- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
18th Sep 2021
GUPTA PERIOD STAIRS, PILLARS FOUND IN ETAH
The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) discovered the remnants of an ancient temple dating back to the 5th century CE, the Gupta period, in Etah, Uttar Pradesh.
 Discovery:
Discovery:

 Babuyan Islands:
Babuyan Islands:
 Highlights:
Highlights:
 Discovery:
Discovery:
- The stairway includes Shankhalipi inscriptions which state ‘Sri Mahendraditya,' the title of the Gupta emperor Kumaragupta I.
- Shankhalipi is an elaborate, stylized ancient script that was employed for names and signatures between 4th and 8th century CE.
- There were two ornamental pillars that were near to one other and had human sculptures on them.
- The writing discovered on the Etah skeletons has previously been discovered on a horse statue in Lakhimpur Kheri.
- The bones were dated to Kumaragupta 1's reign.
- The Etah ruins are the third Gupta era structure temple discovered so far.
- Earlier, only two structural temples were found — Dashavatara Temple in Deogarh and Bhitargaon Temple in Kanpur Dehat.
- Kumaragupta 1 was the son and successor of Chandragupta II.
- Reign: 414 - 455 AD
- Adopted the titles of ‘Shakraditya’ and ‘Mahendraditya’.
- Performed ‘Ashvamedha’ sacrifices.
- He laid the foundation of Nalanda University which emerged as an institution of international reputation.
- These are – Karandanda, Mandsor, Bilsad inscription (oldest record of his reign) and Damodar Copper Plate inscription.
- Gupta period marks the beginning of Indian temple architecture.
- Manuals were written regarding how to form temples.
- Square building with flat roof
- Shallow pillared porch
- Sanctum (garbhagriha) at the center of the temple
- A single entrance & porch (Mandapa)
- Mandapa appears to originate 1st from here
- Example- Vishnu Varaha temples in (MP)
- Square temple with a squat tower (shikhara) above
- Pillared approach, a high platform at the base
- Examole- Ladkhan Temple at Aihole (Karnataka)
- An elaboration of the first type
- Addition of an ambulatory (paradakshina) around the sanctum
- Most unique achievement of this stage was “Curvilinear tower” i.e., “Shikhara”.
- “Nagara Style” of temple making.
- Example- Dasavatara temple (Deogarh, Jhansi)
- Rectangular temple with an apsidal back
- Barrel-vaulted roof above
- Example- Kapoteswara temple at Cezarla (Andhra Pradesh)
- Circular temples with shallow rectangular projection
- Example- Maniyar Math shrine at Rajgir, Bihar
ATAL INNOVATION MISSION LAUNCHES SPACE CHALLENGE IN COLLABORATION WITH ISRO & CBSE ACROSS INDIA Atal Innovation Mission and Atal Tinkering Labs jointly with Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) have launch ATL Space Challenge 2021 for young students during World Space Week from October 4 to 10.
Objective:

- To enable young innovators of schools across India to learn and engage in creating new, efficient and innovative solutions for specific, real-world challenges in the space sector and develop solutions which address the key problem areas of the challenge.
- Explore Space: gaming technology, app development, robotics
- Reach Space: 3D technology, artificial intelligence or machine learning in space, space apps
- Inhabit Space: 3D technology, healthcare, AI/ML in space
- Leverage Space: geospatial technology, drone Technology, visualize data
- Students from both ATL and non-ATL schools from Classes 6 to 12 can submit their entries in the space challenge.
- It is a special campaign for Digital Onboarding and Training for street vendors under PM SVANidhi scheme launched across 223 cities in the country.
- The Bharat Pe, Mswipe, Phone Pe, Paytm, Ace ware will participate in this drive to issue UPI IDs, QR code and provide digital training.
- Digital Payment Aggregators will help the street vendors to bring enhanced adoption of digital transactions and behaviour change.
- To promote digital transactions the Lending Institutions will train the beneficiaries for conducting digital receipt and payment transactions.
- Out of 22.41 lakh digitally on-boarded street vendors, 7.24 lakh street vendors are digitally active and have recorded 5.92 Cr number of digital transactions.
 Babuyan Islands:
Babuyan Islands:
- Babuyan Islands are a group of volcanic islands forming the northern extension of the Philippine Archipelago, located in the Pacific Ocean.
- They are made up of five principal islands and a collection of smaller islands surrounding them.
- The Babuyan Islands are situated in the Luzon Strait, to the north of Luzon Island and to the south of the Batanes archipelago.
- These islands are separated from the Balintang Islands in the northeast by the Balintang Channel and from the Luzon Island by the Babuyan Channel in the south.

- Women’s Reservation Bill [108th Constitution Amendment Bill] is one of the longest pending legislations in the Indian Parliament.
- The Bill seeks to reserve 33.33% seats in the Lok Sabha or the Lower House of Indian Parliament and in the State Legislative Assemblies for women.
- This would be in accordance with the 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendments which reserved the same percentage of seats for women in rural and urban local bodies respectively.
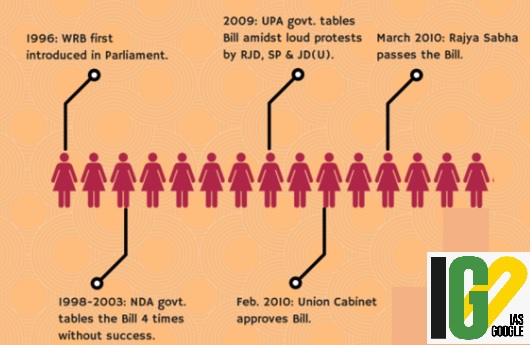
- The Bill was initially launched in 1996, and has been introduced in the Indian Parliament several times. However, the status of the bill remains undecided primarily due to lack of political consensus.
- The Constitution Bill seeks to reserve one-third of all seats for women in the Lok Sabha and the State Legislative Assemblies.
- The allocation of reserved seats shall be determined by such authority as prescribed by the Parliament.
- One third of the total number of seats reserved for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes shall be reserved for women of those groups in Lok Sabha and State Legislative Assemblies.
- Reserved seats may be allotted by rotation to different constituencies in the States or Union Territories.
- Reservation of seats for women shall cease to exist 15 years after the commencement of this Amendment Act.
- Proponents of the bill stress the necessity of affirmative action to improve the condition of women.
- Some recent studies on panchayats have shown the positive effect of reservation on empowerment of women and on allocation of resources.
- Major political parties are reluctant to give more tickets to women candidates.
- Majority of the female candidates contested as independents or from smaller parties in 2019 Lok Sabha elections.
- While women made up only 9% of the candidates in 2019, they won 14% of the seats, indicating that women significantly outperformed men.
- The Bill would benefit only women from privileged strata of the society. The reservation should contain 33% reservation within the women’s category for women belonging to Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes and Other Backward Classes.
- The Bill would only help female relatives of current politicians to enter public space and thereby defeat the very purpose of the Bill.
- There are instances of women being used as proxies by men to win elections.
- Women in modern India do not need reservation. It would be perceived that they are not competing on merit.
- Rotation of reserved constituencies in every election may reduce the incentive for an MP to work for his constituency as he may be ineligible to seek re-election from that constituency.
- The first Lok Sabha (constituted on 17 April 1952) only had 24 women members.
- There are 78 women MPs in the 2019 Lok Sabha, highest number in the history of the House.
- NCLT deals with matters related to companies’ law and the insolvency law, while ITAT deals with income tax matters.
 Highlights:
Highlights:
- The appointments came after Supreme Court flagged concerns regarding vacancies in the tribunals.
- There are around 250 posts lying vacant at various key tribunals and appellate tribunals such as NCLT, DRT, TDSAT and SAT.
- The appointments for NCLT will be for five years from the date of assumption of charge or till attaining the age of 65 or until further orders.
- The appointments in ITAT were made for a period of four years.
- NCLT is a quasi-judicial body in India that adjudicates issues relating to Indian companies.
- NCLT was constituted on 1st June 2016 under the Companies Act, 2013 on the recommendations of justice Eradi committee.
- It has been set up to govern companies registered in India and is a successor to the Company Law Board.
- The benches of NCLT are headed by the President and 16 Judicial Members and 9 Technical Members at different locations.
- NCLT is required to dispose the appeal within six months from the date of the receipt of the appeal.
- Appeals can be made by any person aggrieved by an order or decision of the NCLT, within a period of 45 days from the date on which a copy of the order or decision of the Tribunal.
- Decisions of the NCLT may be appealed to the National Company Law Appellate Tribunal (NCLAT).
- The decisions of NCLAT may be appealed to the Supreme Court of India.
- No civil court has the jurisdiction to consider any suit or proceeding with reference to any matter which the Tribunal or the Appellate Tribunal is empowered to decide.
- ITAT is a quasi-judicial institution which specializes in dealing with appeals under the Direct Taxes Acts.
- The oldest Tribunal in the country was constituted in January 1941 under section 5A of the Income Tax Act, 1922.
- Orders passed by the ITAT are final. An appeal lies to the High Court only if a substantial question of law arises for determination.
- The tribunal is divided in various zones. The headquarter being at originally at New Delhi but since 1952 at Mumbai.
- A sitting or retired judge of a High Court is appointed as President.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies