- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
19th Oct 2021
INDIAN ARMY WINS GOLD MEDAL AT CAMBRIAN PATROL EXERCISE IN UK
A team from 4/5 Gorkha Rifles (Frontier Force) which represented the Indian Army at the prestigious Cambrian Patrol Exercise at Brecon, Wales, UK from 13th to 15th October 2021 has been awarded Gold medal.






- The Indian Army team competed against a total of 96 teams which included 17 international teams representing Special Forces and prestigious Regiments from around the world.
- Ex Cambrian Patrol organised by the UK Army is considered the ultimate test of human endurance, team spirit.
- It is sometimes referred as the Olympics of Military Patrolling among militaries in the world.
- During the exercise, teams were assessed for their performance under harsh terrain and inclement cold weather conditions which presented various challenges in addition to the complex real world situations painted to them so as to assess their reactions in combat settings.
- Out of 96 participating teams, only three international patrols have been awarded a gold medal till phase 6th of this Exercise.

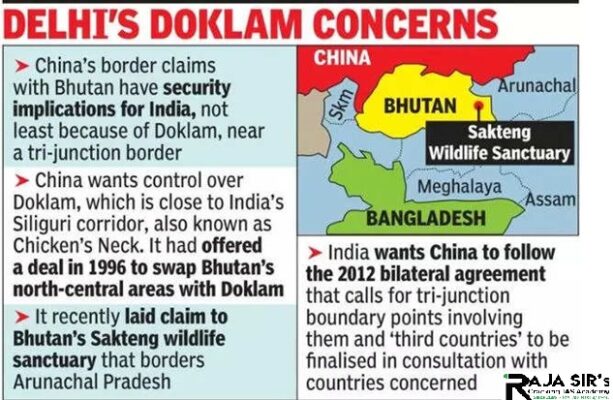
- The roadmap "for Expediting the Bhutan-China Boundary Negotiations", is expected to kickstart progress on the boundary talks process that has been delayed for five years, first due to the Doklam standoff in 2017, and then by the Covid Pandemic.
- The three-step roadmap had been finalised during the 10th Expert Group meeting in Kunming in April 2021.
- Since 1984, talks between Bhutan and China have largely focused on two separate areas of dispute, including Doklam and other areas in Bhutan’s West, near the India-China-Bhutan trijunction, and the Jakarlung and Pasamlung valleys located near Tibet to Bhutan’s North.
- More recently, China has also laid claims to Bhutan’s Eastern Sakteng region.

- Aim: To address concerns about many low- and middle-income countries that were hit hard by the COVID-19 pandemic, leaving them fewer resources to prepare for and deal with extreme weather events.
- The RST will allow the IMF members to lend or donate their share of the IMF's $650 billion in new SDRs to offer long-term financing to small island states and vulnerable middle-income countries, as well as low-income countries already served by the Poverty Reduction and Growth Trust.
- This will be the 17th Edition of the joint exercise.
- The previous version of this exercise was held at Mahajan Field Firing Ranges in Bikaner, Rajasthan in February 2021.

- Exercise Yudh Abhyas is the largest running joint military training and defence cooperation endeavor between India and USA.
- It is hosted alternately between both countries.
- The exercise aims at enhancing understanding, cooperation and inter-operability between two Armies.
- The joint exercise will focus on Combined Arms Manoeuvres in cold climatic conditions and is primarily aimed at sharing tactical level drills and learning best practices from each other.
- India lost almost 2 million hectares (Mha) of tree cover between 2001 and 2020, a decrease of nearly 5% since 2000.
- Seven states in the northeast accounted for three-fourths of that loss. The seven north-eastern states were among top 10 states with maximum tree cover loss in past 20 years.
- Odisha (7th), Kerala (9th) and Chattisgarh (10th) made up the rest.
- In past two decades, India’s north-eastern states accounted for 76.7% of the 1.93 Mha of lost tree cover.
- Assam accounted for the highest share of national tree cover loss in past 20 years at 14.1%.. From 2001 to 2020, the state lost 269 kilohectare (kha) of tree cover, equivalent to a 9.8% decrease in the state’s overall tree cover since 2000.
- In Assam, two hill districts of Karbi Anglong (97.4 kha) and Dima Hasao (63.2 kha) accounted for the majority share (60%) of tree cover loss.
- On the other hand, from 2001 to 2012, Assam added 29.9 kha of tree cover, equal to 12% of tree cover gain across India during that period.
- Mizoram lost 247 kha of tree cover, contributed 13% of India’s total tree-cover loss.
- The three districts of Champhai (67.6 kha), Lunglei (46 kha) and Aizawl (42.1 kha) accounted for 63% of the loss.
- Mizoram’s tree cover gain between 2001 and 2012 was 26.3 kha.
- Nagaland lost 225 kha of tree cover, which was 11.9% of India’s total loss during that period. It lost 17% of its total tree cover in those 20 years– the sharpest decline in the country.
- Mon, Tuensang, Mokokchang and Peren districts accounted for 57% of the state’s total loss.
- Nagaland witnessed 44 kha of tree cover gain from 2001 to 2012.
- Arunachal Pradesh, the largest state in northeast, lost 222 kha of tree cover from 2001 to 2020 which was 11.6% of India’s total loss. The state saw 3.5% decline in its tree cover in that period.
- The districts of West Siang, Lohit, Changland, Longding and Lower Dibang Valley accounted for 51% of Arunachal’s total loss.
- The state gained 47.8 kha of tree cover from 2001 to 2012.
- Manipur was the 5th highest contributor of tree-cover loss among all states, accounting for 10.3% of the total with a loss of 196 kha.
- There was a 12% decrease in the state’s tree cover in past 20 years.
- Charachandpur and Tameglong districts contributed 52% of the total loss.
- The state gained 33.8 kha of tree cover from 2001 to 2012, which was 13% of the country’s total gain in that period.
- Meghalaya lost 195 kha of tree cover in past 20 years, which was 10.3% of the country’s overall loss.
- The state lost 12% of its tree cover in that period and the three districts of South Garo Hills, East Khasi Hills and South West Khasi Hills were responsible for 56% of that.
- Meghalaya gained 19.1 kha of tree cover from 2001 to 2012.
- Tripura was the lowest contributor among the north-eastern states to the national figure with 102 kha of tree cover loss (or 5.5% of India’s total loss).
- But from 2001 to 2020, the state lost 15% of its tree cover, the second highest after Nagaland (17%).
- The state gained just 1.18 kha of tree cover from 2001 to 2012.
- Tree cover can refer to trees in plantations as well as natural forests, and tree cover loss is the removal of tree canopy due to human or natural causes, including fire.

- Manipur played a significant role in resisting the British in the Northeast during the 1857 revolution and in 1891.
- It was the only state to implement its own constitution.
- During the Anglo-Manipur War 1891, the Manipur war hero Yubraj Tikendrajit and General Thangal were publicly hanged in Fida, Imphal.
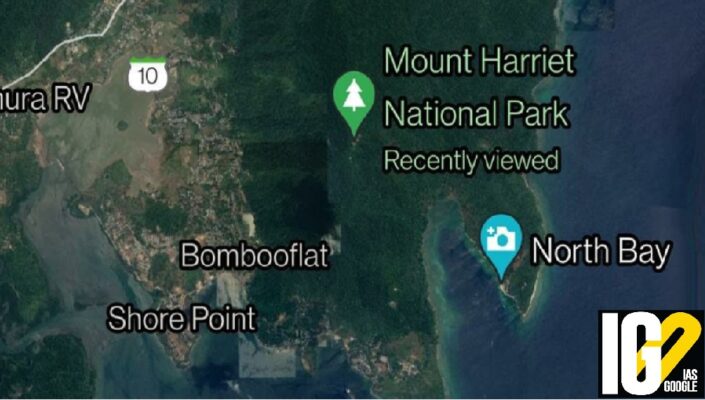
- After that, Maharaja Kulachandra Dhwaja Singh and 22 freedom fighters were sent to Kalapani and imprisoned on Mount Harriet.
- In their memory and contribution, the Mount Harriet was renamed as the Mount Manipur.

- The Anglo-Manipur War was an armed conflict between the British Empire and the Kingdom of Manipur.
- The war lasted between 31 March and 27 April 1891, resulting in a British victory.
- The Manipuri soldiers fought against three sides of British attack i.e., from Silchar, Kohima and Myanmar.
- The battle was fought at the Kheba hills of Khongjom in Manipur, hence called Khongjom war.
- Mount Harriet National Park is located in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The Park was established in 1969 and covers about 4.62 km2.
- Mount Harriet (383 metres), which is part of the park, is the third-highest peak in the Andaman and Nicobar archipelago.
- It is next to Saddle Peak (732 metres) in North Andaman and Mount Thullier (568 metres) in Great Nicobar.
- Important fauna: Andaman wild pigs (an endangered species), saltwater crocodiles, turtles, and robber crabs. The Park is also a butterfly hotspot.
- The 12 km long tunnel will enhance military capabilities in combating the threat of China's Western Theatre Command.

- The Sela Pass is located between the Tawang and West Kameng districts of Arunachal Pradesh.
- The construction of the tunnel started on April 01, 2019, and is expected to be over by June 2022.
- Being constructed by the Border Roads Organisation (BRO), it will be the world’s longest bi-lane road tunnel in the world at an altitude above 13,000 feet upon completion.
- The tunnel would cut the travel time between the Army's 4 Corps headquarters at Tezpur in Assam and Tawang by at least an hour.
- It will contribute towards security as well as socio-economic development of the region.
- The focus will be on the creation of a “virtuous cycle of growth and distribution” of wealth.
- Income redistribution to rebuild a broader middle class accomplished through the 1960 “income-doubling plan”.
- Focus will be on post-covid economic recovery, in order to achieve strong economic growth.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies