- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
16th Aug 2021
VIRENDRA KUMAR LAUNCHES TAPAS
Recently, the Union Minister for Social Justice & Empowerment has launched an online portal TAPAS (Training for Augmenting Productivity and Services).
TAPAS Initiative





- TAPAS is the initiative of National Institute of Social Defence (NISD).
- TAPAS is a standard MOOC (Massive Open Online Course) platform with course material such as filmed lectures and e-study material.
- It also includes discussion forums to support and encourage interactions among students and course coordinators.
- The five basic courses are on Drug (Substance) Abuse Prevention, Geriatric/Elderly Care, Care and Management of Dementia, Transgender Issues and on comprehensive course on Social Defence Issues.
- Its primary objective is to impart training and enhance the knowledge and skills for the capacity building of the participants.
- It seeks to provide access to lectures by subject experts, study material and more, but in a manner that it supplements the physical classroom without compromising on the quality of teaching.
- The TAPAS portal is developed by the National Institute of Social Defence, Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment.
- The idea of TAPAS was conceptualized at a time when exploring the online medium for work and education had become imperative due to the outbreak of Covid 19 pandemic.

- It is the nationwide programme as part of Azadi ka Amrit Mahotsav which celebrates 75 years on India’s Independence.
- It will be organized in nearly 750 Districts, 75 villages in each of the Districts across the country.
- It was launched at 75 other locations across the country, including Delhi’s Major Dhyan Chand National Stadium, the Cellular Jail in Port Blair, Kaza Post in Lahaul Spiti, Mumbai’s Gateway of India and the Attari Border in Punjab among many others.
- The Freedom Run event will also connect the country with their national heroes who got India its freedom.
- It aims to promote the Fitness ki Doze, Aadha Ghunta Roz campaign.
- The key activities of Fit India Freedom Run 2.0 include pledge, rendering of National Anthem, Freedom Run, cultural functions at venues and awareness among Youth Volunteers to participate.
- The Fit India Freedom Run 2.0 aims at "Jan Bhagidari se Jan Aandolan".
- It was launched on 29th August, 2019 by the Prime Minister with a view to make fitness an integral part of our daily lives.
- Its mission is to bring about behavioural changes and move towards a more physically active lifestyle.
- It proposes to undertake various initiatives and conduct events to achieve the following objectives:
- To promote fitness as easy, fun and free
- To spread awareness on fitness and various physical activities that promotes fitness through focused campaigns
- To encourage indigenous sports
- To make fitness reach every school, college/university, Panchayat/village, etc.
- To create a platform for citizens of India to share information, drive awareness and encourage sharing of personal fitness stories

- It was declared that August 14 would now be observed as “Partition Horrors Remembrance Day” to commemorate the “struggles and sacrifices” of millions who were displaced and who lost their lives during Partition.
- It aims to keep reminding us of the need to remove the poison of social divisions, disharmony and further strengthen the spirit of oneness, social harmony and human empowerment.
- The official drew a parallel with how other countries mark dark chapters of their history such as Holocaust, Slave Trade, and Bangladesh’s March 25 as Genocide Day to mark the brutal Pak crackdown.
- It holds significance in the backdrop of the deteriorating situation in Afghanistan and the steady advance of the Taliban raising old spectres in the region.
- In February, 1947, Lord Mountbatten was sent as the Viceroy to India to ensure early transfer of power. He put up his plan on June 3, 1947 which included partition of India.
- Following the Mountbatten Plan, June 3, 1947, India was made free, but by partitioning India the new state of Pakistan was created.
- The major points of the plan were as follows:
- Dominion Status
- The 3rd June, 1947 Plan, famously came to be known as the Mountbatten Plan.
- It sought to affect an early transfer of power.
- This transfer of power was to be done on the basis of Dominion Status to two successor states, India and Pakistan.
- Partition
- The members of the Legislative Assemblies of Bengal and the Punjab should meet separately in two groups i.e. representatives of the predominantly Hindu areas, and representatives of the predominantly Muslim areas.
- If both sections of each of these Assemblies voted for partition, then that province would be partitioned.
- Partition will be followed by creation of two dominions and two constituent assemblies.
- If Bengal decided in favour of partition, a referendum was to be held in the Sylhet District of Assam to decide its fate.
- Similarly, a referendum was proposed to decide the future of the North West Frontier Province.
- Sindh Legislative Assembly of was to decide either to join the existing Constituent Assembly or the New Constituent Assembly.
- Boundary Commission
- In case of partition, the viceroy would set up a Boundary Commission to demarcate the boundaries of the province on the basis of ascertaining the contiguous majority areas of Muslims and non-Muslims.
- Thus, a boundary commission was set up under the chairmanship of Sir Cyril Redcliff for demarcating the boundaries of new parts of the Punjab and Bengal.
- Princely States
- The British suzerainty over these Princely states was terminated.
- They were given the choice to remain independent or accede to dominions of India or Pakistan.
- Transfer of Power
- Mountbatten announced at a press conference that the British would soon leave India for good on 15 August 1947.
- Thus, an early date was decided by the British to leave India as compared to 30th June 1948 as decided earlier.
- Thus, the League’s demand for creation of Pakistan was conceded to the extent that it would be created, but taking Congress’ position on unity into account Pakistan would be made as small as possible. Mountbatten’s formula was to divide India but retain maximum unity.
- Rationale for an early date
- One of the major reasons for an early date for withdrawal was the desperation of the British to secure Congress’s agreement on dominion status.
- The British also wanted to escape responsibility for the rapidly deteriorating communal situation.
- Dominion Status
- Mountbatten’s formula was to divide India and at the same time retain maximum possible unity.
- The actual division between the two new dominions of India and Pakistan was accomplished according to what has come to be known as the 3rd June Plan or Mountbatten Plan
- It was announced at a press conference by Mountbatten on 4 June 1947, and the date of independence was also announced – 15 August 1947.
- Congress accepted the dominion status provided under this Plan for various reasons:
- To ensure a peaceful and quick transfer of power
- It was more important for the Congress to assume authority to check the explosive situation
- It would allow for some much-needed continuity in the bureaucracy and the army
- It provided for two dominion states: India and Pakistan
- The boundaries between the two dominion states were to be determined by a Boundary Commission which was headed by Sir Cyril Radcliff.
- It provided for partition of Punjab & Bengal and separate boundary commissions to demarcate the boundaries between them.
- Pakistan was to comprise the West Punjab, East Bengal, Territories of the Sind, North West frontier provinces, Syllhat divisions of Assam, Bhawalpur, khairpur, Baluchistan and 8 other princely states of Baluchistan.
- The authority of the British Crown over the princely states ceased and they were free to join either India or Pakistan or remain independent.
- Both the dominions of India and Pakistan were to have Governor Generals to be appointed by the British King.
- The constituent assemblies of both the states were free to make constitutions of their respective countries.
- Any modification or omission could be done by the Governor General.
- British Government would not continue any control on any dominion.
- The Governor General was invested with adequate powers until March 1948 to issue orders for effective implementation of the provisions of the Indian independence act 1947.
- Those civil servants who had been appointed before the August 15, 1947, will continue in service with same privileges.
- SAMVAD is Support, Advocacy & Mental health interventions for children in Vulnerable circumstances And Distress.
- It is a National Initiative and Integrated Resource that works in child protection, mental health and psychosocial care.
- Its vision is to enhance child and adolescent psychosocial well-being, particularly of children in difficult circumstances, through promotion of integrated approaches to mental health and protection.
- It has been instrumental in providing coping mechanism for children in distress by training close to 1 lakh stakeholders comprising of Child Protection Functionaries, tele-counsellors, educators etc.
- To develop standardized child-centric modules and resources for the capacity building of primary, secondary and tertiary level psychological and mental healthcare service providers.
- To strengthen knowledge and skills in child and adolescent protection and psychological care in various cadres of child care service providers in the country.
- To enhance child and adolescent protection and psychological care implemented by government and NGOs by providing technical support.
- To undertake studies, audits, research and advocacy on issue pertaining to child and adolescent protection and related issues of mental health and psychological care.
- To utilize the experiences of capacity building, technical programmatic report and research in informing child and adolescent laws and policies in the country.
- It will engage for the first time in independent India with functionaries in Panchayats thereby ushering in a silent revolution in addressing psychosocial challenges amongst vulnerable children.
- It is slated to begin work with Panchayati Raj systems to:
- Integrate child protection and mental health in aspirational districts across the country; and
- Facilitate awareness generation and improve service delivery at the grassroot level
- Its new initiatives with regards to mental health and psychosocial care of children in difficult circumstances have encompassed:
- Specialized training curriculum on childhood trauma;
- Interventions for children in conflict with the law;
- Forensics in child and adolescent psychiatry and mental health; and
- Education and mental health support to children with special needs, protection and care
- The 2021 meeting was aimed to promote tourism cooperation among the member states and reviewed the intra IBSA Tourism cooperation.
- The meeting emphasised the importance of domestic tourism in reigniting the tourism economy as it can prepare the domestic tourism industry for the arrival of international visitors.
- It recognized the importance of strengthening cooperation in tourism to overcome the impact of Covid 19 pandemic on the tourism sector.
- The adoption of the IBSA Tourism Ministers Joint Statement was a significant moment during the 2021 meeting of tourism minister.
- It is an outcome document on cooperation and promotion for speedy recovery of travel and tourism.
- It is a unique forum which brings together India, Brazil and South Africa, three large democracies and major economies from three different continents, facing similar challenges.
- It is a trilateral, developmental initiative between the Government of India, The Government of Federative Republic of Brazil and The Government of the Republic of South Africa.
- The grouping was formalised and named the IBSA Dialogue Forum when the foreign ministers of the three countries met in Brasilia on June 6, 2003 and issued the Brasilia Declaration.
- It aims to promote South-South cooperation and exchange.
- The aim of the IBSA Tripartite Agreement is:
- For strengthening relations between the member countries for economic development;
- For promoting cooperation in the field of tourism; and
- Expansion of tourism relations with a view to understand and appreciate each other's history, culture and way of life
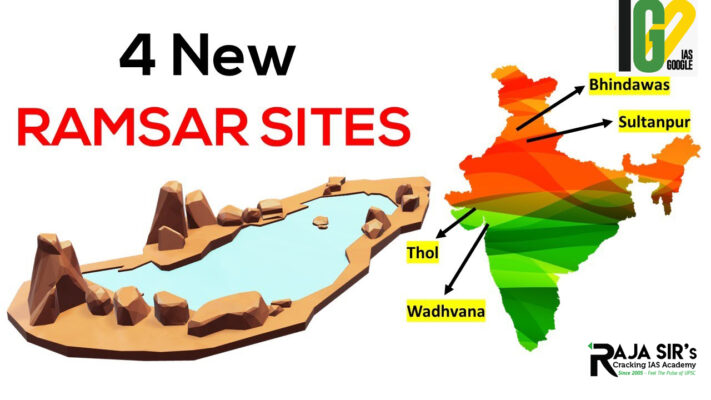
- The 46 Ramsar sites in India include the Chilika Lake in Odisha, Keoladeo National Park in Rajasthan, Harike Lake in Punjab, Loktak Lake in Manipur and Wular Lake in Jammu and Kashmir.

- The Convention on Wetlands is an intergovernmental treaty adopted on 2 February 1971 in the Iranian city of Ramsar.
- It is the first of the modern global intergovernmental treaties on the conservation and sustainable use of natural resources.
- All Parties to the Convention have the obligations to include in the List at least one site that meets the criteria established by the Conference of the Parties.
- It is the intergovernmental treaty that provides the framework for the conservation and wise use of wetlands and their resources.
- The Ramsar Convention has adopted a very inclusive definition of Wetlands:
- "Wetlands are areas of marsh, fen, peatland or water, whether natural or artificial, permanent or temporary, with water that is static or flowing, fresh, brackish or salt, including areas of marine water the depth of which at low tide does not exceed six metres".
- The Ramsar list aims to conserve an international network of wetlands that are important for sustaining biological diversity.
- It manifests India’s century old ethos of preserving natural habitats, working towards flora and fauna protection, and building a greener planet.
- It aims at sustaining human life through the maintenance of their ecosystem components, processes and benefits.

- It is a human-made freshwater wetland and the largest one in Haryana.
- The sanctuary is used throughout the year as a resting and roosting site by over 250 bird species.
- It supports more than 10 globally threatened species including the endangered Egyptian Vulture, Steppe Eagle, Pallas’s Fish Eagle, and Black-bellied Tern.
- It was established as a Bird Sanctuary by the Government of India in 3rd June, 2009.
- It is located in Gurgaon district of Haryana.
- It supports more than 220 species of resident, winter migratory and local migratory waterbirds at critical stages of their life cycles.
- More than 10 of these are globally threatened, including the critically endangered sociable lapwing, and the endangered Egyptian Vulture, Saker Falcon, Pallas's Fish Eagle and Black-bellied Tern.
- It lies on the Central Asian Flyway and supports more than 320 bird species, including more than 30 threatened waterbird species.
- It is home to critically endangered White-rumped Vulture and Sociable Lapwing; and the vulnerable Sarus Crane, Common Pochard and Lesser White-fronted Goose.
- It is an open water habitat surrounded by cropland, fallow land and scrubland, which helps other mammals to co-exist.
- It is made up of a reservoir that was created in 1912 as an irrigation tank when the Maharajas of Baroda (Gaekwads) ruled the region.
- The lake, and the area around, was declared a sanctuary only in 1988, as it is home to a large number of avian species.
- It is important as it provides wintering ground to migratory waterbirds, including over 80 species that migrate on the Central Asian Flyway.
- They include some threatened or near-threatened species such as the endangered Pallas’s fish-eagle, the vulnerable Common Pochard, and the near-threatened Dalmatian Pelican, Grey-headed Fish-eagle and Ferruginous Duck.
- The nodal laboratory is CSIR-Central Institute of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants (CSIR-CIMAP), Lucknow
- The participating laboratories are CSIR-Institute of Himalayan Bioresource Technology (CSIR-IHBT), Palampur; CSIR-Indian Institute of Integrative Medicine (CSIR-IIIM), Jammu; CSIR-National Botanical Research Institute (CSIR-NBRI), Lucknow; and CSIR-North-East Institute of Science and Technology (CSIR-NEIST), Jorhat.
- It is envisaged to bring transformative change in the aroma sector through desired interventions in the areas of agriculture, processing and product development for fuelling the growth of aroma industry.
- It will promote the cultivation of aromatic crops for essential oils that are in great demand by aroma industry.
- It will to enable Indian farmers and aroma industry to become global leaders in the production and export of some other essential oils on the pattern of menthol mint.
- Under the CSIR Aroma Mission, important medicinal and aromatic plants are being cultivated in 6,000 hectares of land.
- It will put a mechanism in place for timely agro-advisory, ensuring optimal productivity and fair price of the produce to the farmers and reducing the import of essential oils.
- Bring about 5500 ha of additional area under captive cultivation aromatic cash crops particularly targeting rain-fed /degraded land across the country
- Provide technical and infrastructural support for distillation and values-addition to farmers/growers all over the country
- Enabling effective buy-back mechanisms to assure remunerative prices to the farmers/growers
- Value-addition to essential oils and aroma ingredients for their integration in global trade and economy
- It has generated rural employment of farmers, spurred entrepreneurship in aromatic oils and other aromatic products manufacturing.
- The Mission has generated 10 to 12 lakh man-days of rural employment and more than 500 tonnes of essential oil worth Rs.60 crores was produced during the last two years.
- It has lowered the import of essential and aromatic oils.
- The activities of the Mission will improve availability of quality material on sustainable basis for a boom in the herbal industry based on essential oils.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies