- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
August 30, 2024 Current Affairs
Prime Minister pays tribute to Major Dhyan Chand on National Sports Day
- National Sports Day is celebrated on August 29, every year. It celebrates the spirit of sportsmanship, honours our athletes, and remembers the legends who have brought glory to India. August 29, marks the birth anniversary of Major Dhyan Chand.
National Sports Day 2024 Theme
- The National Sports Day 2024 theme is “Sport for the Promotion of Peaceful and Inclusive Societies.”
- It underscores the vital role that sports play in fostering unity, inclusion, and peace, within communities. It highlights how sports can bring people together across different backgrounds, promoting mutual respect, understanding, and cooperation.
Significance of National Sports Day
- The National Sports Day is celebrated in memory of Major Dhyan Chand and also with the objective to highlight the significance of sports in our lives and staying fit and healthy.
- The President of India gives away the prestigious Rajiv Gandhi Khel Ratna, Arjuna Award and Dronacharya Award on this day at the Rashtrapati Bhavan to sportsmen and coaches across various sports.
- This day has been used as a platform by the government to launch various schemes or programmes.
Major Dhyan Chand
- Birth: Dhyan Chand was born on August 29, 1905, in Allahabad, India.
- His incredible ball control and vision on the field earned him the titles “Hockey Wizard” and “The Magician.” Due to his regimental duties, he used to practice under the moonlight earning the nickname “Chand,” meaning moon in Hindi.
Olympic Success:
- 1928 Amsterdam Olympics: India won the gold medal, and Dhyan Chand was instrumental in the victory, scoring numerous goals.
- 1932 Los Angeles Olympics: India retained the gold medal, with Dhyan Chand playing a crucial role and scoring 12 out of 35 goals.
- 1936 Berlin Olympics: India won their third consecutive gold medal, and Dhyan Chand was a key player, scoring eight goals in the tournament.
Awards and Honors:
- Padma Bhushan: India’s third-highest civilian award was bestowed upon him in 1956.
- Major Dhyan Chand National Stadium: The stadium in Delhi is named in his honor, serving as a prominent venue for hockey events.
- Dhyan Chand Award: Instituted by the Government of India in 2002, this award recognizes lifetime achievements in sports and games.
- Death: He passed away on December 3, 1979.
Awards named after Major Dhyan Chand:
- Major Dhyan Chand Khel Ratna Award (highest sporting honour of India)
- Dhyan Chand Award (highest award for lifetime achievement in sports)
Government initiatives to promote sports in India:
Khelo India Program:
- Objective: Revive sports culture at the grassroots level.
- Components: Includes Khelo India Youth Games and support for talent identification.
Sports Authority of India (SAI):
- Role: Provides training, coaching, and infrastructure development.
National Sports Development Fund (NSDF):
- Purpose: Financial support for sports infrastructure and talent development.
National Sports Awards:
- Includes: Rajiv Gandhi Khel Ratna, Arjuna Awards, Dronacharya Awards, Dhyan Chand Awards for recognizing achievements in sports.
Fit India Movement:
- Objective: Promote fitness and a healthy lifestyle through awareness campaigns and events.
Ayurvedic Whole System effective in Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis: Study
- Objective: To evaluate the effectiveness of the Ayurvedic Whole System (AWS) in managing Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA).
- Findings: AWS significantly alleviated RA symptoms and induced a metabolic shift towards normalization.
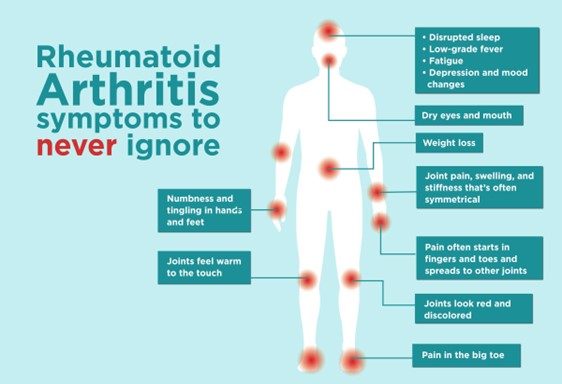
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA):
- It is an autoimmune and inflammatory disease, which means that your immune system attacks healthy cells in your body by mistake, causing inflammation (painful swelling) in the affected parts of the body.
- RA mainly attacks the joints, usually many joints at once. RA commonly affects joints in the hands, wrists, and knees.
- In a joint with RA, the lining of the joint becomes inflamed, causing damage to joint tissue. This tissue damage can cause long-lasting or chronic pain, unsteadiness (lack of balance), and deformity (misshapenness).
- RA can also affect other tissues throughout the body and cause problems in organs such as the lungs, heart, and eyes.
Cause:
- The exact cause of RA is unknown, but researchers believe that it involves a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
- Some people may have certain genes that make them more susceptible to developing RA,but these genes are not enough to cause the disease by themselves. There may be other triggers, such as infections, stress, hormones, or smoking, that activate the immune system and cause inflammation in the joints.
Treatment:
- There is no cure for RA, but there are treatments that can help control the symptoms and prevent or slow down joint damage.
- Various medications are used to manage rheumatoid arthritis (RA) symptoms.These include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen, corticosteroids for rapid relief (with potential side effects), disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) to slow down disease progression, and biologic agents that target specific inflammatory molecules.
- Physical therapy is an integral part of RA treatment,aiming to improve joint function and mobility. Therapeutic approaches may include exercises, stretching, massage, and heat/cold therapy.
- Occupational therapy helps enhance daily activities and overall quality of life for individuals with RA.It involves the use of assistive devices, adaptive equipment, and ergonomic advice to facilitate better functioning.
- In cases of severe joint damage or deformity unresponsive to other treatments, surgery may be considered.Surgical options include repairing, replacing, or fusing affected joints to alleviate pain and improve joint function.
Department of Economic Affairs amends Securities Contracts Regulation Rules (SCRR), 1956, facilitating direct listing of securities by public Indian companies on International Exchanges of GIFT IFSC
Amendment Overview:
- Objective: Ease listing requirements for Indian companies on international exchanges within International Financial Service Centres (IFSCs).
Regulatory Framework:
Schemes Involved:
- ‘Direct Listing of Equity Shares of Companies Incorporated in India on International Exchanges Scheme’ under the Foreign Exchange Management (Non-Debt Instruments), 2019.
- Companies (Listing of Equity Shares in Permissible Jurisdictions) Rules, 2024.
Minimum Public Offer Requirements:
- Threshold: At least 10% of the post-issue capital must be offered and allotted to the public for companies listing solely on international exchanges in IFSCs.
Continuous Listing Requirements:
- Requirement: Set at 10% as per Rules 19 (2)(b) and 19A of the SCRR.
Securities Contracts Regulation Rules (SCRR), 1956
- The Securities Contracts Regulation Act, 1956 (SCRA) is a legislation in India designed to oversee and control the functioning of securities markets and stock exchanges. Its primary objectives are to ensure fair and ethical trading practices, safeguard the interests of investors, and promote systematic growth within the securities market.
Significance of SCRA, 1956
Recognition of Stock Exchanges
- Section 3 outlines how stock exchanges can get government recognition.
- SEBI can also grant recognition.
- The government ensures that stock exchange rules protect investors and ensure fair dealings.
Corporatization of Stock Exchanges
- Amended in 2004, Section 4(B) requires stock exchanges to become corporate entities.
- Ownership and management must be separate from trading rights.
- The public must hold at least 51% of the stock exchange’s shares.
Central Government’s Control
- Sections 6, 7, and 8 allow the government and SEBI to oversee stock exchanges.
- They can act to support investment growth, trade protection, and public welfare.
- Stock exchanges must submit periodic returns and follow set rules for good governance.
Provisions Related to Listing of Securities
- The SCRA sets rules for listing securities on recognized stock exchanges.
- Section 21 requires compliance with listing conditions.
- Section 21A allows for delisting securities based on specific grounds.
GIFT IFSC
- The Gujarat International Finance Tec-City International Financial Services Centre (GIFT IFSC) is an International Financial Services Centre (IFSC) created to serve as a financial centre and hub, supporting major international financial activities including banking, insurance, capital market activities, asset management etc, besides providing world class infrastructure.
- It was established by the Gujarat Government and supported by the Government of India. The GIFT IFSC is the first IFSC in India and it was operationalised in April 2015 when the Reserve Bank of India granted license to operate an International Financial Services Centre (IFSC) within GIFT IFSC.
Union Minister of Women and Child Development launches new She-Box Portal to make Workplaces safer for Women
Launch of New Website
- Objective: The new website aims to create a cohesive visual identity for the Ministry, enhancing engagement with national and global audiences.
- National Goal: The initiative aligns with India’s vision for “Viksit Bharat” by 2047, focusing on women''s participation in economic growth.
- Legislative Framework: The SHe-Box portal supports the Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition, and Redressal) Act, 2013, which aims to protect women from sexual harassment and address grievances in the workplace.
SHe-Box
- The Ministry of Women & Child Development has launched Sexual Harassment electronic Box (SHe-Box) as an effort to provide a single window access to every woman, irrespective of her work status, whether working in organised or unorganised, private or public sector, to facilitate the registration of complaint related to sexual harassment.
- Any woman facing sexual harassment at the workplace can register their complaint through this portal. Once a complaint is submitted to the ‘SHe-Box’, it will be directly sent to the concerned authority having jurisdiction to act into the matter.
Features:
- Confidentiality: Complaints are handled confidentially to protect the privacy of the complainants.
- Accessibility: It is designed to be easily accessible to women across various sectors and regions.
- Response Mechanism: The portal is linked to internal committees within organizations responsible for handling such complaints, ensuring that they are addressed promptly.
Limitations of the She Box Portal
- Awareness and Accessibility:
- Limited Reach: Not all women, especially in remote areas or informal sectors, might be aware of the portal or have access to it.
- Digital Divide: Women with limited access to technology or the internet may find it difficult to use the portal.
- Privacy and Confidentiality:
- Data Security: Ensuring the confidentiality and security of the complaints and personal information is crucial. There may be concerns about data breaches or misuse.
- Fear of Stigmatization: Women might still fear retaliation or social stigmatization despite the portal’s confidential nature.
- Effective Resolution Mechanism:
- Implementation Delays: Complaints may not always be addressed in a timely manner, leading to prolonged stress for the complainants.
- Inadequate Action: There might be instances where complaints are not adequately followed up or resolved, impacting the effectiveness of the portal.
- Lack of Awareness Among Employers:
- Compliance Issues: Some organizations may not be fully aware of or comply with the requirements to address complaints effectively, even if they are reported through the She Box Portal.
Way Forward for the She Box Portal
- Increasing Awareness and Accessibility:
- Outreach Programs: Conduct awareness campaigns to inform women about the portal and how to use it. This can include educational workshops, community programs, and collaborations with NGOs.
- Improving Digital Literacy: Offer training programs to enhance digital literacy among women, especially in rural and underserved areas.
- Enhancing Privacy and Confidentiality:
- Strengthening Data Security: Invest in robust cybersecurity measures to protect data and ensure that complaints are handled with the highest level of confidentiality.
- Clear Guidelines: Establish clear protocols for handling sensitive information and managing complaints to prevent any potential misuse.
- Strengthening Employer Compliance:
- Training for Organizations: Provide training for employers and organizations on how to handle complaints effectively and ensure they adhere to the guidelines set by the POSH Act.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits of organizations to ensure compliance with the Act and the effective use of the She Box Portal.
India commissions its second nuclear-submarine INS Arighaat
- The second Arihant-Class submarine ‘INS Arighaat’ was commissioned into the Indian Navy at Visakhapatnam
About INS Arighat:
- It is India’s second indigenously built nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarine (SSBN), following India''s first nuclear submarine, INS Arihant,commissioned in 2018.
- It was constructed at the Indian Navy''s Ship Building Centre (SBC) in Visakhapatnam.
- It represents a critical component of India''s nuclear triad, enabling the nation to launch nuclear missiles from land, air, and sea.
Features:
- It measures 111.6 meters in length, has a beam of 11 meters, a draught of 9.5 meters, and a displacement of 6,000 tonnes.
- It will have one seven-blade propeller powered by a pressurised water reactor.
- It can achieve a maximum speed of 12–15 knots (22–28 km/h) when on surface and 24 knots (44 km/h) when submerged.
- It can carry up to four nuclear-capable K-4 SLBMs (Submarine Launched ballistic Missile) with a range of over 3500 kilometers or twelve conventional warhead K-15 SLBMs with a range of about 750 kilometers.
- The K-15 can also carry a strategic nuclear warhead.
- It also carries torpedoes and mines.
- Additional safety measures include two standby auxiliary engines and a retractable thruster for emergency power and mobility.
Strategic Importance:
- Deterrence: The submarine enhances India''s second-strike capability, which is crucial for maintaining a credible nuclear deterrent. A second-strike capability ensures that India can respond to a nuclear attack even after suffering a first strike.
- Stealth and Mobility: The submarine''s nuclear propulsion allows it to stay submerged for extended periods, making it harder to detect and increasing its operational effectiveness.
Development and Indigenous Capability:
- The Arihant-class submarines are developed under the Advanced Technology Vessel (ATV) program, which is part of India’s efforts to bolster its indigenous defense capabilities. This program marks a significant achievement in India’s defense research and production.
Arihant-Class Submarines
- The Arihant-class is India''s first series of nuclear-powered submarines, developed under the Advanced Technology Vessel (ATV) program.The project aims to bolster India''s nuclear deterrence by providing a credible sea-based leg to its nuclear triad.
- The name Arihant translates to "Destroyer of Enemies" in Sanskrit, reflecting the strategic importance of these submarines.
Capabilities:
- Nuclear Propulsion: Provides significant operational advantages, including long-duration submerged patrols and the ability to avoid detection.
- Missile Launch System: Vertical launch system for ballistic missiles, designed for strategic deterrence.
- Stealth: Advanced design and technology aimed at reducing noise and improving stealth to avoid detection.
Strategic Importance:
- Sea-Based Deterrent: The Arihant-class submarines form a critical part of India’s nuclear triad, which also includes land-based missiles and air-delivered nuclear weapons. They provide a reliable second-strike capability, enhancing India''s strategic deterrence.
- Survivability: Submarines are less vulnerable to preemptive strikes compared to land-based assets, ensuring that India can retaliate even after a nuclear attack.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies