- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
03rd Sep 2021
BANGLADESHI VACCINE SCIENTIST, PAKISTANI MICROFINANCEER AMONG THIS YEAR'S RAMON MAGSAYSAY AWARDEES
A Bangladeshi vaccine scientist and a microfinance pioneer from Pakistan were among the five recipients of this year’s Ramon Magsaysay Award -- regarded as the Asian version of the Nobel Prize.
2021 Awardees:




- Apart from Firdausi Qadri from Bangladesh and Muhammad Amjad Saqib from Pakistan, the other winners are Roberto Ballon, American Steven Muncy and Indonesian torch bearer for investigative journalism, Watchdoc.
- Qadri who is 70 years old has a doctorate from Liverpool University, U.K.
- She joined International Centre For Diarrhoeal Disease Research, Bangladesh, in 1988.
- She was recognised for “her passion and life-long devotion to the scientific profession”.
- Muhammad Amjad Saqib founded one of the largest microfinance institutions in Pakistan, servicing millions of families.
- Watchdoc is a production house that ingeniously combines documentary filmmaking and alternative platforms to highlight underreported issues in Indonesia.
- Steven Muncy, a humanitarian who has been helping the displaced refugees of Southeast Asia rebuild their lives.
- Roberto Ballon, a fisherman from Southern Philippineswho has led a community in restoring their rich aquatic resources and their primary source of livelihood.
- It is established in 1957, the Ramon Magsaysay Award was founded to preserve former Phillippine President Ramon Magsaysay's example of integrity in governance and idealism in a democratic society.
- It was funded by the Rockefeller Brothers trustees with Philippine government's agreement.
- Ramon Magsaysay Award is regarded as the Asian version of the Nobel Prize.
- The foundation gives the prize to Asians achieving excellence in their field.
- Six categories, five of which were discontinued in 2009:
- Government Service (Until 2008)
- Public Service (Until 2008)
- Community Leadership (Until 2008)
- Journalism, Literature, and Creative Communication Arts (Until 2008)
- Peace and International Understanding (Until 2008)
- Emergent Leadership (2001)
- Uncategorized (2009)
- Deendayal Port Trust has bagged the highest Rajbhasha Kirti Award for 2020-21.
- It was award for excellent performance in the field of Official Language Implementation amongst various Boards/Autonomous Bodies/Trusts/Societies etc. of Government of India.
- Hindi language was first adopted by the Constituent Assembly of India as the official language of India on September 14, 1949.
- The resolution 2593 (2021) was adopted by a vote of 13 in favour with two abstentions (Russia and China).
- It has 15 members- 5 Permanent + 10 Non-Permanent.
- Demanded that Afghan territory should not be used to threaten or attack any country or to plan or to finance terrorist acts.
- Reiterated the importance of combating terrorism in Afghanistan.
- Condemned the deplorable attacks of August 26, 2021, near Hamid Karzai International Airport in Kabul, Afghanistan.
- Reaffirmed the importance of upholding human rights, including those of women, children and minorities.
- Encouraged all parties to seek an inclusive, negotiated political settlement, with full, equal and meaningful participation of women.
- Called for enhanced efforts to provide humanitarian assistance to Afghanistan and called on all parties to allow safe, unhindered access for the UN and its agencies, including with respect to internally displaced persons.

- Sukhet model is named after Sukhet village in Madhubani district of Bihar.
- It is being implemented by the scientists of Dr Rajendra Prasad Central Agriculture University, Pusa (Samastipur).
- It is promoting cleanliness and organic manure to the farmers.
- It is also helping the village in getting rid of pollution.
- Under this project, garbage and dung from houses are collected door-to-door and then converted into vermicompost (organic manure).
- From the income generated from the sale of organic manure, every family is provided LPG cylinders every two months in exchange of the waste and cow dung.
- This project also provides employment to 14 to 15 people at the village.
- The grants have been released as per the recommendations of 15th Finance Commission.
- To improve sanitation and maintenance of open-defecation free (ODF) status.
- To improve supply of drinking water, rain water harvesting and water recycling.
- Out of the total Grant-in-aid allocated for Panchayati Raj institutions, 60 percent is ‘Tied Grant’.
- It is meant for national priorities like drinking water supply, rainwater harvesting and sanitation.
- Tied grants are meant to ensure availability of additional funds to the Rural local bodies over and above the funds allocated by the Centre and the State for sanitation and drinking water under the Centrally Sponsored Schemes.
- Remaining 40 percent is ‘Untied Grant’ and is to be utilized at the discretion of Panchayati Raj institutions for location specific felt needs, except for payment of salaries.
- The States are required to transfer grants to Rural local bodies within 10 working days of their receipt from the Union Government.
- Any delay beyond 10 working days requires the State Governments to release the grants with interest.
- Constitutional body set up by the President of India every five years to decide the share of the Union government and state governments in the divisible pool of tax revenue.
- Decides the share of each state from the share of states in the divisible pool.
- Recommends the share of funds and grants to be transferred to local bodies.
- In the Union Budget, these transfers are called ‘Finance Commission Grants’ and ‘Other Transfers’.
- The Finance Commission recommendations ensure that the Gram Panchayats are adequately funded.
- Nearly half of the Finance Commission Grants in Union Budget goes to village local bodies.
- Urban local bodies like municipal councils receive the largest chunk of Finance Commission Grants.
- Central government also provides funds to State Disaster Relief Funds in addition to funding the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA).
- The assistance is provided as per the recommendations of the Finance Commission.
- About a third of total revenue collected by the Centre is directly transferred to states as their share in the divisible pool.
- Finance Commission also provides a mechanism for compensation of any loss incurred by states, which is called post-devolution revenue deficit grants.
- This Grant forms the second largest chunk of Finance Commission transfers after the assistance to local rural bodies.
- Assistance to states from NDRF.
- Central pool of resources for north-eastern region and Sikkim.
- Externally aided project grants.
- Externally aided project loans.
- Schemes for north-east council.
- Schemes under Article 275 (1) of the Constitution.
- Special assistance under the demand: Transfers to states. Special central assistance to scheduled castes and special central assistance to tribal area.

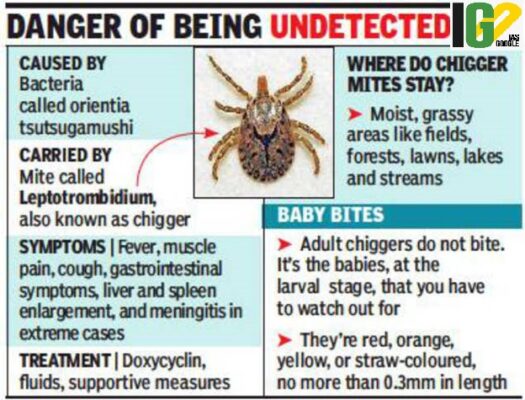
- Scrub typhus or bush typhus is a disease caused by a bacterium Orientia tsutsugamushi.
- It is spread to people through bites of infected chiggers (larval mites).
- It is prevalent in many parts of India, including outbreaks in the sub-Himalayan belt, from Jammu to Nagaland.
- Fever, headache, body aches, and sometimes, rash.
- Dark, scab-like region can be noticed at the site of the chigger bite.
- Mental changes ranging from confusion to coma or enlarged lymph nodes.
- People with severe illness may develop organ failure and bleeding.
- Antibiotics are most effective if given soon after symptoms begin.
- It should be treated with the antibiotic doxycycline.
- People who are treated early with the antibiotic recover quickly.
- Reduce the risk of getting scrub typhus by avoiding contact with infected chiggers.
- When travelling to areas where the disease is common, avoid areas with lots of vegetation and bush where chiggers may be found.
- Plastic pollution impacts migratory and resident species that live in freshwater environments including fish.
- Migratory species are likely among the most vulnerable to plastic pollution.
- Ingestion of microplastics can impact species along the food web.
- Ganges and Mekong River basins, together contribute 200,000 tonnes of plastic pollution to the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean every year.
- Gangetic dolphins were the among most vulnerable species at risk of entanglement.
- Dugong is often seen to drown after getting entangled in fishing nets.

- Plastics increases the vulnerability of already endangered species such as Gangetic and Irrawaddy dolphins, Asian elephants, and Black-footed Albatrosses.
- Migratory seabirds, such as Black-footed Albatrosses and Laysan Albatrosses, can accidentally eat floating debris or making nests out of plastics, using fishing lines, and shipping debris.
- Plastic could build up in their guts and nests can cause entanglement of their chicks.
- Discarded fishing gear and kite strings are among the major threats.
-
- Not only aquatic species, but also mammals and birds encounter these discarded materials on land.
- Kite strings are been estimated as the second-most frequent source of plastic hazards.
- CMS is an environmental treaty of the UN.
- The pact was signed in 1979 in Germany and known as Bonn Convention.
- Provides a global platform for conservation and sustainable use of migratory animals and their habitats.
- Appendix I of the Convention lists ‘Threatened Migratory Species’.
- It strives towards strictly protecting these animals, conserving or restoring the places where they live, mitigating obstacles to migration and controlling other factors that might endanger them.
- Appendix II lists ‘Migratory Species requiring international cooperation’.
- India has been a party to the CMS since 1983.
- India is a temporary home to several migratory animals and birds.
- Indian sub-continent is also part of the major bird flyway network, i.e., the Central Asian Flyway (CAF) that covers areas between the Arctic and Indian Oceans.
- India launched the National Action Plan for the conservation of migratory species under the Central Asian Flyway.
- India has MoUs with the CMS on the conservation and management of Siberian Cranes, Marine Turtles, Dugongs and Raptors.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies