- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
JANUARY 29, 2026 Current Affairs
WaSH Warriors
- The Ministry of Jal Shakti honoured WaSH Warriors from across India at a special Samvad Samaroh in New Delhi in January 2026, recognising grassroots leadership in water and sanitation.
WaSH Warriors:
- WaSH Warriors are grassroots champions—individuals from rural communities—who lead efforts in Water, Sanitation and Hygiene (WaSH), especially under the Jal Jeevan Mission and allied programmes.
Aim
- To promote safe drinking water, sanitation, and hygiene through community ownership (Jan Bhagidari).
- To ensure inclusive, equitable, and sustainable WaSH outcomes, particularly for women and vulnerable groups.
Functions:
- Mobilising communities for water conservation and safe water practices.
- Supporting implementation and sustainability of Har Ghar Jal tap connections.
- Promoting ODF Plus behaviours and hygiene awareness under Swachh Bharat Mission (Grameen).
- Encouraging local monitoring, maintenance, and long-term functionality of water assets.
Significance:
- Reduces women’s drudgery and improves health outcomes (lower diarrhoeal disease burden).
- Strengthens last-mile governance and accountability in rural service delivery.
- Demonstrates the success of people-centric development and decentralised implementation.
New Aadhaar App
- The Government of India has launched the New Aadhaar App in January 2026, dedicated to the nation.
- This next-generation app, introduces a Privacy-First approach, allowing users to update mobile numbers from home.
About New Aadhaar App:
- The New Aadhaar App is a secure, next-generation mobile platform designed by the Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI).
- It is significantly different from the old mAadhaar app, focusing on consent-based control and data minimization in line with the DPDP Act.
- Developed by: This next-generation app, developed by UIDAI.
Aim & Objectives:
- Eliminate Photocopies: To stop the misuse of Aadhaar data during routine checks at hotels and airports.
- Resident-Centricity: To provide Identity at Fingertips while allowing users to choose exactly what data they share.
- Ease of Living: To reduce physical visits to Aadhaar Seva Kendras for routine updates.
Key Features
Secure Offline Verification (No Internet Needed):
- Users can now verify their identity without an active internet connection or sharing their 12-digit number.
- Share ID: Generate a password-protected file with only limited fields (e.g., just Name and Age).
- QR Scanning: Scan an entity’s QR code to provide instant, digitally signed proof of identity.
Update Mobile Number & Address from Home:
- For the first time, residents can update their registered mobile number directly through the app using Face Authentication.
- Fee: A nominal fee of ₹75 is applicable.
- Timeline: Updates are typically reflected within 15 days.
One Family – One App:
- The app allows the management of up to five Aadhaar profiles on a single smartphone. This makes it a perfect tool for parents to manage their children’s or elderly dependents’ digital IDs.
Selective Data Sharing:
- Users no longer have to share their full digital card. You can choose to share only Photo and Age for a movie ticket or Name and Address for a hospital visit, masking the Aadhaar number entirely.
Biometric Lock & Unlock:
- A single-click feature allows you to lock your biometrics, ensuring no one can use your fingerprint or iris data without your permission through the app.
Significance for the Common Man:
- Aligns with the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act by ensuring only digitally signed credentials are shared, not the actual Aadhaar number.
- Enables safe and instant verification for service partners and gig workers without exposing sensitive details.
Overseas Citizen of India (OCI)
- President of the European Council, Antonio Costa, known as the “Gandhi of Lisbon,” publicly showcased his OCI card at the conclusion of the India–EU Free FTA.
- An Overseas Citizen of India (OCI) is a foreign national of Indian origin granted a lifelong visa to reside and work in India. It is an immigration status, not dual citizenship.
- The OCI scheme was introduced by the Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2005; the legal status of an OCI is defined under Section 7A of the Citizenship Act, 1955.
- In 2015, the Government of India merged the Persons of Indian Origin (PIO) scheme with OCI into a single “OCI Cardholder” category.
Eligibility Criteria
- Foreign nationals (excluding those with any link to Pakistan or Bangladesh) are eligible if they:
- Were Indian citizens at, or anytime after, the Constitution’s commencement on 26 January 1950.
- Were eligible to become Indian citizens on 26 January 1950.
- Belonged to territories that became part of India after 15 August 1947.
- Are children, grandchildren, or great-grandchildren of such citizens mentioned above.
- A minor child is eligible if both parents are Indian citizens or if at least one parent is an Indian citizen; also, if the child is of any person covered under the categories mentioned above.
- A foreign spouse of an Indian citizen or an OCI cardholder is eligible if the marriage is registered and has subsisted continuously for at least two years before the application.
Mandatory Disqualifications
- Any person who is or was a citizen of Pakistan or Bangladesh, or whose ancestors held such citizenship.
- Serving or retired persons from foreign military, defence, or police (with limited exceptions).
- Applicants posing security risks or found guilty of fraud or material concealment.
Key Benefits of OCI Cardholders
- Lifelong Visa: OCI cardholders receive a multi-entry, multi-purpose lifelong visa for visiting India.
- FRRO Exemption: They are exempt from registration with the Foreigners Regional Registration Officer, irrespective of the duration of stay.
- Economic Parity: They have parity with Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) in economic, financial, and educational matters, including ownership of non-agricultural property.
- Public Services: They are treated on par with Indian citizens for domestic airfares and entry fees to national parks, monuments, and museums.
Major Restrictions for OCI Cardholders
- Political Exclusion: OCI cardholders cannot vote, contest elections, or hold legislative offices.
- Constitutional Offices: They are ineligible to hold posts such as President, Vice-President, or Judges of the Supreme Court and High Courts.
- Public Employment: They cannot hold government jobs unless allowed by the Central Government.
- Land Ownership: OCI holders cannot acquire agricultural land, farmhouses, or plantations.
Recent Updates related to OCIs
- Special Permissions: OCI cardholders now require special permits for activities such as missionary work, journalism, research, or mountaineering.
- Restricted Area: They need permits similar to those of other foreign nationals to visit notified regions.
- Revocation Provisions: OCI status may be cancelled for acts showing disaffection towards the Constitution or if the holder is sentenced to imprisonment of two years or more.
Social Representation Patterns in Central Government Employment
- DoPT’s Annual Report 2024–25 shows significant Group C safai karmacharis belong to SC, ST and OBC communities, highlighting continued caste concentration in sanitation roles.
Caste Concentration in Central Government Employment
- Occupational Segregation: Over 66% of safai karmacharis come from SC, ST and OBC groups, reflecting the persistence of caste-linked sanitation work.
- Under-Representation: In Group A services, SCs hold only 14.20%, STs 6.54% and OBCs 19.14% positions, far below combined reservation entitlements.
- Data Transparency Gaps: Absence of EWS representation figures despite 10% quota weakens monitoring of inclusive recruitment outcomes.
- Slow SC Progress: SC share declined from 17.49% in 2018–19 to 16.84% in 2024–25, showing stagnation despite the long-standing reservation policy.
- Uneven Reservation Gains: OBC representation increased sharply from 21.57% to 26.32%, while SC and ST growth remained marginal over six years.
- Reporting Delays: For several years after 2019, DoPT released only partial workforce data covering only 19–20 lakh employees instead of the full 32 lakh employees.
Way Forward
- Upward Mobility: Expand structured leadership training, promotions and skill enhancement for reserved category employees; E.g., Mission Karmayogi competency-based capacity building.
- Occupational Diversification: Enable transition from sanitation roles into technical and administrative posts through targeted skilling; E.g., Skill India Mission and PM Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY).
- Data Disclosure: Mandate annual publication of complete caste-wise and EWS-wise workforce data across all departments; E.g., digitised HR dashboards under e-Office reforms.
- Reservation Compliance: Strengthen periodic compliance audits and corrective recruitment drives; E.g., special recruitment campaigns by DoPT for backlog vacancies.
- Institutional Support: Provide mentoring, coaching and preparatory assistance for higher service examinations; E.g., SC/ST/OBC coaching schemes under the Ministry of Social Justice and Tribal Affairs.
.
India and EU Commit to Collaborate on Peaceful Nuclear Applications
- At the 16th India-EU Summit, India and the European Union reaffirmed their cooperation on peaceful nuclear energy applications.
- Agreement Scope: The collaboration is based on the 2020 India-Euratom Agreement, covering peaceful, non-explosive nuclear energy uses.
- Fusion Research: Both parties are committed to better coordination in the ITER project to accelerate fusion energy development as a clean power source.
- Non-Power Use: The partnership prioritises non-power nuclear uses, notably radiopharmaceuticals for cancer treatment and radioactive waste management.
- Strategic Diversification: This cooperation expands India’s energy diplomacy by diversifying access to advanced nuclear safety technologies beyond Russia and the USA.
International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER)
- Project Overview: ITER is the world’s largest experimental nuclear fusion project, currently under construction in Saint-Paul-lès-Durance, France.
- Global Partnership: It comprises seven members, including the European Union, India, China, Japan, South Korea, Russia, and the United States.
- Core Objective: ITER aims to demonstrate the scientific and technological feasibility of nuclear fusion as a clean, carbon-free energy source.
- Energy Target: It plans to generate 500 MW of fusion power from a 50 MW input, achieving an energy gain of Q=10.
- Key Component: India has built the world’s largest cryostat for ITER to maintain the ultra-low temperatures required for fusion.
France Social Media Controls
- France’s National Assembly passed a bill banning social media use for minors under 15 and restricting mobile phones in high schools to protect child mental health.
Key Features of the Bill
- Phased Rollout: Restrictions on new social media accounts to begin from the 2026 school year, allowing transition for platforms and users.
- School Phone Ban: Prohibits mobile phone use in high schools, extending earlier restrictions imposed in middle schools since 2018.
- Account Deactivation Rule: Social media companies must disable existing accounts that violate age limits by 31 December after enforcement begins.
- Mental Health Focus: Targets harms linked to excessive screen exposure, such as emotional stress and declining adolescent well-being.
- Algorithm Safeguard: Shield minors from behavioural manipulation driven by platform algorithms.
- Foreign Influence Check: Aims to limit external digital influence shaping youth opinions.
- Platform Exemptions: Excludes online encyclopedias and educational websites from the ban.
About Social Media Usage in India
- India regulates social media through the IT Act, 2000, IT (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules, 2021, and the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023.
- India hosts 820+ million internet users and 500+ million social-media users, making online safety a national-scale governance challenge.
- India recorded a 65% surge in cybercrimes between 2019 and 2023; child-related cyber offences rose over 400%, per NCRB, highlighting the urgent need for stronger controls.
- India reports the world’s highest WhatsApp misinformation spread, contributing to mob violence and public disorder events documented by law enforcement agencies.
- Under the DPDP Act 2023, minors (<18) require verifiable parental consent, and platforms cannot track, profile or target-advertise to children, ensuring a privacy-first architecture.
Health Impacts of Plastics
- A global lifecycle assessment published in The Lancet Planetary Health warns that health burdens from plastic-related emissions will drastically increase.
Key Findings of the Study
- Doubling of Health Burden: Emissions from plastics are expected to cause more than double the increase in disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) by 2040 under business-as-usual trends.
- Delayed Production Peak: Global plastic production is unlikely to peak before 2100, prolonging environmental and health pressures worldwide.
- Global Lifecycle Estimate: The study provides the first comprehensive global-scale quantification of health impacts across the entire plastics lifecycle using DALYs as a unified health metric.
- Chemical Opacity: Limited transparency and non-disclosure of plastic chemical compositions severely restrict precise health risk evaluation and evidence-based policymaking.
- Disability-Adjusted Life Years (DALYs): A measure combining years of life lost due to premature death and years lived with illness or disability to reflect total health burden.
Major Health Impacts Identified
- Air Pollution Exposure: Fine particulate matter from production and open burning increases risks of asthma, cardiovascular diseases and premature deaths.
- Toxicity-Induced Illnesses: Release of hazardous chemicals across plastic lifecycles is strongly linked to rising cancers and long-term non-communicable diseases globally.
Recommendations by the Lancet Study
- Reduce Virgin Plastic Production: Call for deep cuts in primary (new) plastic manufacturing, especially for non-essential and single-use applications.
- Full Lifecycle Policies: Urges governments to regulate plastics from raw material extraction to disposal and environmental leakage stages.
- Chemical Transparency: Recommends mandatory disclosure of plastic chemical composition to improve health risk assessments and policy design.
- Global Coordinated Action: Emphasises fast-tracking a legally binding Global Plastics Treaty to control pollution and health impacts worldwide.
V-BAT Autonomous Drones
- The Indian Army officially selected the US-based firm Shield AI to supply its cutting-edge V-BAT autonomous drones.
- This emergency procurement deal marks a milestone as India integrates the Hivemind AI software, allowing for sovereign development of autonomous military capabilities.
About V-BAT Autonomous Drones:
- The V-BAT is a Group 3 Vertical Take-Off and Landing (VTOL) Unmanned Aircraft System (UAS).
- Unlike traditional drones that require runways, the V-BAT uses a unique ducted-fan design to take off and land vertically like a rocket, then transition to horizontal flight for surveillance.
Developed By:
- Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM): Shield AI (US-based Deep-Tech firm).
- Indian Partner: JSW Defence, which is establishing a $90 million manufacturing hub in Hyderabad to make India a global production base for the V-BAT.
Aim & Objectives:
- To provide persistent Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR) in high-threat zones where GPS or communication might be jammed.
- To eliminate the need for runways, catapults, or recovery nets, making it deployable from ship decks, rooftops, and remote forward posts.
- Through the Hivemind SDK, the aim is to allow Indian engineers to build mission-specific AI behaviors tailored to India’s unique borders.
Key Features:
Vertical Take-Off & Landing (VTOL):
- The V-BAT’s single-engine, enclosed-rotor design allows it to operate in austere environments. It can launch from a 12×12 foot clearing, making it ideal for the narrow ridges of the Himalayas or crowded Indian Navy ship decks.
Hivemind Autonomy Software
- The brain of the drone, Hivemind, enables the V-BAT to:
- Sense & Act: Navigate without GPS or human input.
- Threat Avoidance: Dynamically change paths when targeted by electronic warfare.
- Team Operations: Allows multiple drones to collaborate autonomously on a single mission.
Operational Specs
- Endurance: Over 12 hours of continuous flight.
- Engine: Heavy-fuel engine (logistically compatible with standard military fuel).
- Payload: High-definition ISR sensors and targeting systems.
Significance for Indian Defence:
- The V-BAT is uniquely suited for India’s varied terrain—from the high-altitude LAC/LOC to the vast Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- The deal isn’t just a purchase; it’s a technology transfer. The Hyderabad facility ensures that V-BATs are Made in India for the world.
Sunabeda Wildlife Sanctuary
- The Sunabeda Wildlife Sanctuary in Odisha was officially declared ‘Maoist-free’ in January 2026, leading to a major breakthrough in wildlife monitoring.
- Recent camera trap data reveals a flourishing leopard population (estimated over 70), marking its transition from a conflict zone to a potential Leopard Haven.
About Sunabeda Wildlife Sanctuary:
- Sunabeda Wildlife Sanctuary is a sprawling biodiversity hotspot and a proposed Tiger Reserve located in the western reaches of Odisha.
- Established in 1983, it is part of the Deccan Peninsula biogeographic zone and serves as a vital ecological bridge in Central India.
Located in:
- District: Nuapada, Odisha.
- Border: Adjoins the Sitanadi and Udanti Sanctuaries of Chhattisgarh.
- Area: Approximately 600 sq. km (proposed reserve extends over 956 sq. km).
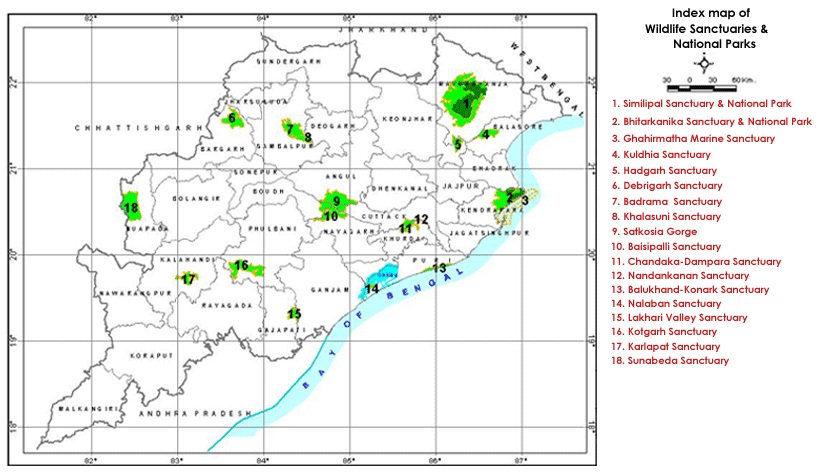
Key Geological & Natural Features
- Terrain: A vast, high-altitude grass-covered plateau characterized by deep canyons, multiple valleys, and gorges.
- Hydrology: It forms the primary catchment area for the Jonk River, a tributary of the Mahanadi. The sanctuary is also the source of the Sunder and Indra
- Waterfalls: Home to 11 magnificent waterfalls, making it a prime destination for eco-tourism.
- Vegetation: Predominantly Dry Deciduous Tropical Forest. Key flora includes Bija, Teak, Sissoo, and Sandalwood.
Significance
- Acts as a critical corridor for Wild Water Buffalo migrating between Odisha and Chhattisgarh.
- One of the few ideal habitats left for the Hard-ground Barasingha (Swamp Deer) and Nilgai.
- Over 200 bird species have been reported, including the elusive Forest Owlet and the Banded Bay Cuckoo.
Sufi Poet Bulleh Shah
- Recently, a shrine dedicated to the 17th-century Sufi poet Bulleh Shah in Mussoorie, Uttarakhand, was vandalised.
- Bulleh Shah (1680–1757) was a prominent Punjabi Sufi poet associated with the Qadiriyya Silsila.
- He adopted a highly individualistic and non-conformist approach, emphasising Tariqat (esoteric practice) over the orthodox Shariat.
- Poetic Form: He used the Kafi style, a musical form of poetry widely sung in qawwalis and folk music.
- Philosophy: His work combined Sufi mysticism with Hindu Vedanta, emphasising Wahdat-al-Wujud or the unity of existence.
- Secular Humanism: He advocated universal love (ishq) and compassion, transcending caste, creed, religion, and gender divisions.
- Social Reformer: He challenged the social hierarchy by accepting Shah Inayat Qadiri, a lower-caste farmer, as his spiritual guide.
- Religious Critique: He openly criticised ritualism and fundamentalism among Mullahs and Brahmins, emphasising inner spiritual realisation.
- Major Works: Kafian, Barah Maha, Siharfi, and Athwara are foundational to Punjabi Sufi literature.
Mir Alam Tank
- Stranded engineers and workers were rescued from the Mir Alam Tank lake by the Hyderabad Disaster Management and Asset Protection Agency (HYDRAA).
- Mir Alam Tank is a historic reservoir in Hyderabad, Telangana, located south of the Musi River. It lies adjacent to Nehru Zoological Park.
- It was built in 1806 during the reign of Nizam Asaf Jah III and named after his prime minister, Mir Alam.
- It is regarded as the world’s first multi-arch dam, featuring 21 semi-circular arches that efficiently distribute water pressure.
- The dam was designed by French engineer Michel Joachim Marie Raymond, or Monsieur Raymond.
- Mir Alam Lake was Hyderabad’s main drinking water source for almost 125 years until Osman Sagar and Himayat Sagar reservoirs were built.
Lepidagathis konkanensis
- Scientists have discovered a new wildflower species, Lepidagathis konkanensis, from the lateritic plateaus of the Konkan region in Maharashtra.
- Floral Morphology: The plant bears bright yellow, bilabiate flowers arranged in short, compact, and densely packed spikes.
- Reproductive Traits: It shows smaller seeds and a distinctly shorter style than closely allied Lepidagathis species.
- Habitat Adaptation: The species thrives on iron-rich lateritic plateaus, locally known as ‘sadas’, in harsh, rocky environments.
- Survival: It survives in extremely thin soil layers with high exposure to sunlight, wind, and seasonal moisture stress.
- Key Threats: Agricultural expansion, mango orchards, tourism growth, and rapid urbanisation
Scabies
- A global resurgence in scabies cases has revived public health concerns about it.
- Scabies is a contagious skin infestation caused by the microscopic mite Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis.
- Infection Mechanism: Female mites burrow into the upper layer of the skin (epidermis) to lay eggs, triggering allergic itching from mite proteins and faeces.
- Transmission: Scabies spreads mainly through prolonged direct skin-to-skin contact.
- Types: Classic scabies occurs with a low mite burden and intense itching, or as crusted (Norwegian) scabies with massive mite infestation and thick crusts in immunocompromised individuals.
- Symptoms: Intense itching (pruritus), especially at night, and pimple-like rashes.
- Complications: Scratching facilitates Staphylococcus or Streptococcus infection, potentially causing septicaemia, heart disease, or kidney damage.
- Treatment: Standard management involves topical Permethrin cream or oral Ivermectin.
- Disease Burden: Scabies affects over 200 million globally, mainly in tropical and crowded areas.
- Indian prevalence ranges from 13–59%, with rural household attack rates as high as 30.9%.
- Vulnerable Groups: Children, the elderly, and institutional populations face a higher risk due to close contact and limited access to hygiene.
- NTD Recognition: The World Health Organisation (WHO) declared scabies a Neglected Tropical Disease in 2017.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies