers of sediment preserved the annual impact of human activities on the Earth’s soil, atmosphere and biology. |
B |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
3. |
· Fossils, the preserved remains of animal and plant life, are mostly found embedded in sedimentary rocks. · In sedimentary rocks, most fossils occur in shale, limestone, conglomerate, and sandstone. o Sedimentary rocks look like layered pancakes. · Granite is a light-colored igneous rock with grains large enough to be visible with the unaided eye. o It forms from the slow crystallization of magma below Earth''s surface. o Granite is composed mainly of quartz and feldspar with minor amounts of mica, amphiboles, and other minerals. · Conglomerates form by the consolidation and lithification of gravel. They can be found in sedimentary rock sequences of all ages. · Shale is a fine-grained sedimentary rock that forms from the compaction of silt and clay-size mineral particles that we commonly call "mud". · Sandstone is a sedimentary rock composed mostly of quartz sand, but it can also contain significant amounts of feldspar, and sometimes silt and clay. o Sandstone that contains more than 90% quartz is called quartzose sandstone. o Sandstone contains more than 25% feldspar, it is called arkose or arkosic sandstone. |
A |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
4. |
Size of the moon is roughly one-fourth of the size of earth; thus, the moon casts a smaller shadow which falls upon a limited portion of the earth. Thus, solar eclipse achieves totality only in a limited portion on Earth. Though it is true that earth is not a smooth surface but it does not contribute significantly to the limited totality of the solar eclipse. |
A |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
5. |
B |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
6. |
|
C |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
7. |
C |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
8. |
C |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
9. |
gRNA stands for Guide RNA while Single guide RNA (sgRNA) is made use to describe the gRNA. As the name suggests, sgRNA is the single RNA molecule, containing a custom-designed short crRNA sequence (both) united to the scaffold tracrRNA sequence. It is possible to synthetically generate sgRNA or can be made in vivo, or in vitro from the template of DNA. Typically, gRNA is used to explain all the CRISPR guide formats of RNA while the sgRNA corresponds to the uncomplicated option, which takes into consideration both the tracrRNA and crRNA components into one molecule of RNA. As such, both the terms gRNA and sgRNA are interchangeably used to explain the same molecule, hence there are no such dissimilarities between gRNA and sgRNA. sgRNA (single guide RNA)
gRNA (Guide RNA)
sgRNA is another phrase for gRNA. gRNA is synthetic and short RNA sequences utilised in specifying target sequence in the genome for endonuclease in the CRISPR system. Both these form the elements of CRISPR-based genome editing. |
C |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
10. |
Relief Rainfall
Convectional Rainfall
Frontal Rainfall
|
B |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
11. |
A rift valley is a long, low area between mountains or hills that is created when two tectonic plates move away from each other. Erosion also deepens the valley. An example of this is Death Valley in California, USA. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
12. |
Jhelum River: · It is a river that flows in India and Pakistan. · It is a tributary of the Indus River. · The Jhelum (Vyeth in Kashmiri, Vetesta in Sanskrit and Hydaspes in Greek) is the main waterway of the Kashmir valley. · It is the largest and most western of the five rivers of Punjab and passes through the Jhelum District in the North of Punjab province, Pakistan. · Course: o Origin: It originates at the Verinag Spring at Anantnag, at the foot of the Pir Panjal range in the Kashmir Valley. o It then flows via Srinagar and Wular Lake prior to entering Pakistan. o The river makes a deep, narrow gorge on its way to Pakistan. o It joins the Chenab River near Trimmu, Pakistan. o Length: It has a total length of about 725 km (450 mi). · Major Tributaries: o The largest tributary of the Jhelum is the Kishenganga (Neelum) River, which joins near Muzaffarabad and enters the Punjab province, Pakistan. o Kunhar River is the second largest tributary of the river, which connects Pakistan-occupied Kashmir (PoK) and Pakistan on the Kohala Bridge of Kanghan valley. o Other tributaries include Sandran River, Bringi River, Arapath River, Watlara River, Lidder River and Veshaw River. |
A |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
13. |
B |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
14. |
B |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
15. |
|
B |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
16. |
 |
A |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
17. |
C |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
18. |
https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/what-are-el-ni%C3%B1o-and-la-ni%C3%B1a/article66563217.ece |
C |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
19. |
Planets revolve around the sun in an elliptical orbit. They are non-luminous bodies that do not twinkle. Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars are called terrestrial planets, and Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune are called gaseous planets. The sequence of planets according to their size (in descending order) is Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, Earth, Venus, Mars, and Mercury.
|
A |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
20. |
· RBI’s Updated Categorization: RBI moved State Bank of India (SBI) and HDFC Bank to higher buckets in its latest update. At the same time, ICICI Bank continues to be in the same bucketing structure as last year. o SBI (buckets 3 to 4) and HDFC Bank (buckets 1 to 2). · Basis of Updation: The current update is based on the factoring in the increased systemic importance of HDFC Bank post the merger of erstwhile HDFC Limited into HDFC Bank on July 1, 2023. · Common Equity Requirement: Based on the bucket in which a D-SIB is placed, an additional common equity requirement must be applied. o Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1) is a component of Tier 1 capital primarily common stock held by a bank or other financial institution. About Domestic Systemically Important Banks (D-SIBs) · The Reserve Bank issued the Framework for dealing with Domestic Systemically Important Banks (D-SIBs) in 2014. · The D-SIB framework requires the Reserve Bank to disclose the names of banks designated as D-SIBs starting from 2015 and place them in appropriate buckets depending on their Systemic Importance Scores (SISs). o Based on the bucket in which a D-SIB is placed, an additional common equity requirement must be applied. o ‘Too big to fail’: D-SIB means that the bank is ‘too big to fail’. o Potential Ramifications of Failure: If a bank fails, there would be significant disruption to the essential services it provides to the banking system and the overall economy.
Key Features of the Domestic Systemically Important Banks (D-SIBs) · Government Support: The too-big-to-fail tag also indicates that the government is expected to support these banks in case of distress. · Classification: RBI classifies the banks under five buckets depending on the order of importance. · Factors Contributing to Systemic Importance: These banks become systemically important due to their size, cross-jurisdictional activities, complexity and lack of substitute and interconnection. · Quantitative Criterion: Banks whose assets exceed 2% of GDP are considered part of this group. · Enhanced Capital Requirements: Due to their economic and national importance, the banks need to maintain a higher share of risk-weighted assets as tier-I equity.
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
21. |
D |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
22. |
|
D |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
23. |
A |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
24. |
The Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) is an atmosphereocean coupled phenomenon in the tropical Indian Ocean (like the El Nino is in the tropical Pacific), characterised by a difference in Sea-Surface Temperatures (SST). A ‘positive IOD’ is associated with cooler than normal sea-surface temperatures in the eastern equatorial Indian Ocean and warmer than normal sea-surface temperatures in the western tropical Indian Ocean. The opposite phenomenon is called a ‘negative IOD’, and is characterised by warmer than normal SSTs in the eastern equatorial Indian Ocean and cooler than normal SSTs in the western tropical Indian Ocean. Also known as the Indian Nino, it is an irregular oscillation of sea-surface temperatures in the Indian Ocean in which the western Indian Ocean becomes alternately warmer and colder than the eastern part of the Indian Ocean. The IOD is one aspect of the general cycle of global climate, interacting with similar phenomena like the El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) in the Pacific Ocean. An IOD can either aggravate or weaken the impact of El Nino on Indian monsoon. If there is a positive IOD, it can bring good rains to India despite of an El Nino year. |
B |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
25. |
Equatorial rainforests are lush, biodiverse forests found near the equator in tropical regions. These forests typically lie within 10 degrees latitude north or south of the equator and are characterized by high temperatures and heavy rainfall throughout the year. Climate: They experience a hot and humid climate with temperatures consistently high year-round, usually averaging around 25-27°C (77-81°F). Rainfall is abundant, often exceeding 2,000 millimeters (80 inches) annually, leading to the term "rainforest." Biodiversity: Equatorial rainforests are among the most diverse ecosystems on Earth, housing an incredibly rich variety of plant and animal species. These forests contain a myriad of species of trees, plants, insects, birds, mammals, and other organisms, many of which are endemic to these regions. Flora and Fauna: The vegetation in equatorial rainforests is characterized by tall trees forming a dense canopy that shades the forest floor, creating a multi-layered ecosystem. A variety of plant species, including epiphytes (plants growing on other plants), lianas (climbing vines), and numerous species of trees, contribute to the rich biodiversity. Importance: Equatorial rainforests play a crucial role in regulating the Earth''s climate and carbon cycle. They absorb carbon dioxide through photosynthesis and act as carbon sinks, helping mitigate climate change. Additionally, they provide habitat for countless species, support indigenous communities, and are centers of medicinal plant resources. Threats: Unfortunately, these rainforests face significant threats from deforestation, logging, agriculture, mining, and other human activities. The loss of equatorial rainforests not only endangers the vast array of species that call these forests home but also contributes to climate change and the disruption of global ecosystems. |
D |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||









 Latest News
Latest News


 General Studies
General Studies