- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
BLACK CARBON
- Black Carbon (BC) is a short-lived pollutant that is the second-largest contributor to warming the planet behind carbon dioxide (CO2).
- Unlike other greenhouse gas emissions, BC is quickly washed out and can be eliminated from the atmosphere if emissions stop.
- Unlike historical carbon emissions it is also a localised source with greater local impact.
- Black carbon is a kind of an aerosol.
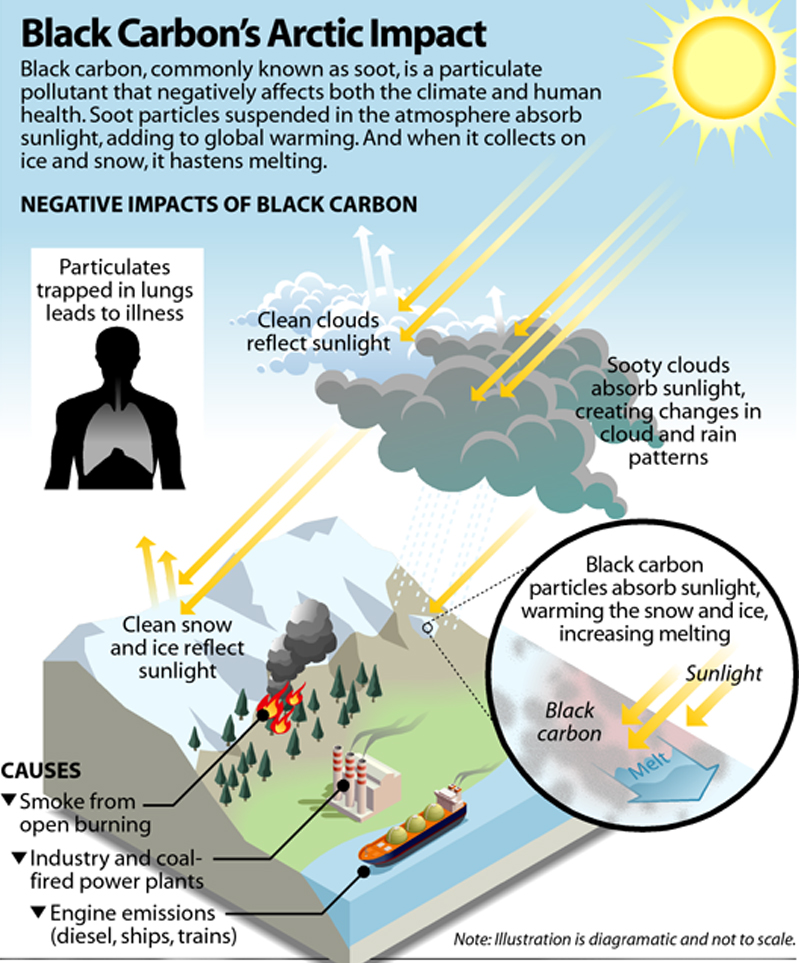
- General Impacts: Among aerosols (such as brown carbon, sulphates), Black Carbon has been recognized as the second most important anthropogenic agent for climate change and the primary marker to understand the adverse effects caused by air pollution.
- Black carbon absorbs solar energy, it warms the atmosphere. When it falls to earth with precipitation, it darkens the surface of snow and ice, reducing their albedo (the reflecting power of a surface), warming the snow, and hastening melting.
- Emission: It gets emitted from gas and diesel engines, coal-fired power plants, and other sources that burn fossil fuel. It comprises a significant portion of particulate matter or PM, which is an air pollutant.
 Various Measures taken
Various Measures taken
- Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana:
- Under this initiative, the government is promoting use of cleaner household cooking fuels.
- BS VI Emission Norms:
- Leapfrogging from BS-IV to BS-VI norms for fuel and vehicles from 1st April, 2020.
- Introducing Cleaner Fuels:
- Introduction of cleaner / alternate fuels like gaseous fuel (CNG, LPG etc.), ethanol blending.
- SATAT Scheme:
- A new initiative, “Sustainable Alternative Towards Affordable Transportation (SATAT), has been launched to set up 5000 Compressed Bio-Gas (CBG) production plants and make CBG available in the market for use.
- Managing Crop Residue:
- Agricultural machines and equipment for in-situ crop residue management in Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh and NCT of Delhi are promoted under the Central Sector Scheme on Promoting Agricultural Mechanization for in-situ Crop Residue Management with 50% subsidy to individual farmers and 80% subsidy to the establishment of Custom Hiring Centres.
- National Clean Air Programme:
- The Central Government is implementing the National Clean Air Programme as a long-term, time-bound, national-level strategy to tackle the air pollution problem across the country in a comprehensive manner.
- The Centre has set a new target of a 40% reduction in particulate matter concentration in cities covered under the scheme by 2026, updating the earlier goal of 20 to 30% reduction by 2024.
- City specific Clean Air Action Plans:
- The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) has identified 131 cities based on ambient air quality levels exceeding national ambient air quality standards, and cities with a million plus population.
- City specific Clean Air Action Plans have been prepared and rolled out for implementation in these cities.
- These plans define time bound targets to control city specific air polluting sources (soil & road dust, vehicles, domestic fuel, municipal solid waste burning, construction material and industries, etc.).
- FAME Scheme:
- Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles (FAME) phase-2 scheme has been rolled out.
|
BROWN CARBON More recently, “brown carbon” (light-absorbing organic carbon) has attracted interest as a possible cause of climate change. This class of organic carbon, known for its light brownish color, absorbs strongly in the ultraviolet wavelengths and less significantly going into the visible. Types of brown carbon include tar materials from smoldering fires or coal combustion, breakdown products from biomass burning, a mixture of organic compounds emitted from soil, and volatile organic compounds given off by vegetation.
|









 Latest News
Latest News

 General Studies
General Studies