- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
27th Sep 2021
PROPOSED HERITAGE VILLAGE AT SINGAPERUMAL KOIL UNDER RURBAN MISSION TO BOOST TOURISM
The government proposed a plan to create a heritage village and boost tourism at Singaperumal Koil and nearby villages, Chennai.
Highlights:






- Government has sanctioned ₹25 lakh under the Shyama Prasad Mukherji Rurban Mission to promote heritage villages and tourism in the region.
- The ‘Rurban Mission’ covers Singaperumal Koil and six nearby villages — Appur, Chettipuniyam, Guruvanmedu, Kolathur, Reddipalayam, and Venkatapuram.
- The funds are allotted to develop infrastructure including:
- Drainage system, citizen service centres, common service centres
- Upgradation of schools with smart classrooms, piped water supply
- Skill development centres, solid and liquid waste management, and tourism promotion.
- SPMRM was launched in 2003, is in lines with Provision of Urban Amenities to Rural Areas (PURA).
- As per Census of India statistics, the rural population in India, stands at 833 million, constituting almost 68% of the total population.
- The rural population has shown a growth of 12% during the 2001-2011 period and there has been an increase in the absolute number of villages by 2279 units.
- Large parts of rural areas in the country are part of cluster settlements, these clusters have a potential for social and economic growth and development
- The mission would lead to the holistic development of the region and encourage integrated and inclusive rural development.
- 24×7 water supply
- Solid and Liquid Waste Management facilities at household and cluster level
- Provision of Inter and Intra village roads within the cluster
- Installation of street lights
- Transport facilities using green technologies
- Comprises various thematic areas in the sectors of Agri Services and Processing, Tourism, and Skill Development to promote Small and Medium Scale Enterprises
- Sanitation
- Access to Village Streets with Drains
- Agri-Services Processing and Allied Activities
- Education and Digital Literacy
- Sports and Social Infrastructure
- Healthy Environment
- 300 Rurban clusters are envisaged to be developed in a timebound manner. The number of Integrated Cluster Action Plans (ICAPs) approved are 288.
- Total investment approved in 288 ICAPs is Rs. 28,075 crores.
- NITI Aayog has proposed a new and extended Programme for over 1,000 clusters in the next 3 years.
- Import sector:
- India will become the world’s third largest importer by 2050 with a share of 5.9% of global imports, right behind China and the US.
- This will be due to its growing middle class and rising discretionary spending.
- At present, India is ranked eighth among largest importing nations with a 2.8% import share and is set to become the fourth largest importer by 2030.
- The US’s and the EU’s share of most import sectors is expected to decline out to 2030.
- This due to growing purchasing power of Asia’s middle-class, which accounts for a rising share of global import demand.
- This change is particularly marked in the food, travel and digital services sectors.
- Centre of economic gravity: Indo-Pacific:
- Between 2019 and 2050, 56% of global growth is expected to come from the Indo Pacific, compared with a quarter from the EU and North America combined.
- Growth within the Indo Pacific is expected to rebalance over time, with South Asia’s contribution (driven by India) rising.
- The world’s centre of economic gravity is shifting eastward for decades due to the rapid growth in Indo Pacific.
- China is a major driver of this eastward economic shift & is expected to become the world’s largest economy by 2030.
- China already displaced the US in Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) terms (which account for differences in local prices) in the mid-2010s.
- India would be the world’s third largest economy in 2050, ranking just behind China and the US, with a share of 6.8% in global GDP.
- At present, India is ranked fifth in size of world’s economies with a share of 3.3%.
- India’s GDP is projected to cross Germany by 2030 to become the fourth largest economy.
- Emerging economies:
- The role of emerging economies in the trading system will rise over time, consistent with their growing weight in the global economy.
- The ‘E7 group’ is the group of the seven largest emerging economies—China, India, Brazil, Russia, Indonesia, Mexico and Turkey.
- They are projected to equal the G7 countries’ share of global import demand by 2050.
- The action came after an external investigation’s found that the rankings were manipulated by “undue pressure” by top bank officials.
- The manipulated data had resulted in country rankings changed to favour China.
- The manipulation likely involves the then World Bank chief executive Kristalina Georgieva and the former World Bank president Jim Yong Kim.
- The report, considered a global benchmark to judge investment climate across nations, had boosted China’s ranking in 2017.
- Azerbaijan (DBR 2020): Azerbaijan’s global ranking should have been 28 (instead of 34) and it would have been on the list of top 10 improvers in the Doing Business 2020.
- Saudi Arabia (DBR 2020): Saudi Arabia’s global ranking would have been 63 (and not 62), and it would not have been the top improving economy in Doing Business 2020.
- United Arab Emirates (DBR 2020): UAE’s global ranking would have been unchanged at 16.
- China (DBR 2018): China’s global ranking in Doing Business 2018 would have been 85 instead of 78, a decline of 7 places.
- The Doing Business report outlined the levels of business regulation in 190 economies.
- The last report was launched in 2020, which was the 17th in the series of annual studies.
- It assessed the business climate on 12 broad parameters integral to starting, sustaining and winding down a business.
- The quantitative indicators ranged from dealing with construction permits, getting electricity, getting credit, protecting minority investors, paying taxes, and trading across borders.
- The study presented a detailed analysis of costs, requirements and procedures that a specific type of private company is subjected to in all countries and provided nations with specific prescriptions on how and when to reform key laws.
- Nations around the world monitored the annual reports since they set the Ease of Doing Business Index for the next year.
- The index is the formal ranking of nations – from most business-friendly to worst.
- This report card showed whether nations had improved or degenerated in their efforts to create a more liberal economic ecosystem, at least for the average business.
- Among 190 countries, India ranked 63rd in Doing Business in 2020.
- India was ranked 142 in 2014.
- India has improved its ranking by 79 positions in the five years between 2014 and 2019.
- India was also placed in the list of “economies with the most notable improvement” for the third year in a row.
- Humboldt penguin is a South American penguin. It grows about 26 to 28 inches long and weighs about 10.4 pounds.
- It has blackish-gray upperparts, white underparts, a black breast band, and a black head with white stripes running from the eyes around the ear-coverts to join beneath the chin.
- The penguins have the ability to withstand warmer climates.
- It nests on islands and rocky coasts and feeds in surrounding waters. Its habitat is highly influenced by the cold, nutrient-rich Humboldt Current flowing northward from Antarctica.
- They live along the coasts of Chile and Peru in the southeastern Pacific Ocean.
- The lifespan is about 20 years.
- They feed primarily on fish, especially anchovies, herring and smelt.
- They were first devastated by the mining of guano deposits in which the species prefers to nest for fertilizer.
- The penguin is threatened by intense commercial fishing and oil pollution.
- IUCN status: Vulnerable
- CITES: Appendix I

- The 'Helina' and 'Dhruvastra' are third generation anti-tank guided missiles that can engage targets both in direct hit mode as well as top attack mode.
- Helina (the Army version) and Dhruvastra (IAF version) have been designed and developed indigenously by Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- Helina is a fire and forget class ATGM mounted on an indigenous Advanced Light Helicopter (ALH) and has a minimum range of 500 m and a maximum range of 7 km.
- Once the Electro-Optic (EO) system of ALH identifies the target, it automatically hands over target to the missile.
- It is lock-on before launch.
- The system has all- weather day and night operational capabilities and can defeat battle tanks with conventional armour as well as explosive reactive armour (ERA).
- The Helina missile can engage targets both in direct hit mode as well as top attack mode.
- Third-generation anti-tank guided missile.
- Range: 500 m – 4 km
- The Nag Missile system fired from a Nag Missile Carrier (NAMICA) can take out targets at ranges of 4 to 7 kilometres.
- Named after: Former DRDO chief B D Nagchaudhuri
- Developed under: Integrated Guided Missile Programme
- Fire-and-forget and top-attack with capabilities of:
- Passive homing guidance
- It can target all types of tanks in day and night conditions.
- Produced by: Bharat Dynamics Limited (defence public sector undertaking)
- Missile Launcher of NAG: A BMP-II based system with amphibious capability
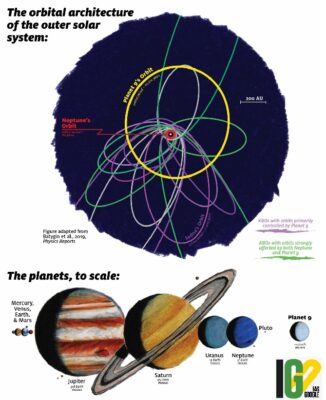
- According to the paper- The Astronomical Journal, Planet Nine has a mass of 6.2 (+2.2/-1.3) Earth masses.
- The paper explains about Planet Nine’s semimajor axis, inclination, and perihelion.
- The data only talks about the orbital path of Planet Nine but not where in the orbital path it is located.
- The planet Nine is likely to be very reminiscent of a typical extrasolar super-Earth.

- Planet Nine also known as Planet X, is a massive, hypothetical object in an elliptical orbit far beyond Pluto, at a distance that would take 10,000 to 20,000 Earth years for it to complete a single trip around the Sun.
- No direct observations have been made of an object fitting the description of Planet Nine.
- Unexpected patterns in the orbits of other, smaller objects in the icy outer reaches of the Solar System could be explained by the gravitational pull of such a body.
- The evidence of an undiscovered planet in the farthest reaches of our Solar System remains this clustering, along with a strange inclination of their orbits.
- A likely scenario explaining the body's far-flung position puts its origins somewhere between the orbits of Jupiter to Neptune.
- Despite its large, slow orbit, enough time should have passed since the dawn of the Solar System for it to have cleared its orbit of frozen chunks of dust and rock.
- The Karma puja is one of the most important festival in Jharkhand. It is performed by the Baiga, Oraon, Binjhwari and Majhwar tribes of the state.
- The spiritual and religious festival is associated with harvest, which is symbolized through a Karam tree.
- The tribal community believes that due to Karam Devta they have a good harvest.
- The festival is very auspicious and a symbol of fertility and prosperity.
- It is celebrated in the 11th moon of the Hindu month of Bhadrapada (August/September).
- Villagers go to the forest and collect the branch of Karam tree. They sing the traditional songs that praise the deity.
- They collect fruits and flowers which are essential for the Karma puja.
- Planting the tree of Karma initiates the process of Karma Puja. The branch of Karma tree is washed with milk and handia, the rice beer and then raised at the center of the dancing arena.
- Branches are decorated with garlands and curd; rice and flowers are offered by the devotees.
- Grains are filled in the red-colored baskets and offered to the branches.
- The young devotees wear barley seedlings on their head which are distributed among them.
- In 2019, a consortium of 12 national research and development laboratories joined hands in a rare effort to transform livelihoods in Odisha’s Nabarangpur.
- Central Institute of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants (CIMAP) in Lucknow is one of the five Council of Scientific and Industrial Research laboratories involved in the effort.
- Women SHGs have been asked to donate seeds after the annual harvest to prospective farmers, which would lessen their dependency on the market.
- CIMAP is promoting cultivation of lemon grass, Japanese mint and vetiver, and seeing the promise of a better return, farmers here are replacing eucalyptus plantations with the aromatic plants.

- Ghost net is fishing gear which are lost, voluntarily abandoned or dumped at sea by fishermen.
- These inevitably go on to kill marine life for several years, making it the most-deadly form of marine plastic debris.
- Based on the aim to address this growing issue, Visakhapatnam-based Greenwaves Environmental Solutions is working at coastal Andhra Pradesh along with WWF India.
- The project was initiated in Visakhapatnam in June 2021.
- The discarded fish nets and glass bottles collected during beach clean-ups are untangled and segregated as per type, size and colour
- It upcycles these nets to make products like bracelets, pouches, doormats and pots.
- The concept of upcycling fish nets is aimed at reducing the impact of marine pollution and also provides alternative livelihoods for fisherwomen.
- The International Union for Conservation of Nature estimates that at least eight million tons of plastic waste are discarded into the ocean every year.
- This is said to be 80% of the marine debris.
- The Minister also announced that “JIGYASA” will be extended to cover schools in over 700 districts of India within one year.
- It is a student- scientist connect programme of the Ministry of Science & Technology.
- The programme is inspired by Prime Minister’s vision of a new India and Scientific Social Responsibility (SSR) of Scientific Community and Institutions.
- Implemented by the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) in collaboration with Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan (KVS).
- The focus is on connecting school students and scientists to extend student's classroom learning with a well planned research laboratory based learning.
- The program will also enable the students and teachers to practically live the theoretical concepts taught in science by visiting CSIR laboratories and by participating in projects.
- Sea cucumbers are marine animals with a leathery skin and an elongated body containing a single, branched gonad.
- They are found on the sea floor worldwide. Many of these are gathered for human consumption and some species are cultivated in aquaculture systems.
- They serve a useful role in the marine ecosystem as they help recycle nutrients, breaking down organic matter after which bacteria can continue the degradation process.
- Sea cucumber in India is treated as an endangered species listed under schedule I of Wildlife Protection Act of 1972.
- It is primarily smuggled from Tamil Nadu to Sri Lanka in fishing vessels from Ramanathapuram and Tuticorin districts.
- Sea cucumbers are in high demand in China and Southeast Asia.
- These 41 trainers are from several initiatives and training programmes of Skill India— Directorate General of Training (DGT), Apprenticeship, Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY), Jan Shikshan Sansthan (JSS) and Entrepreneurship.
- The award is an annual celebration that focuses on honouring the skill trainers, their contribution to the skill ecosystem and the impact created by them on India's youth.
- Initiative of: Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship
- Category 1 National Award for Excellence- Trainer (Excellence in Training)
- Category 2 National Award for Excellence – Master Trainers (Excellence in Providing Training of Trainers)
- These committees would exercise oversight over all power-related schemes and its impact on the provision of services to the people.
- The composition of the committee would be:
- Most Senior member of Parliament (MP) in the district: Chairperson
- Other MPs in the district: Co-chairpersons
- District Collector: Member Secretary Chairperson/President of the District Panchayat: Member (e) MLAs of the district: Members
- All States and Union Territories will have to notify and ensure establishment of these District Electricity committees.
- The committee of a district will meet at the district headquarters at least once in three months to review and coordinate the overall development of power supply infrastructure in the district.
- All Government of India Schemes (power related), including their progress and quality issues.
- Development of Sub-transmission and distribution network including regular operations and maintenance of network - identifying further areas where strengthening is needed.
- Impact of the works on quality and reliability of power supply.
- Standards of Performance and consumer services quality of supply.
- Complaints and Grievance Redressal System.
- Purty Aggrotech pearls will be sold through 141 Tribes India outlets, apart from various e-commerce platforms.
- The aggrotech centre will be developed into a Van Dhan Vikas Kendra Cluster (VDVKC).
- There is a plan to develop 25 VDVKCs for pearl farming in Jharkhand.
- The breeding of oysters and development of pearls is a sustainable business and can be easily practiced by tribals who have access to nearby water bodies.
- The Trifed has signed an MoU with e-grocery platform Big Basket to promote and sell natural ‘Van Dhan’ products.
- Pearls are the only gemstones in the world that come from a living creature.
- Mollusks such as oysters and mussels produce these precious jewels.
- Freshwater pearls are pearls that are grown on pearl farms using freshwater mussels.
- Mussels are the organic hosts, the pearls can grow up to 10 times bigger than those made by saltwater oysters, naturally.
- Pearl farming is eco-friendly. Being Filter feeder oysters purify the water.
- Shellfish farming provides habitat for fish and improves species diversity.
- Reduces turbidity, improves light penetration, improves water quality reduces anoxia and nitrification
- A single oyster clears over 15 gallons of water a day, retaining particles as small as 2 microns.
- A small oyster farm clears 30 to 100 million gallons of water each day.
- The industry promotes foreign exchange earnings to the country.
- It supports tourism, its technology and the product are of interest to tourist.
- Jammu & Kashmir has abundant stock of Animal Husbandry and Dairy resources.
- The resources can be effectively integrated with Aroma Mission which was launched in J&K by Council of scientific and Industrial Research.
- It will pave the way for integrated Aroma Dairy Entrepreneurship, ensuring sustainable growth, increased income, and fresh avenues of livelihood for farmers.
- The focus will be on productivity rather than production.
- The CSIR Aroma Mission is envisaged to bring transformative change in the aroma sector through desired interventions in the areas of agriculture, processing, and product development for the growth of aroma industry and rural employment.
- It will promote the cultivation of aromatic crops for essential oils that are in great demand by the aroma industry.
- Launch: 2016
- Aim:
- To develop superior aroma crop varieties and their Agro-technologies and assessment of their suitability for the large-scale cultivation in specific Agro-climatic regions.
- Promotion of cultivation and processing of aromatic crops.
- Skill development activities
- Intellectual property generation, valuation, and management
- Entrepreneurship development/Spin-offs
- Business development
- CSIR-Central Institute of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants (CSIR-CIMAP), Lucknow
- CSIR-Institute of Himalayan Bioresource Technology (CSIR-IHBT), Palampur
- CSIR-Indian Institute of Integrative Medicine (CSIR-IIIM), Jammu
- CSIR-National Botanical Research Institute (CSIR-NBRI), Lucknow.
- CSIR-North-East Institute of Science and Technology (CSIR-NEIST), Jorhat.
- It enables Indian farmers and aroma industry to become global leaders in the production and export of other essential oils on the pattern of menthol mint.
- Provide substantial benefits to the farmers in achieving higher profits, utilization of waste lands and protection of their crops from wild and grazing animals.
- It will improve availability of quality material on sustainable basis for growth herbal industry based on essential oils.
- To bring 5500 hectares of additional area under captive cultivation aromatic cash crops particularly targeting rain-fed /degraded land across the country.
- Provide technical and infrastructural support for distillation and values-addition to farmers all over the country.
- Enabling effective buy-back mechanisms to assure remunerative prices to the farmers.
- Value-addition to essential oils and aroma ingredients for their integration in global trade and economy.
- The uniform specifications of food grains for Central Pool procurement for the ensuing Kharif Marketing season (KMS) 2020-21 has also been issued.

- 1 per cent of fortified rice kernels should be blended with normal rice stocks.
- These specifications as per standard practice have been issued in respect of Paddy, Rice and other coarse grains namely Jowar, Bajra, Maize, Ragi.
- It also includes standards of rice for issue to States/Union Territories for distribution under targeted public distribution scheme and other welfare schemes based on the uniform specifications of rice for kharif marketing season.
- The fortified rice is to be distributed under various government schemes, including the public distribution system (PDS) and midday meals in schools, by 2024.
- The State Governments are requested to ensure that wide publicity of the Uniform Specifications is made among the farmers to ensure that they get due price for their produce and any rejection of the stocks is completely avoided.
- All states and Union Territories, as well as the Food Corporation of India, are advised to carry out the procurement during KMS 2020-21 in accordance with the uniform specifications.
- Fortification refers to deliberately increasing the content of essential micronutrients in a food so as to improve the nutritional quality of food and to provide public health benefit with minimal risk to health.
- 1 kg fortified rice will contain iron (28 mg-42.5 mg), folic acid (75-125 microgram) and Vitamin B-12 (0.75-1.25 microgram).
- Rice may also be fortified with micronutrients, singly or in combination, with zinc (10 mg-15 mg), Vitamin A (500-750 microgram RE), Vitamin B1 (1 mg-1.5 mg), Vitamin B2 (1.25 mg-1.75 mg), Vitamin B3 (12.5 mg-20 mg) and Vitamin B6 (1.5 mg-2.5 mg) per kg.
- Every second woman in the country is anaemic and every third child is stunted.
- India ranks 94 out of 107 countries and is in the ‘serious hunger’ category on the Global Hunger Index (GHI).
- The study was based on data sourced from India’s decennial census and the National Family Health Survey (NFHS).
- It looked at the three main factors that are known to cause changes in religious composition of populations — fertility rate, migration, and conversions.

- The religious composition of India’s population since Partition has remained largely stable showing not only a marked decline but also a convergence in fertility rates.
- It includes the two largest religious groups- Hindus and Muslims.
- Every religious group in India has seen its fertility fall, including the majority Hindu population and Muslim, Christian, Sikh, Buddhist and Jain minority groups.
- While Muslims have the highest fertility rate among India’s major religious groups, their total fertility rate has declined dramatically.
- There are usually three factors that cause religious groups to shrink or expand– migration, religious conversion and fertility.
- Migrants leaving India outnumber immigrants three-to-one, and religious minorities are more likely than Hindus to leave.
- Religious conversion had a “relatively small impact” on India’s overall composition, with 98 per cent of Indians still identifying with the religion in which they were raised.
- Sex selective abortions have caused an estimated deficit of 20 million girls compared with what would naturally be expected between 1970 and 2017.
- Women in central India tended to have more children, with Bihar and Uttar Pradesh showing a total fertility rate (TFR) of 3.4 and 2.7 respectively, in contrast to a TFR of 1.7 and 1.6 in Tamil Nadu and Kerala respectively.
- Between 1951 and 1961, the Muslim population expanded by 32.7%, 11 percentage points more than India’s overall rate of 21.6%.
- From 2001 to 2011, the difference in growth between Muslims (24.7%) and Indians overall (17.7%) was 7 percentage points.
- India’s Christian population grew at the slowest pace of the three largest groups in the most recent census decade– gaining 15.7% between 2001 and 2011.
- It shows lower growth rate than the one recorded in the decade following Partition (29.0%).
- In percentage terms, between 1951 and 2011, Muslims grew by 4.4 percentage points to 14.2% of the population, Hindus declined by 4.3 points to 79.8%.
- Hindus comprised 84.1 per cent of the population in 1951, and 79.8 per cent in 2011, while Muslims comprised 9.8 per cent of the population in 1951, and 14.2 per cent in 2011.
- All the six major religious groups– Hindus, Muslims, Christians, Sikhs, Buddhists, and Jains– have grown in absolute numbers.
- Parsis are in exception, whose number halved between 1951 and 2011, from 110,000 to 60,000.
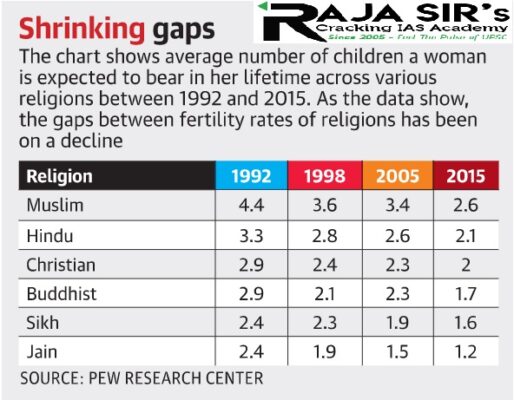
- Gaps in fertility rates between India’s religious groups have shrunk over the years.
- Fertility rate refers to the average number of children born to a woman in childbearing age (15-44 years).
- While Muslim women were expected to have an average of 1.1 more children than Hindu women in 1992, the gap had shrunk to 0.5 by 2015.
- If all the women had an average amount of wealth and education, were the same age and lived in the same places, Hindu women would be predicted to have 0.9 fewer children than their Muslim counterparts, on average.
- Analysed using multilevel mixed-effects analysis- a statistical technique.
- All religious groups have shown a major decline in fertility rates between 1992 and 2015.
- Muslims have the highest fertility rate, followed by Hindus. This reflects a long-standing pattern since 1992.
- India’s population has more than tripled since Partition and, accordingly, all religious groups have grown in size.
- Indian Christian rose to 2.8 crore from 0.8 crore, siting this could be an undercount.
- People who indicate that they are Christian on the census are not able to also identify as belonging to Scheduled Castes.
- Members of Scheduled Castes are eligible for government benefits, reportedly prompting some people in that category to identify as Hindu when completing official forms.
- Dalits who identify as Christians and Muslims can’t avail of reservation benefits and remain excluded from the Constitution (Scheduled Castes) Order, 1950.

- With an overall score of 72%, Gujarat has been adjudged the best performing state among major states of the country.
- The index ranks States on food safety parameters.
- Gujarat, Kerala and Tamil Nadu are the top three States in large States category.
- Goa, Meghalaya and Manipur are the top three States in the smaller States category.
- Among UTs, Jammu & Kashmir, Andaman & Nicobar Islands and New Delhi secured the top ranks.
- The index ranks States on five parameters of food safety including:
- Human resources and institutional data
- Compliance
- Food testing facility
- Training and capacity building
- Consumer empowerment
- The results of PAN-India survey for identifying the presence of industrially produced trans fatty acid content in the selected foods was released.
- Samples of various packaged food items under six pre-defined food categories were collected from 419 cities/districts across 34 States/UTs.
- Overall, only 84 samples, i.e., 1.34% have more than 3% industrially produced trans fats from the total of 6245 samples.
- Various innovative initiatives by FSSAI were released including:
- Eat Right Research Awards and Grants to encourage and recognize high-quality research in the area of food safety and nutrition in India
- Logo for Vegan Foods for easy identification and distinction from non-vegan foods for empowering consumers to make informed food choices.
- As per the report, Modern slavery — including debt bondage, bonded labour, early / forced marriage and human trafficking converge with climate change, particularly climate shocks and climate-related forced displacement and migration.
- The report established close relationship between lack of resources, alternative livelihoods, safety nets and the protection against loss and damage as well as debt and exploitation.
- The report observed that the Sundarbans delta region is characterised by intense, recurrent and sudden onset disasters and ecological degradation.
- Rising sea levels, erratic rainfall, increased frequency of cyclones, tidal surges and floods would mean that millions of people across Sundarbans are unable to work for most of the year.
- These events can leave locals vulnerable to traffickers and drive them into forced labour, particularly women and children who are at the risk of trafficking, hard labour and prostitution.
- Policymakers should develop targeted actions, at national and international levels, to address the issue of trafficking and slavery risks due to climate shocks.
- Several ongoing initiatives including Warsaw International Mechanism Task Force on Displacement, Sendai Framework, etc. should be coordinated to increase understanding of growing risks of climate-induced migration/ displacement and exposure to modern slavery.
- Recognising slavery as a mainstream policy issue alongside poverty and climate change will help to:
- Develop understanding of the underlying drivers that push disadvantaged communities into slavery.
- Identify risky migration pathways that lead to exploitative work situations.
- Identify gaps in existing climate and development policies that leave communities facing climate crises exposed to slavery.


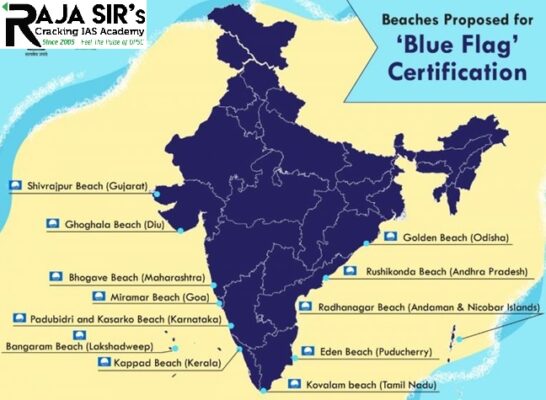
- The two beaches to receive the certification are Kovalam in Tamil Nadu and Eden in Puducherry.
- The Foundation for Environment Education (FEE), Denmark gave re-certification for eight nominated beaches in 2020.
- The Beaches are:
- Shivrajpur in Gujarat
- Ghoghla in Daman & Diu
- Kasarkod beach in Karnataka
- Padubidri beach in Karnataka
- Kappad in Kerala
- Rushikonda in Andhra Pradesh
- Golden beach of Odisha
- Radhanagar beach in Andaman and Nicobar
- Blue Flag is one of the world’s most recognised voluntary eco-labels awarded to beaches, marinas, and sustainable boating tourism operators.
- To qualify for the Blue Flag, a series of stringent environmental, educational, safety, and accessibility criteria must be met and maintained.
- There are 33 criteria that must be met to qualify for a Blue Flag certification, such as the water meets certain quality standards, waste disposal facilities, being disabled-friendly, first aid equipment etc.
- Blue Flag Programme for beaches and marinas is run by the international, non-governmental Organisation FEE (the Foundation for Environmental Education).
- FEE was established in France in 1985.
- Spain tops the list with 566 such beaches.
- India has launched its own eco-label BEAMS (Beach Environment & Aesthetics Management Services) under ICZM (Integrated Coastal Zone Management) project.
- It is launched by the Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- Abate pollution in coastal waters,
- Promote sustainable development of beach facilities,
- Protect & conserve coastal ecosystems & natural resources,
- Strive and maintain high standards of cleanliness,
- Hygiene & safety for beachgoers in accordance with coastal environment & regulations.
- It is a process for the management of the coast using an integrated approach, regarding all aspects of the coastal zone, including geographical and political boundaries, to achieve sustainability.
- It was established in 1992 during the Earth Summit.
- It is a World Bank assisted project and is implemented by the Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- The National Centre for Sustainable Coastal Management (NCSCM), Chennai, provide scientific and technical inputs.
- This was announced by the state Cabinet after weeks of ‘rhino horn reverification’ exercises by the Forest Department across the state.
- The ceremony scheduled in Kaziranga National Park (KNP) has been publicised as a “milestone towards rhino conservation” aimed at “busting myths about rhino horns”.
- The destruction of horns is in compliance with Section 39(3)(c) of the Wildlife (Protection) Act of 1972.

- World Rhino Day is observed on September 22 every year to celebrate all the five species of rhinoceroses - black and white (in Africa), and greater one-horned, Sumatran and Javan (in Asia).
- Both African species and the Sumatran rhinoceros have two horns, while the Indian and Javan rhinoceros have a single horn.
- Aim: To raise awareness about the African and Asian species of rhinos and encourage people to take steps for their conservation.
- World Rhino Day was announced by World Wildlife Fund -South Africa in 2010.
- The day got international recognition in 2011.
- World Rhino Day 2021 theme: 'Keep the Five Alive'.
- The greater one-horned rhino (or “Indian rhino”) is the largest of the rhino species.
- The greater one-horned rhino is identified by a single black horn about 8-25 inches long and a grey-brown hide with skin folds, which gives it an armor-plated appearance.
- The species is solitary, except when adult males or rhinos nearing adulthood gather at wallows or to graze.
- Males have loosely defined home ranges that are not well defended and often overlap.
- They primarily graze, with a diet consisting almost entirely of grasses as well as leaves, branches of shrubs and trees, fruit, and aquatic plants.
- Gestation lasts approximately 15 – 16 months, and mothers give birth to one calf every 2 – 3 years.
- Northern India and southern Nepal, in riverine (floodplain) grasslands and adjacent woodland.
- Listed as Vulnerable under IUCN Red list.
- Listed in Appendix I with convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES).
- Listed in Schedule I in Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
- Ground rhino horn is used in traditional Chinese medicine to cure a range of ailments, from cancer to hangovers, and also as an aphrodisiac.
- In Vietnam, possessing a rhino horn is considered a status symbol.
- In 2019, the Assam government constituted a dedicated “Special Rhino Protection Force” to keep a check on rhino poaching and related activities at KNP.
- It has so far provided drinking water to 152.16 lakh tap connections.
- It aims to provide piped clean drinking water to every citizen of Bihar in the homes of approximately 2 crore households in the state, without any discrimination.
- It is a cluster of four state schemes:
- Mukhyamantri Gramin Peyjal Nishchay Yojana
- Mukhyamantri Gramin Peyjal Nishchay Yojana (Gunvatta Prabhavit Kshetr)
- Mukhyamantri Gramin Peyjal Nishchay Yojana (Gair Gunvatta Prabhavit Kshetr)
- Mukhyamantri Shahri Peyjal Nishchay Yojana.
- As per the perspectives of the NEP 2020, the Committee will develop four National Curriculum Frameworks:
- National Curriculum Framework for School Education,
- National Curriculum for Early Childhood Care and Education,
- National Curriculum Framework for Teacher Education,
- National Curriculum Framework for Adult Education.
- Discuss different aspects of School Education, Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE), Teacher Education and Adult Education keeping in focus all the recommendations of NEP 2020 related to these four areas for proposing curriculum reforms.
- Discuss the position papers finalised by the National Focus Groups on different aspects of all the above four areas.
- Draw inputs from State Curriculum Frameworks received on the Tech Platform for the National Curriculum Frameworks.
- Finalise National Curriculum Frameworks after incorporating suggestions received from various stakeholders, i.e., states/UTs and also in the meetings of Executive Committee (EC) and General Body (GB) of the NCERT and Central Advisory Board on Education(CABE).
- Tenure of the National Steering Committee will be three years from the date of its notification.
- Director NCERT shall assist the SC to complete its module.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies