- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
12th Sep 2021
DELHI GOVT TO PROVIDE FUNDS TO SCHOOL CHILDREN FROM SEPT 7 TO START THEIR OWN BUSINESS
The Delhi Government announced that it will provide start-up funds to students of Government schools.
 About:
About:

- The Government termed this fund as seed money and the programme as ‘Business Blasters’ to help young students in starting their own business.
- Business Blaster Program (BBP) was started at the School of Excellence, Khichripur under a pilot project.
- Aim: To inculcate the belief in children that whatever work they do, they should do it with an entrepreneurial mindset.
- Objective: To encourage children to adopt an entrepreneurship mindset when taking up any kind of job.
- A seed money amount of Rs 2000 will be provided to every student of class 11th and 12th to start a business.
 About:
About:
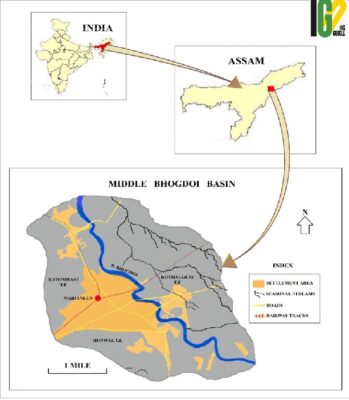
- It originates from Mokokchung in Nagaland where it is also known as Tsujenyong nullah and is the south bank tributary of the River Brahmaputra.
- It is an inter-state river (flowing between Assam and Nagaland) and joins Dhansiri river near its confluence with Brahmaputra.
- Coal mining in Nagaland introduced high levels of manganese in the river.
- Chemical waste from the tea gardens is turning the river poisonous and polluted.
- The drains carry industrial and residential wastes. The river has become heavily silted, reducing its carrying capacity.
- The high BOD (Biological Oxygen Demand) indicates low water quality and less oxygen for aquatic life.
- The massive encroachments along the river bank have been not only making the river narrower but also increasing the filth and garbage.
- Disposing human excreta and cremating dead bodies along the river bank are gradually contaminating the soil and water of the region. This is increasing the threat of water-borne diseases.
- Tributaries: Dihing River, Dibang River, Lohit River, Dhansiri River, Kolong River, Kameng River, Manas River, Beki River, Raidak River, Jaldhaka River, Teesta River, Subansiri River.
- The total catchment area of the inter-state river is 1,545 square kilometres and travels 160 kilometres before joining Dhansiri river near its confluence with Brahmaputra.
- Water pollution by organic wastes is measured in terms of BOD.
- BOD is the amount of Dissolved Oxygen (DO) needed by bacteria in decomposing the organic wastes present in water. It is expressed in milligrams of oxygen per litre of water.
- The higher value of BOD indicates low DO content of water.
- Since BOD is limited to biodegradable materials, it is not a reliable method of measuring water pollution.
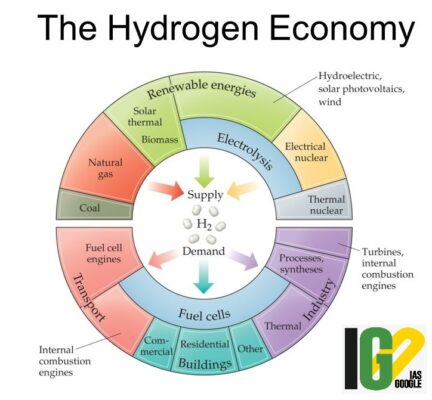
- This is aimed for contributing to PM' agenda of a hydrogen-based economy in a clean manner.

- Identification of role to be played by each stakeholder Ministry.
- Coordination with Stakeholder Ministries.
- Monitoring of activities towards achieving coal-based Hydrogen production and usage.
- Setting up sub committees to achieve the objective.
- To coordinate with Coal Gasification Mission and NITI Aayog.
- Identifying experts in India and co-opting as members.
- Desk based review of progress in hydrogen technology and also review ongoing research projects in Hydrogen technology.
- Coordinate with various national/international technology institutions in hydrogen.
- Prepare a road map for coal based Hydrogen production and usage including economic viability, environmental sustainability and policy enablers required.
- Identifying activities for implementation of coal based hydrogen production and usage.
- Assisting Task force in implementation of Coal based Hydrogen production.

- Aim: To highlight importance of literacy for individuals, communities and societies and the need for intensified efforts towards more literate societies.
- Theme 2021: Literacy for a Human-centred Recovery: Narrowing the Digital Divide.
- Literacy goals are a key part of UN’s Sustainable Development Goals 2030.
- SDG agenda contains 17 goals and 169 targets, adopted in 2015, to build on Millennium Development Goals, which were adopted in 2000.
- As per the last census (2011) in India, a total of 74.04% are literate.
- Due to confusion over reservation, the government had not been able to conduct elections to urban local bodies, which are currently being governed by bureaucrats.
- The move has paved way for conducting elections to urban local bodies in the State.
- Under the campaign, a three-day certification drive for rural citizens especially women and disadvantaged communities will be conducted.
- Pradhan Mantri Gramin Digital Saksharta Abhiyaan is a flagship Digital Literacy scheme of the Government for rural areas introduced in February, 2017.
- It is proposed to make all the Digital Villages 100 percent Digital Literate.
- The Scheme envisages to make six crore persons in rural areas digitally literate, reaching to around 40% of rural households by covering one member from every eligible household by 31st March, 2020.
- Aim: To bridge the digital divide, specifically targeting the rural population including the marginalised sections of society like Scheduled Castes (SC)/ Scheduled Tribes (ST), Minorities, Below Poverty Line (BPL), women and differently-abled persons and minorities.
- Objective: To make a person digitally literate, so that he/she can operate digital devices (like Tablets, Smart phones etc.) send and receive emails & browse Internet for information and undertake digital payment etc.
- Eligibility Criteria: Nominated digitally illiterate person from every eligible rural household.
- Age: 14 to 60 years
- Course Duration: 20 Hours (Minimum 10 Days and Maximum 30 Days)
- Implementing authority: CSC e-Governance Services India Limited, a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) incorporated under the Companies Act 1956.

- PLI scheme for textiles is part of overall announcement of PLI schemes for 13 sectors made during the Union Budget 2021-22 with an outlay of ₹ 1.97 lakh crore.
- Budgetary outlay: Rs. 10,683 crores.
- Aim: To provide a major boost to domestic production and exports of synthetic fibers and technical textiles.
- The approved incentive of 3-11% of annual incremental revenue will be provided to eligible units over a period of five years.
- For eligibility under the scheme, two types of investments are possible.
- Any person (which includes firm/company) willing to invest a minimum of ₹300 crore in plant, machinery, equipment and civil works to produce products of notified MMF fabrics & technical textiles, shall be eligible to apply for participation in first part of the scheme.
- In the second part, any person, firm or company, willing to invest minimum ₹100 crore shall be eligible to apply.
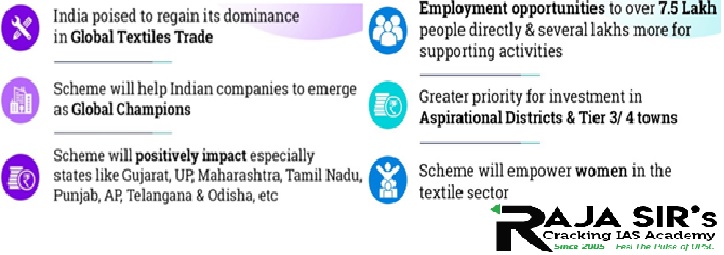
- Factories based around aspirational districts or Tier-3 & Tier-4 cities will be given priority.
- It will especially benefit Gujarat, Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Punjab, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana etc.
- It is expected to generate an additional direct employment of 7.5 lakh and indirect employment of several lakhs more.
- A fiber is a long and thin strand or thread of material that can be knit or woven into a fabric.
- They are made by chemical synthesis, as opposed to natural fibers that are directly derived from living organisms.
- MMFs such as nylon, polyester, acrylic, rayon, viscose and polyolefin dominate global apparel production.
- They account for 75% of all fibers produced worldwide, and 80% in developed markets such as Europe and North America.
- Applications: Clothing, carpets and household textiles, tyres, conveyor belts, cold-weather clothing, air and water filters.
- These are materials and products manufactured primarily for their technical and performance properties rather than their aesthetic or decorative characteristics.
- Applications: Automobiles, civil engineering and construction (roads, railway tracks), agriculture, healthcare, industrial safety, personal protection, military and disaster management.
- In India, Technical textiles segment is estimated at $16 billion or 6% of $250-billion global market.
- India has primarily focused on cotton textile. But two-thirds share of the international textile market is of man-made and technical textile.
- The share of export of textiles from India has fallen from 24% in 2000 to just 11% in 2020. Indian companies and exporters have lost market share to China, Bangladesh and Thailand.
- MMF (man-made fibre) and technical textiles sectors account for less than 20% of India's total textile production.
- The penetration level of technical textiles is low in India, varying between 5-10% against 30-70% in developed countries.
- The textiles (including apparel) industry in India provides direct employment to 45 million people and 60 million in allied industries.
- India is among the world’s largest producers of textiles products and apparel.
- The domestic textiles and apparel industry contributes 5% of India’s GDP, 7% of industry output in value terms and 11% of export earnings.
- Issues include: Lack of working capital, outdated technology, fragmented nature of supply chains etc.
- The Cabinet has approved Rs 1480 crore National Technical Textiles Mission in 2020, set to run till 2024. The mission targets an average growth rate of 15-20% annually and a domestic market size of $40-50 billion by 2024.
- As many as 92 categories of technical textiles, including fire-resistant curtains, geogrid for railways, high-altitude combat gear, bulletproof jackets, leno bags for transporting farm commodities, and architectural membranes for tents, had been identified for mandatory use by central ministries and public agencies.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies