- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
16th Sep 2021
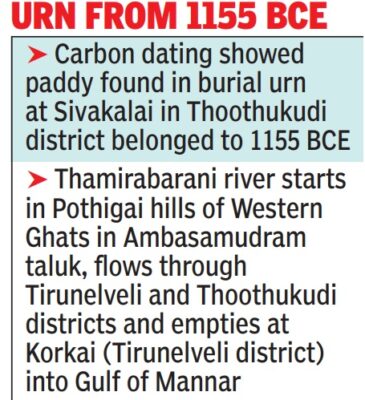
THAMIRABARANI CIVILISATION IN TAMIL NADU A carbon dating analysis of rice with soil, found in a burial urn at Sivakalai in Thoothukudi district of Tamil Nadu has yielded the date of 1155 BC, indicating that the Thamirabarani civilisation dates back to 3,200 years. Announcement made following the excavation:
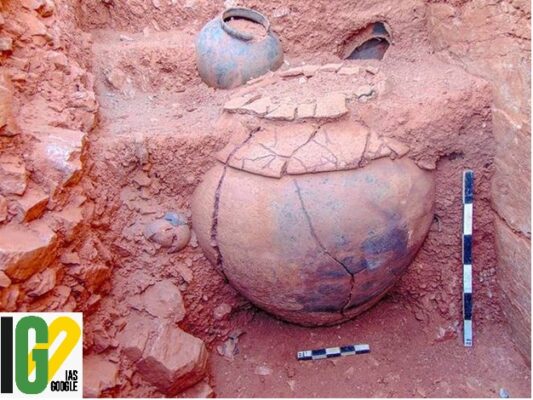

- Chief Minister of Tamil Nadu announced the establishment of Porunai Museum in Tirunelveli at a cost of ₹15 crore.
- The state archaeological department will conduct research in Quseir al-Qadim in Egypt, which was once part of the Roman empire, as well as in Khor Rori in Oman to establish Tamils’ trade relations with these countries.
- The government will also conduct similar studies in southeast Asian countries like Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia and Vietnam (conquered by Tamil king Rajendra Chola).
Thamirabarani River:
- The Thamirabarani is a perennial river that originates from the Agastyarkoodam peak of Pothigai hills of the Western Ghats.
- It flows through districts of the Tamil Nadu and into the Gulf of Mannar.
- The river forms the Paanatheertham waterfalls as it enters the Kariyar reservoir.
- The river descends down the mountains near Papanasam, where it forms the Kalyanatheertham falls and Agasthiar falls.
- Tributary rivers: Karaiyar, Maniamuthar river, Peyar, Servalar river, Gadananthi river, Ullar, Pachaiyar river, Pambar and the Ramanathi river.
History:
- The river got its name from the Tamil word “tamiran” which means copper. Since the traces of the copper metal was found in this river, this river is known as Thamirabarani.
- It was called the Tamraparni River in the pre-classical period, a name it lent to the island of Sri Lanka.
- Apart from the metal traces, a lot of medicinal properties are found in this river, as this flows from the Podhigai hills where many of the medicinal plants and shrubs grow.
- The old Tamil name of the river is Porunai.
THE MISSION THAT NEVER ENDED: KNOW ALL ABOUT SIGNIFICANT FINDINGS BY CHANDRAYAAN-2 The Orbiter part of Chandrayaan-2 has gathered a wealth of information about the Moon and its environment. About the Information gathered: Water Molecule:

- Imaging Infra-Red Spectrometer (IIRS) has been able to distinguish between hydroxyl and water molecules.
- It has found signatures of water at all latitudes, in the Polar Region of Moon.
- The IIRS characterized hydration features in the north polar region on the far side of the Moon and quantified the hydration within a crater.
- Dual Frequency Synthetic Aperture Radar has reported unambiguous detection of potential water ice at the poles.
Minor Elements:
- Large Area Soft X-Ray Spectrometer (CLASS) has detected minor elements chromium and manganese through remote sensing.
- The finding can lay the path for understanding magmatic evolution on the Moon and deeper insights into the nebular conditions.
- CLASS has mapped nearly 95% of the lunar surface in X-rays.
- Sodium, a minor element on the Moon surface, was detected without any ambiguity.
Studying the Sun:
- Solar X-ray Monitor (XSM), has collected information about solar flares.
- XSM has observed many microflares outside the active region.
- This has great implications on the understanding of the mechanism behind heating of the solar corona.
Chandrayaan-2:
- It is the second lunar mission of India after the success of Chandrayaan 1.
- It was conducted for the understanding of the Moon’s origin and evolution.
- It was launched from Satish Dhawan Space on July 22, 2019, by GSLV Mk III-M1.
Highlights of Chandrayaan 2:
- Fostered the findings of Chandrayaan 1 reported by the ISRO.
- The mission targeted the South Polar region of the Moon which was completely unexplored.
- Focused on the extensive mapping of the lunar surface for studying variations in its composition and tracing the Moon’s origin and evolution.
The mission consisted of three main modules:
- Lunar orbiter
- Vikram lander (named after Vikram Sarabhai, the father of India’s space program)
- Lunar rover named Pragyan
Significance of Chandrayaan 2:
- On October 14, 2019, Chandrayaan-2 detected the presence of Argon-40 in the lunar exosphere.
- On July 30th, 2020 Chandrayaan-2 imaged the Sarabhai Crater located on the north-east quadrant of the moon.
South Pole of the moon:
- Due to the moon’s axis, few regions on the South Pole always remains dark especially the craters and have higher chances of containing water.
- The craters might have never received sunlight and thus, increasing the chances of presence of ice on such surfaces.
- The lunar surface area at the south pole of the Moon that remains in shadow is thus making moon’s South Pole interesting.
- This increases the probability of the existence of water in permanently shadowed areas around it.
INDIA, U.S. AGREE TO COLLABORATE ON EMERGING FUELS Minister of Petroleum and Natural Gas co-chaired a virtual Ministerial meeting with U.S. Secretary of Energy to launch the U.S.-India Strategic Clean Energy Partnership (SCEP).
 SCEP:
SCEP:
- SCEP is launched in accordance with U.S.-India Climate and Clean Energy Agenda 2030.
- SCEP organizes inter-governmental engagement across five pillars of cooperation:
- Power and Energy Efficiency
- Responsible Oil and Gas
- Renewable Energy
- Sustainable Growth
- Emerging Fuels
Highlights of the Meeting:
- The revamped clean energy partnership will intensify the efforts from both sides to take advantage of the complementarities that exist between US and India.
- Emphasis on upscaling cooperation under the renewable energy pillar.
- India’s renewable energy target is 450 GW by 2030.
- Strengthening electric grid in India to support large-scale integration of renewables, as well as promoting energy efficiency and conservation measures.
- India-US Low Emissions Gas Task Force, on innovative projects to support India’s vision of gas-based economy.
- Institutionalization of India Energy Modeling Forum with the constitution of Six Task Forces for carrying out research and modeling in different areas.
- Expanding the scope of smart grid and storage as part of the Partnership to Advance Clean Energy (PACE)-R initiative.
KONGTHONG AMONG 3 INDIAN ENTRIES FOR UNWTO ‘BEST VILLAGE CONTEST Meghalaya’s whistling village – Kongthong has been selected as one of three India entries for the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) 'Best Tourism Village' contest.
- The other two villages that have been selected are Pochampally of Telangana and Ladhpura Khas in Madhya Pradesh.
Whistling village:

- Kongthong located in East Khasi Hills district of Meghalaya. It is popularly known as “whistling village”.
- The village is talked about for its unique tradition called 'Jingrwai Iawbei' where a mother assigns a tune or lullaby to a child within a week of birth, which becomes his/her unique identity, instead of a name.
- The village is nestled in the Khat-ar Shnong area, is famous for its panoramic view, unique culture and virgin beauty.
- Khat-ar-shnong, a valley region in East Khasi Hills, Meghalaya reportedly has several other villages where people call each other by a tune and talk through whistling, apart from Kongthong.
- However, Meghalaya Rural Tourism Forum chairman said that it does not depict the real practice which is called ‘rwai sur iaw-bei’.
- The unique tradition is by assigning a song as a name to a newborn child in no way is associated with whistling.
- The individual actually produces verbal utterance of words in the form of a song when naming a child which is totally different from someone who is producing a sound from their mouth in the form of whistling.
MUMBAI TEEN NAMED 2021 INTERNATIONAL YOUNG ECO-HERO FOR ENVIRONMENT PROJECT A 12-year-old environmental activist from Mumbai- Ayaan Shankta has been named as a 2021 International Young Eco-Hero in recognition of his efforts to solve tough environmental problems.
- He won the third place in the 8-14 age category for his project Conservation and Rehabilitation of Powai Lake.
International Young Eco-Hero:

- Every year since 2003, Action For Nature (AFN) has sought to recognize and reward young people who are taking action to solve the world’s tough environmental problems.
- Youth from countries around the globe send in their stories and explain their work.
-
Each Eco-Hero Award winner receives a cash prize of up to $500, a certificate of achievement, media coverage, and exclusive access to the eco-hero alumni facebook group.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies