- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
20th July 2021
GOVT ANNOUNCES LAUNCH OF NATIONAL LOGISTICS EXCELLENCE AWARDS
Recently, the Ministry of Commerce & Industry has launched the National Logistics Excellence Awards.
National Logistics Excellence Awards
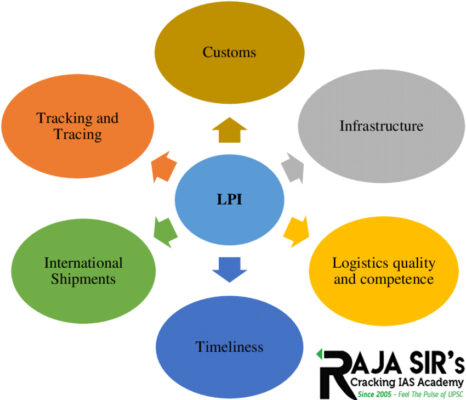




- The framework of awards has been finalized in consultation with the logistics associations and forum user industry partners.
- The award has been categorized into two groups:
- The first group includes logistics infrastructure/service providers; and
- The second one is for various user industries.
- They will highlight best practices including consolidation, process standardization, technological upgrade, digital transformations, and sustainable practices.
- The awards aim to turn the spotlight on logistics service providers who have attained operational excellence, adopted digitization and technology, improved customer service and pursued sustainable practices.
- The awards will showcase efforts towards supply chain transformation, supplier ecosystem development, skill development, automation, and other similar endeavours.
- They will be an opportunity to laud the extraordinary measures organisations have taken to address the deficiencies exposed by the COVID-19 pandemic.
- It includes last-mile delivery start-ups, development of cold storage facilities, effective transportation of oxygen, and uninterrupted supply of essential goods and services to the needy.
- The awards will help in improving India’s ranking in the global Logistics Performance Index (LPI).
- The Indian logistics sector has been growing at a CAGR of 10.5%, reaching approximately USD 215 billion in value in 2020.
- There are systemic, interconnected problems that must be addressed to enhance its efficiency.
- The comprehensive logistics costs amount to almost 14% of India’s GDP.
- The closing of India’s competitiveness gap vis-à-vis the global average of 8 percent, would make the Indian logistics sector advanced, organised and efficient, on par with global peers.

- It is located near Lala village of Abdasa taluka of Kutch.
- It is one of the smallest bird sanctuaries of the country, but a thriving breeding ground for the endangered birds.
- It is a semi-desert area allows for the ‘ghorad’ (local name) to feed on cereal crops that grow in the region.
- The Bustard sanctuary was set up in 1992.
- It is internationally acclaimed for successfully saving this precious species from the brink of extinction.
- It was declared as a sanctuary in 1965 and subsequently, an area of 258.71 sq. km. was declared a National Park.
- The endangered species like lesser florican, chinkara and wolf inhabit this area and this bustard has the rare distinction of being the heaviest flying bird.
- It is one of the two great Indian Bustard sanctuaries in Gujarat also known as Lala-Parjan Sanctuary.
- The varied vegetation, semi-arid grasslands, and marshy swamps make Kutch Bustard Sanctuary an ideal home for Great Indian Bustard.
- Varied vegetation, semi-arid grasslands, and marshy swamps make Kutch Bustard Sanctuary an ideal home for Great Indian Bustard
- It is a region of arid and semi-arid grasslands consisting of deserts, wetlands and marshy swamps. It is a grassland area which comprises of thorns, scattered bushes, and dry grass.
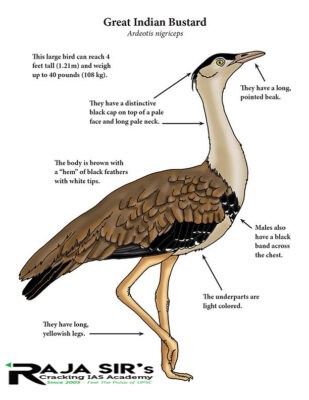
- Characteristics: It can easily be distinguished by its black crown on the forehead contrasting with the pale neck and head.
- They breed mostly during the monsoon season when females lay a single egg on open ground.
- They avoid grasses taller than themselves and dense scrub like thickets.
- Distribution: It was distributed throughout Western India, spanning 11 states, as well as parts of Pakistan.
- It is found scattered throughout the Indian states of Rajasthan, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka and Madhya Pradesh.
- Protection: It is listed in Schedule I of the Indian Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- It is categorized as Critically Endangered under the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.
- Habitat and Ecology: They inhabit dry and semi-dry grasslands with dispersed bushes and patches of scrub.
- The Breeding tends to occur in undisturbed or less degraded grassland sites.
- They are omnivores, feeding on insects, grass seeds, berries, rodents and reptiles.

- It is a small spacecraft, about the size of a big shoebox.
- Its main mission is to fly by and collect data from a near-Earth asteroid.
- It will also be America’s first interplanetary mission using a special solar sail propulsion.
- It will use stainless steel alloy booms and deploy an aluminum-coated sail measuring 925 square feet.
- The spacecraft will take about two years to cruise to the asteroid and will be about 93 million miles away from Earth during the asteroid encounter.
- It is equipped with special cameras and can take pictures ranging from 50 cm/pixels to 10 cm/pixels.
- It can also process the image and reduce the file sizes before sending them to the earth-based Deep Space Network via its medium-gain antenna.
- The images gathered by NEA Scout will provide critical information on the asteroid’s physical properties such as orbit, shape, volume, rotation, and dust & debris field surrounding it.
- It could help us develop strategies for reducing the potential damage caused in the event of an impact.
- The scientists will use this data to determine what is required to reduce risk, increase effectiveness, and improve the design and operations of robotic and human space exploration.
- Asteroids are rocky objects that orbit the Sun, much smaller than planets. They are also called minor planets.
- Asteroids are divided into three classes.
- First, those found in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter, which is estimated to contain somewhere between 1.1-1.9 million asteroids.
- The second group is that of trojans, which are asteroids that share an orbit with a larger planet.
- NASA reports the presence of Jupiter, Neptune and Mars trojans.
- In 2011, they reported an Earth Trojan as well.
- The third classification is Near-Earth Asteroids (NEA), which have orbits that pass close by the Earth.
- It is an online discovery platform for startups of the country.
- It exhibits the finest startups of the country that have been handpicked through various DPIIT and Startup India programs.
- It hosts most promising startups of the country chosen through various DPIIT and Startup India programs exhibited in a form of virtual profiles.
- Application for Startup Showcase: All DPIIT-recognized startups under Startup India are eligible to apply for the Showcase.
- Startups can apply on the Startup India website by filling a form, uploading their pitch deck, and catalogue.
- Final Shortlisting and Publishing on the Showcase platform: An Apex Committee has been constituted by DPIIT for the selection of startups for the Startup India showcase platform.
- It is done from the list of applications of startups, recommendations from states, and any other startup that the Apex Committee deems fit for the showcase platform.
- Visibility: Each startup has a profile page with detailed pitch about their product, innovation, and USP in forms of Videos and PDF links.
- It provides unique visibility to them in front of the entire startup ecosystem.
- The startups act as the flag bearers of good quality of Indian startups.
- Networking: It is also an online networking portal which offers various social and digital connect opportunities on the platform.
- Each startup profile is linked with Social Media Pages, LinkedIn URLs of founders and a direct Connect button which facilitate networking opportunities between users.
- Discovery: It is an online discovery platform for one of the most credible startups out there in our ecosystem.
- The platform is powered with various tools from a powerful search to an intuitive filter which will enable seamless discovery of startups for stakeholders.
- Star Repository: It is an all-star repository as the platform contains startups who have already proved their capabilities via different means (winning competitions, selling on GeM etc.)
- Discovery of startups with credible profiles for potential investment and acceleration opportunities;
- First reference point for new innovations and industry trends across the country
- Pipeline of ready innovative solutions for strategic deployment in your business units;
- Startup products and services for new business opportunities and cost/efficiency improvement; and
- Potential partners for international corporate looking to work with startups in India and expanding the innovation ecosystem across boundaries
- Discover startups that can improve public-service delivery and solve relevant problems under the ambit of Ministry
- Startup Pool that can work with Urban Local Bodies to improve the quality of life of citizens and address local problems in the fields of sanitation, health, waste, water, traffic, taxation, etc.
- Get visibility and recognition through India’s All-star Startup repository
- Discover fellow startups for networking and growth opportunities
- Get pilot opportunities from Governments, Corporate, and International organizations
- Get fund raising opportunities from relevant investors
- The virus was initially isolated in 1932.
- It is an alpha herpes virus enzootic in macaques of the genus Macaca.
- B virus is the only identified old-world-monkey herpes virus that displays severe pathogenicity in humans.
- B virus is also commonly referred to as herpes B, monkey B virus, herpes virus simiae, and herpes virus B.
- It is caused by macaques, a genus of Old World monkeys that serve as the natural host.
- While the virus is transmitted by macaques, chimpanzees and capuchin monkeys can also become infected and die.
- It can be transmitted via direct contact and exchange of bodily secretions of monkeys.
- It has a fatality rate of 70 per cent to 80 per cent.
- Macaque monkeys commonly have this virus, and it can be found in their saliva, feces (poop), urine (pee), or brain or spinal cord tissue.
- The virus may also be found in cells coming from an infected monkey in a lab.
- B virus can survive for hours on surfaces, particularly when moist.
- Till date, only one case has been documented of an infected person spreading B virus to another person.
- Humans can get infected if they are bitten or scratched by an infected monkey.
- Humans can get an infected monkey’s tissue or fluid on broken skin or in eyes, nose, or mouth.
- The scratch or cut oneself on a contaminated cage or other sharp-edged surface or get exposed to the brain (especially), spinal cord, or skull of an infected monkey.
- The symptoms typically start within one month of being exposed to B virus, but could appear in as little as three to seven days.
- The first indications of B virus infection are typically flu-like symptoms such as fever and chills, muscle ache, fatigue and headache.
- The infected person may develop small blisters in the wound or area on the body that came in contact with the monkey.
- The other symptoms of the infection include shortness of breath, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain and hiccups.
- The virus spreads to and causes inflammation (swelling) of the brain and spinal cord, leading to neurologic and inflammatory symptoms.
- India has emerged as the fifth largest foreign exchange reserves holder in the world after China, Japan, Switzerland and Russia.
- India’s foreign exchange reserves position is comfortable in terms of import cover of more than 18 months.
- India’s foreign exchange reserves provides cushion against unforeseen external shocks.
- The variation in India’s FOREX reserves is primarily the outcome of:
- RBI’s intervention in the foreign exchange market to smoothen exchange rate volatility;
- Valuation changes due to movement of US dollar against other international currencies in the reserve basket;
- Movement in gold prices; and
- Interest earnings from deployment of foreign currency assets and inflow of aid receipts
- In 2020-21, India’s balance of payments recorded surplus in both current account and capital account which contributed to the increase in foreign exchange reserves during the year.
- The current account deficit, accompanied by increasing foreign exchange reserves, reflects a surplus on the balance of payments i.e., the magnitude of the net capital inflows exceeds the volume of the current account deficit.
- The overall stability of the external sector depends on other components of balance of payments including remittances (transfers), income in the current account, the size of net capital flows and external debt.

- They are assets such as foreign currencies, gold reserves, treasury bills, etc. retained by a central bank that checks the balance payments and influences the foreign exchange rate of its currency.
- The International Monetary Fund defines reserves as external assets that are readily available to and controlled by monetary authorities for:
- Direct financing of external payments imbalances; and
- Indirectly regulating the magnitudes of such imbalances through intervention in exchange markets to affect the currency exchange rate, and/or for other purposes
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) acts as the custodian of foreign reserves, and manage reserves.
- It consists of cash, gold, bonds, bank deposits and financial assets denominated in foreign currencies.
- The most significant objective behind this is to ensure that RBI has backup funds if their national currency rapidly devalues or becomes altogether insolvent.
- If the value of the Rupee decreases due to an increase in demand of the foreign currency then RBI sells the dollar in the Indian money market so that depreciation of the Indian currency can be checked.
- A country with a good stock of forex has a good image at the international level because the trading countries can be sure about their payments.
- A good forex reserve helps in attracting foreign trade and earns a good reputation in trading partners.

- It is a Balancing Reservoir cum Drinking Water Project in Karnataka.
- It is proposed to be built at a deep gorge situated at the confluence of the Cauvery River and its tributary Arkavathi.
- It is a multipurpose project, which involves building a balancing reservoir, near Kanakapura in Ramanagara.
- It is aimed at ensuring drinking water to Bengaluru and neighbouring areas (4.75 TMC) and also can generate 400 MW power.
- It is aimed at storing Cauvery water going waste and use it during summer season for drinking water purpose.
- A balanced reservoir is planned at the confluence of River Arkavathi and River Cauvery, across the River Cauvery for a comprehensive drinking water scheme to cater to needs of Bengaluru citizens in the future.
- It is a complex situation from Karnataka’s point of view i.e. it is the last catchment that is unregulated below the KRS (Krishna Raja Sagar) dam and the Kabini Reservoir.
- Tamil Nadu fears that if Karnataka controls the water all the way up to Ontigondlu, the latter might not stick to its obligation mandated by the Supreme Court.
- The Mekedatu is one issue in the Cauvery water sharing dispute, which has been a bone of contention between the two since 1892.
- It is known as ‘Ponni’ in Tamil.
- It is the fourth-largest river in south India.
- It originates in the Western Ghats at Talakaveri in Karnataka’s Kodagu district and it passes through Tamil Nadu.
- The river bisects the state into north and south and finally reaches the Bay of Bengal at Poompuhar, also known as Kaveripoompattinam in Tamil Nadu.
- The Cauvery basin is spread over 81,155 sq km in the states of Karnataka (34,273 sq km), Tamil Nadu (43,856 sq km) and Kerala (2,866 sq km) and the Union Territory of Puducherry (160 sq km).
- Its major tributaries, Kabini and Moyar, join it before it reaches the Stanley Reservoir at Mettur in Tamil Nadu’s Salem district.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies