- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
30th June 2021
Electoral Bond Scheme
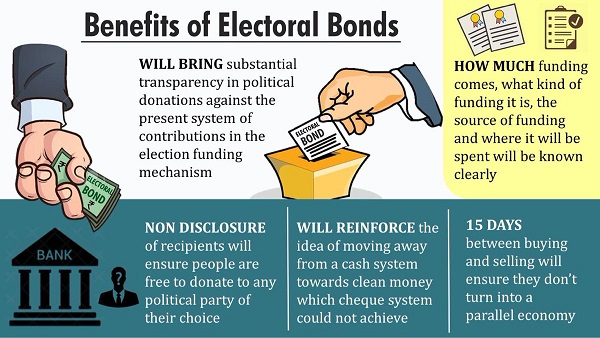
Recently, the Government of India has notified the Electoral Bond Scheme for the sale of electoral bonds by the authorised branches of State Bank of India (SBI).
 Electoral Bonds
Electoral Bonds
 Conditions for Electoral Bonds
Conditions for Electoral Bonds
 Electoral Bonds
Electoral Bonds
- It is similar to promissory note (PN) because it can be bought by any Indian citizen or company incorporated in India from select branches of State Bank of India.
- The citizen or corporate can then donate the same to any eligible political party of his/her choice.
- It is an interest free banking instrument issued on a non-refundable basis and is not available for trading i.e. no loan would be provided against these bonds.
- The bonds are similar to bank notes that are payable to the bearer on demand and are free of interest.
- An individual or party will be allowed to purchase these bonds digitally or through cheques.
- The electoral bonds were introduced with the Finance Bill (2017).
- The bonds will be issued in multiples of Rs 1,000, Rs 10,000, Rs 100,000 and Rs 1 crore.
 Conditions for Electoral Bonds
Conditions for Electoral Bonds
- Any party that is registered under section 29A of the Representation of the Peoples Act, 1951 (43 of 1951) and has secured at least one per cent of the votes polled in the most recent General elections or Assembly elections is eligible to receive electoral bonds.
- The party will be allotted a verified account by the Election Commission of India (ECI) and the electoral bond transactions can be made only through this account.
- The electoral bonds will not bear the name of the donor and the political party might not be aware of the donor's identity.
- The Electoral Bond shall be redeemable in the designated account of a registered political party within the prescribed time limit from issuance of bond.
- The Electoral Bonds would have a life of only 15 days during which it can be used for making donation only to the political parties registered under section 29A.
- The political party needs to disclose the details of non-governmental corporations and persons who donate more than Rs. 20,000 to it in a financial year.
- A donor will get a deduction under section 80GGB and the recipient or the political party, will get tax exemption, provided returns are filed by the political party.
- Every political party would have to file its return within the time prescribed in accordance with the provision of the Income-tax Act.
- One District One Product: The Ministry of Food Processing Industries approved ODOP for 707 districts for 35 States and UTs.
- The GIS ODOP digital map of India has been launched to provide details of ODOP products of all the States and UTs.
- The digital map also has indicators for Tribal, SC, ST, and aspirational districts.
- Convergence: The Ministry signed three joint letters with the Ministry of Rural Development, the Ministry of Tribal Affairs, and the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
- It has signed six Memorandum of Understanding (MoUs) with the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), the National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC), the Tribal Cooperative Marketing Development Federation of India (TRIFED) etc.
- Capacity Building and Incubation Centres: The National Institute of Food Technology Entrepreneurship and Management (NIFTEM) and the Indian Institute of Food Processing Technology (IIFPT) have been performing a key role in providing training and research support.
- Seed Capital: It is being implemented with the support of the National Rural Livelihood Mission (NRLM) and its network of State Rural Livelihood Mission (SRLMs) operating at the state level.
- It envisages financial support of Rs. 40,000 for working capital and purchase of small tools for each member of SHGs engaged in food processing activities.
- Marketing and Branding: The MoUs have been signed with NAFED and TRIFED to take up the marketing and branding support for 10 products each.
- Institutional Mechanism: All the 35 participating States and UTs have constituted/ identified their respective State Nodal Agencies, State Level Approval Committees, District Level Committees, and State Level Technical Institutions.
- It is an all India Centrally Sponsored Scheme under the Aatmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyaan.
- It is aimed at providing financial, technical and business support for upgradation of existing micro food processing enterprises.
- It adopts One District One Product (ODOP) approach to reap benefit of scale in terms of procurement of inputs, availing common services and marketing of products.
- The scheme would provide support to FPOs/SHGs/Producer Cooperatives for capital investment along the entire value chain with credit linked grant at 35%.
- Under the capacity building component, training of the Master Trainers would be delivered through online mode, classroom lecture and demonstration and self-paced online learning material.
- The scheme envisions to directly assist the 2 Lakh micro food processing units over a period of five years from 2020-21 to 2024-25.
- Support for capital investment for upgradation and formalization with registration for GST, FSSAI hygiene standards and Udyog Aadhaar.
- Capacity building through skill training, imparting technical knowledge on food safety, standards & hygiene and quality improvement.
- Hand holding support for preparation of DPR, availing bank loan and upgradation.
- Support to Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), Self Help Groups (SHGs), producers cooperatives for capital investment, common infrastructure and support branding and marketing.
- The scheme would support strengthening of backward and forward linkages, provision of common facilities, incubation centres, training, R&D, marketing & branding, provision of which would primarily be for ODOP products.
- All individuals & institutions members receiving grant would undergo training for upgradation of their skills.
- The scheme lays special focus on SCs/STs, women and aspirational districts and FPOs, SHGs and producer cooperatives.
- It is a High Speed Track (HST) located in Indore (Madhya Pradesh).
- It is Asia’s longest and world’s fifth longest High Speed Track for automobiles.
- It is developed in an area of 1000 acres of land.
- It is a one stop solution for all sorts of high speed performance tests for widest categories of vehicles from 2 wheelers to heavy tractor trailers.
- The HST is used for measuring the maximum speed capability of high-end cars like BMW, Mercedes, Audi, Ferrari, Lamborghini, Tesla etc.
- The NATRAX centre has multiple test capabilities like measurements of maximum speed, acceleration, constant speed fuel consumption, emission tests through real road driving simulation, high speed handling and stability evaluation.
- It is accessible to most of the major Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEMs) because it is centrally located in Madhya Pradesh.
- The foreign OEMs will be looking at NATRAX HST for the development of prototype cars for Indian conditions.
- It is one stop solution for all sorts of high speed performance tests, being one of the largest in the world.
- It can cater to widest category of vehicles i.e. from two wheelers to the heaviest tractor trailers.
- It is a State-of-art Automotive Proving Ground.
- It is a flagship project of the Ministry of Heavy Industries under NATRIP.
- It provides a one-stop solution for comprehensive testing and evaluation, Research & Development and Certification to entire automotive and auto component industries.
- Its objective is to offer world-class testing and evaluation services catering for all categories of vehicles from 2/3 wheelers to heavy commercial vehicles.
- The Department of Space also launched the NHP–Bhuvan portal of National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC).
- It is based on the inventoried glacial lakes in part of Ganga River basin from its origin to foothills of Himalayas.
- The study portion of Ganga River basin covers part of India and transboundary region.
- It is funded by the Department of Water Resources, River Development and Ganga Rejuvenation (DoWR, RD&GR).
- It is a step forward for facilitating acquisition of reliable information and putting the same in public domain which would pave the way for an effective water resource development and management.
- The possible uses of the Glacial Lake Atlas are managing the glacial lakes as well as to mitigate the possible adverse impacts of Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOF) and climate change.
- The expected utility of the atlas is:
- The atlas provides a comprehensive and systematic glacial lake database for Ganga River basin with size > 0.25 ha;
- The atlas can be used as reference data for carrying out change analysis, both with respect to historical and future time periods;
- The atlas also provides authentic database for regular or periodic monitoring changes in spatial extent (expansion/shrinkage), and formation of new lakes;
- The atlas can also be used in conjunction with glacier information for their retreat and climate impact studies;
- The information on glacial lakes like their type, hydrological, topographical, and associated glaciers are useful in identifying the potential critical glacial lakes and consequent GLOF risk; and
- The Central and State Disaster Management Authorities can make use of the atlas for disaster mitigation planning and related program
- Ganga River basin has been divided into 11 sub-basins on the basis of confluence of major rivers contributing into the system.
- They are Yamuna joining the main river on the right, whereas rivers like Sarda, Ghaghara, Gandak, and Kosi joining on the left.
- In India, Ganga River basin extends in two states viz., Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand.
- A total of 4,707 glacial lakes have been mapped in the Ganga River basin using a total of 105 high resolution multispectral RS-2 LISS-IV images.
- Each glacial lake has been given a 12 alpha-numeric unique glacial lake ID, along with several attributes that include hydrological, geometrical, geographical, and topographical characteristics.
- Out of 11 sub-basins, only 6 sub-basins contain glacial lakes, which are predominantly distributed in Kosi sub-basin (51.77%) followed by Ghaghara sub-basin (26.77%).
- Uttarakhand state shares 93.50% of lake count, followed by 6.50% in Himachal Pradesh, with a total lake area of 90.70% and 9.30% respectively.
- The National Hydrology Project or NHP-Bhuvan Portal is a repository of information on the initiatives undertaken by NRSC under NHP.
- It is the national Geo-portal developed and hosted by ISRO comprising of Geo Spatial Data, Services and Tools for Analysis.
- The Satellite Imageries are of Multi-sensor, Multi-platform and Multi-temporal in nature can be visualized in 2D and 3D.
- It is a Central Sector scheme sponsored by Ministry of Jal Shakti.
- It is launched with financial aid from the World Bank.
- Its objective is to improve the extent and accessibility of water resources information and strengthen institutional capacity to enable improved water resources planning and management across India.
- The project comprises four broad components:
- Improving In Situ Monitoring System (IMS)
- Improving Spatial Information System (SIS)
- Promoting Water Resources Operation and Management Applications (WROMA)
- Strengthening Water Resources Institutions and Capacity Building (WRICB)
- It is one of the primary centres of Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), Department of Space (DOS).
- It has the mandate for establishment of ground stations for receiving satellite data, generation of data products, dissemination to the users and development of techniques for remote sensing applications.
- The Doing Business Report of World Bank Group benchmarks business regulations across 191 economies of the world.
- The Ease of Doing Business (EoDB) index is a ranking system which is an indication of an economy’s position relative to that of other economies across 11 areas of business regulation.
- The “Enforcing Contracts” indicator measures time and cost to resolve a standardized commercial dispute as well as a series of good practices in the judiciary.
- It aims to promote ease of doing business and improve ‘Contract Enforcement Regime’ in India.
- It is envisioned to be a comprehensive source of information pertaining to the legislative and policy reforms being undertaken on the “Enforcing Contracts” parameters.
- Its objective is to provide easy access to latest information on commercial cases in Dedicated Commercial Courts of Delhi, Mumbai, Bengaluru and Kolkata.
- It aims to provide access to repository of commercial laws for ready reference.
- The study has found a connection between the formation of the tiny particles, the size of a cloud droplet on which water vapor condenses leading to the formation of clouds and forest fires.
- The quantity of such particles called the cloud condensation nuclei (CCNs) were found to have peaks associated with forest fire events.
- The study measured the activation of cloud condensation nuclei and studied its impact on high altitude cloud formation and complexity of local weather phenomenon.
- The CCNs were measured by a droplet measurement technology’s (DMT) CCN Counter at Himalayan Clouds Observatory (HCO), Garhwal University.
- The observation was carried out under a Climate Change Programme Division, Department of Science & Technology (DST) funded project.
- It showed that the highest concentration of CCN was found to be associated with excessive fire forest activities of the Indian subcontinent.
- The CCN concentration (CCN) was observed at four supersaturation levels (SS: 0.2, 0.5, 0.8, and 1.0%).
- The highest CCN concentration is observed at the time of sunrise and after the sunset for the diurnal variation of monsoon, post-monsoon, and winter season.
- The possible reasons for maximum concentration in morning and evening time could be upliftment and settlement of CCN because of the convection process, anthropogenic emission, vehicular emission, and biomass burning in the residential area and valley region.
- The lowest value of CCN concentration corresponds to the heavy rains and snowfall days, possibly caused by extensive wet scavenging.
- The CCNs are small particles typically 0.2 µm, or 1/100 the size of a cloud droplet on which water vapor condenses.
- It can activate and grow into fog or cloud droplets in the presence of supersaturation (SS).
- It is used in cloud seeding, which tries to encourage rainfall by seeding the air with condensation nuclei.
- It is first-of-its-kind research initiative of the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB).
- It is a novel initiative to bring together industry and academia on a common platform to exchange ground-breaking ideas and co-promote innovative research.
- It is a joint government and industry initiative with a co-funding mechanism to promote innovative technology solutions and strengthen academic research.
- It is a one-of-its-kind collaborative initiative that aims to transform the culture of research in India and strengthen the technology ecosystem.
- It will increase research opportunities in the space of Artificial Intelligence (AI)/Machine Learning (ML), platform systems, circuits & architecture, Internet of Things (IoT) etc.
- It aims to promote research in the upcoming critical areas of science and engineering with Public-Private Partnerships as elaborated in the draft Science, Technology and Innovation Policy 2021.
- It will open many new doors for exploration in scientific research, which could make India a key player in technology-based solutions.
- It promises to bring support for strong ideations, especially in futuristic S&T thematic areas, and aims to bring expertise in academia and industry together.
- It is a statutory body established through an Act of Parliament.
- The primary and distinctive mandate of the Board is supporting basic research in emerging areas of Science & Engineering.
- It aims to build up best management systems which would match the best global practices in the area of promotion and funding of basic research.
- It was created to equip farmers with actionable agricultural insights and early weather alerts.
- The data related to soil type, soil health, moisture, weather, and water table were aggregated and analysed to generate personalized insights.
- The app was envisioned in 5 stages:
- Data aggregation
- Building centralized insights
- Enable local expertise (KVK) supported interactions and insights
- Deriving Machine Learning inferences
- Continuous improvement
- The app brings together data relevant to the farmer and his farm, from various agencies and departments of the Government of India.
- Bengaluru-based Indian Centre for Social Transformation (ICST) Founder Trustee Raja Seva is one of the major stakeholders in the development of Atmanirbhar Krishi App.
- The data has been made comprehensible for farmers by simplifying the language.
- It is available in 12 languages for free of cost for farmers, start-ups, Krishi Vigyan Kendras, Self Help Groups, and NGOs.
- The app has been designed to work on minimal bandwidth considering the connectivity issues in the remote areas of the country.
- The app does not collect any inputs from the farmer.
- The app relies on the geo-location of the farm to provide relevant data.
- The Atmanirbhar Krishi App is a great initiative by the Government of India which provides real time useful and appropriate information to farmers digitally.
- It will facilitate Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs) to interact with farmers more specifically as per the existing ground realities.
- It is situated in the Himalayan foothills between Udalguri and Baksa districts of Assam.
- It flanks Bhutan border and is spread in an area of 26 sq kms.
- It is named after the River Bornadi which flows on the western side of this wildlife reserve.
- It was recognized as a wildlife sanctuary in 1980 and it was established to protect the rare species of Hispid Hare and Pygmy Hog.
- Other animals found in the reserve are golden langur, clouded leopard, hoolock gibbon and white-winged wood duck.
- It is a lagomorph in the Leporidae family (hares and rabbits).
- It is identified by its distinctively short ears and, unlike other members of the Leporidae family, short and stout hind legs barely exceeding the length of the forelegs.
- It is rarely found outside the shelter of the tall grassland habitats in its range.
- Its range historically spanned all suitable tall grassland habitats across much of the terai in north India and southern Nepal, and the floodplain grasslands of north-eastern India and northern Bangladesh
- It is now restricted to small isolated pockets, perhaps only in protected areas (PAs), in southern Nepal and north and northeastern India.
- It is listed as ‘Endangered’ under the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.
- It is listed in Schedule I of the Indian Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies