- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
June 9, Current affairs 2023
Marine species including whales and dolphins under significant threat from noise pollution
Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS):
- CMS also referred to as the Bonn Convention, is an environmental treaty under the aegis of the United Nations Environment Programme.
- It was signed in Bonn, Germany, on 23 June 1979.
- It provides a global platform for the conservation and sustainable use of migratory animals and their habitats.
- CMS is the only global and UN-based intergovernmental organisation established exclusively for the conservation and management of terrestrial, aquatic and avian migratory species throughout their range.
- The parties to the convention acknowledge the importance of conserving migratory species, and the need to pay special attention to species whose conservation status is unfavourable.
- Activities by CMS Parties may range from legally binding treaties (called Agreements) to less formal instruments, such as Memoranda of Understanding.
- The Conference of Parties (COP) is the decision-making organ of this convention.
- CMS has two Appendices. These appendices list migratory species to which the Convention applies.
- Appendix I lists endangered migratory species and includes prohibitions regarding the take of these species.
- Appendix II lists species that have an ‘unfavourable conservation status’ (as per the conditions set out in the Convention) and encourages range states to draft range-wide agreements for conservation and management of these species.
- India and CMS:
- India has been a party to the CMS since 1983.
- India has also signed non-legally binding MOU with CMS on the conservation and management of Siberian Cranes (1998), Marine Turtles (2007), Dugongs (2008) and Raptors (2016).
RBI gives green signal to first loss default guarantee (FLDG) framework; here''s how will fintech, banks, NBFCs benefit
First Loss Default Guarantee (FLDG):
- What is it? FLDG is a lending model between fintech firms and their partner banks and non-banking finance companies where the initial hit on a default is taken by the fintech firm that originated the loan.
- Under these agreements, the fintech originates a loan and promises to compensate the partners up to a pre-decided percentage in case customers fail to repay.
- The bank/NBFC partners lend through the fintech but from their books.
- Advantages:
- FLDG helps expand the customer base of traditional lenders but relies on the fintech''s underwriting capabilities.
- It will also rationalise the existing prudential norms to implement resolution plans in respect of exposures affected by natural calamities.
FinTech
- Fintech, a combination of the terms “financial” and “technology,” is the application of new technological advancements to products and services in the financial industry.
- It refers to the application of software and hardware to financial services and processes, making them faster, easier to use and more secure.
- The fintech industry includes everything from payment processing solutions to mobile banking apps.
- Some examples include mobile banking, peer-to-peer payment services, automated portfolio managers or trading platforms.
Pakistan, Turkmenistan ink Joint Implementation Plan for TAPI gas pipeline
TAPI Pipeline
- It is an 1,814kilometre pipeline that aims to transport 33 billion cubic metres of gas from Turkmenistan to Afghanistan, Pakistan and finally, India.
- It is also called the ‘Peace Pipeline’.
- Route:
- It will start from the Galkynysh gas field in Turkmenistan.
- It will then pass through Afghanistan and Pakistan to finally reach the Indian town of Fazilka(near the Indo-Pak border).
- Capacity: At full capacity, the pipeline will transport 33 billion cubic meters (bcm) of natural gas annually from TKM to respective buyers in AFG (5%), PAK (47.5%) and IND (47.5%) during the 30-year commercial operations period.
- The Project comprises the procurement, installation and operation of the pipeline and related facilities within Afghanistan and Pakistan.
- Timeline:
- The project was originally conceived in the 1990s, and an inter-governmental agreement was signed in 2010 by the heads of four member nations.
- A Gas Pipeline Framework Agreement was signed in December 2010, and a bilateral gas sale agreement was signed in May 2013.
- In February 2018, a ground-breaking ceremony for Afghanistan''s section of the TAPI gas pipeline was held in the western Afghan city of Herat.
- Financing:
- The TAPI project is being funded by the Asian Development Bank (ADB), which is also acting as transaction adviser for the development.
- Turkmenistan took a loan of $700m from the Islamic Development Bank for financing the project in December 2016.
- The remaining three countries made an initial investment of $200m in the TAPI project.
Fame India Scheme
The Department of Heavy Industry is administering the scheme “Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric and Hybrid Vehciles in India”, popularly known as FAME India scheme since 01st April 2015.
- FAME India is a part of the National Electric Mobility Mission Plan.
- Main thrust of FAME is to encourage electric vehicles by providing subsidies.
- Vehicles in most segments – two wheelers, three wheelers, electric and hybrid cars and electric buses obtained the subsidy benefit of the scheme.
FAME focuses on 4 areas i.e.
-
- Technology development,
- Demand Creation,
- Pilot Projects and
- Charging Infrastructure.
- To promote manufacturing of electric and hybrid vehicle technology and to ensure sustainable growth of the same, Department of Heavy Industry is implementing FAME-India Scheme Phase – I [Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of (Hybrid &) Electric Vehicles in India] from 1st April 2015.
- The scheme was initially up to 31st April 2017, has been extended up to 31st March 2019 or till Notification of FAME-II, whichever is earlier.
FAME-India Scheme Phase – II
Aims to boost electric mobility and increase the number of electric vehicles in commercial fleets.
Target
- The outlay of ₹10,000 crore has been made for three years till 2022 for FAME 2 scheme.
- The government will offer the incentives for electric buses, three-wheelers and four-wheelers to be used for commercial purposes.
- Plug-in hybrid vehicles and those with a sizeable lithium-ion battery and electric motor will also be included in the scheme and fiscal support offered depending on the size of the battery.
How will FAME 2 scheme help improve charging infrastructure?
- The centre will invest in setting up charging stations, with the active participation of public sector units and private players.
- It has also been proposed to provide one slow-charging unit for every electric bus and one fast-charging station for 10 electric buses.
- Projects for charging infrastructure will include those needed to extend electrification for running vehicles such as pantograph charging and flash charging.
- FAME 2 will also encourage interlinking of renewable energy sources with charging infrastructure.
- The scheme proposes to give a push to electric vehicles (EVs) in public transport and
- It seeks to encourage adoption of EVs by way of market creation and demand aggregation.
Automobile Sector
- 100% FDI by automatic route is permitted in the automobile sector.
- Further, the sector is deregulated, both private sector and public sector are free to carry out investment in the automobile sector, including for manufacturing of Electric Vehicles and E-Buses.
Need of the hour
- India needs auto industry’s active participation to ease electric mobility transition.
- The auto and battery industries could collaborate to enhance customer awareness, promote domestic manufacturing, promote new business models, conduct R&D for EVs and components, consider new business models to promote EVs.
- Government should focus on a phased manufacturing plan to promote EVs, provide fiscal and non-fiscal incentives for phased manufacturing of EVs and batteries.
- Different government departments can consider a bouquet of potential policies, such as congestion pricing, ZEV credits, low emission/exclusion zones, parking policies, etc. to drive adoption of EVs.
It's raining tiger cubs in Amrabad Tiger Reserve
Amrabad Tiger Reserve (ATR)
- Location: It is located in the Nagarkurnool and Nalgonda districts in the southern part of Telangana.
- Spread over 2611.4 square kilometers, it is one of the largest tiger reserves in India.
- It was notified as a sanctuary in 1983, and after the State bifurcation, it was declared as Amarabad Tiger Reserve in 2015.
- ATR covers a part of the Nallamala Forest and is home to a variety of flora and fauna.
- The hilly terrain of this Tiger Reserve, with deep valleys and gorges, forms the catchment of the Krishna River.
- Flora:
- Dense grass occurs in 30% of the area and is scattered in an additional 20%.
- Dominant tree species include Terminalia tomentosa, Hardwickia binata, Madhuca latifolia. Diospyros melanoxylon, Gardenia latifolia etc.
- Fauna:
- Major wild animals found are Tiger, Leopard, Wild dog, Indian Wolf, Indian fox, Rusty-spotted cat, Small Indian civet, Sloth bear, Honeybadger, Wild boar etc.
- Over 303 bird species have been identified in this region. Some important groups include Eagles, Pigeons, Doves, Cuckoos, Woodpeckers, Drongos etc.
Pune astronomers detect two new millisecond pulsars
Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (GMRT):
- GMRT is a low-frequency radio telescope that helps investigate various radio astrophysical problems ranging from nearby solar systems to the edge of the observable universe.
- Location: It is located at Khodad, 80 km north of Pune, Maharashtra.
- It is a project of the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE), operating under the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR).
- The telescope is operated by the National Centre of Radio Astrophysics (NCRA). NCRA is a part of the TIFR, Mumbai.
- It consists of 30 fully- steerable dish-type antennas of 45-meter diameter each, spread over a 25-km region.
- GMRT is presently the world’s largest radio telescope operating at meter wavelength.
- It was recently upgraded with new receivers, after which it is also known as the upgraded Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (uGMRT).
Pulsars
- Pulsars are rotating neutron stars observed to have pulses of radiation at very regular intervals that typically range from milliseconds to seconds.
- Pulsars have very strong magnetic fields which funnel jets of particles out along the two magnetic poles.
- These accelerated particles produce very powerful beams of light.
- Often, the magnetic field is not aligned with the spin axis, so those beams of particles and light are swept around as the star rotates.
- Pulsars are among the few celestial objects that emit circular polarised light.
RBI permits banks to issue RuPay prepaid forex cards
RuPay card
- It is an Indian domestic card scheme conceived and launched by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI).
- Its mission is to fulfil the Reserve Bank of India’s vision of having a domestic, open-loop and multilateral system of payments in India.
- It works to enable electronic payment at all Indian banks and financial institutions.
- Benefits of RuPay Card
- Lower cost and affordability: Since the transaction processing will happen domestically, it would lead to a lower cost of clearing and settlement for each transaction. This will make the transaction cost affordable and will drive the usage of cards in the industry.
- Customized product offering: RuPay, being a domestic scheme is committed towards the development of customized product and service offerings for Indian consumers.
- Protection of information related to Indian consumers: Transaction and customer data related to RuPay card transactions will reside in India.
NPCI
- It is an umbrella organisation launched in 2008 by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and the Indian Banks’ Association (IBA) under the provisions of the Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007.
- It is owned by a consortium of banks, is aimed at creating robust payments and settlement systems.
Indian Oil unveils India's first green hydrogen-run bus that emits just water
Recently, the Indian Army has collaborated with Indian Oil Corporation Limited (IOCL) for demonstration trials of Hydrogen Fuel Cell Bus technology.
- The Indian Army also received its first Hydrogen Fuel Cell Bus, marking stride towards cleaner and greener transport solutions.
- Bus has a seating capacity of 37 passengers and a mileage of 250-300 km on a 30 kg onboard Hydrogen fuel tank.
- Earlier, on 21st March 2023, the Indian Army became the first government entity to sign an MoU with NTPC Renewable Energy Ltd for installation of Green Hydrogen based Microgrid Power Plants along the Northern Borders.
- Hydrogen fuel cell technology provides a clean and efficient solution. It generates electricity through a reaction between hydrogen gas and oxygen, with water vapour as the sole byproduct.
- This makes it a compelling alternative to traditional fuels, especially considering the abundance of hydrogen on Earth.
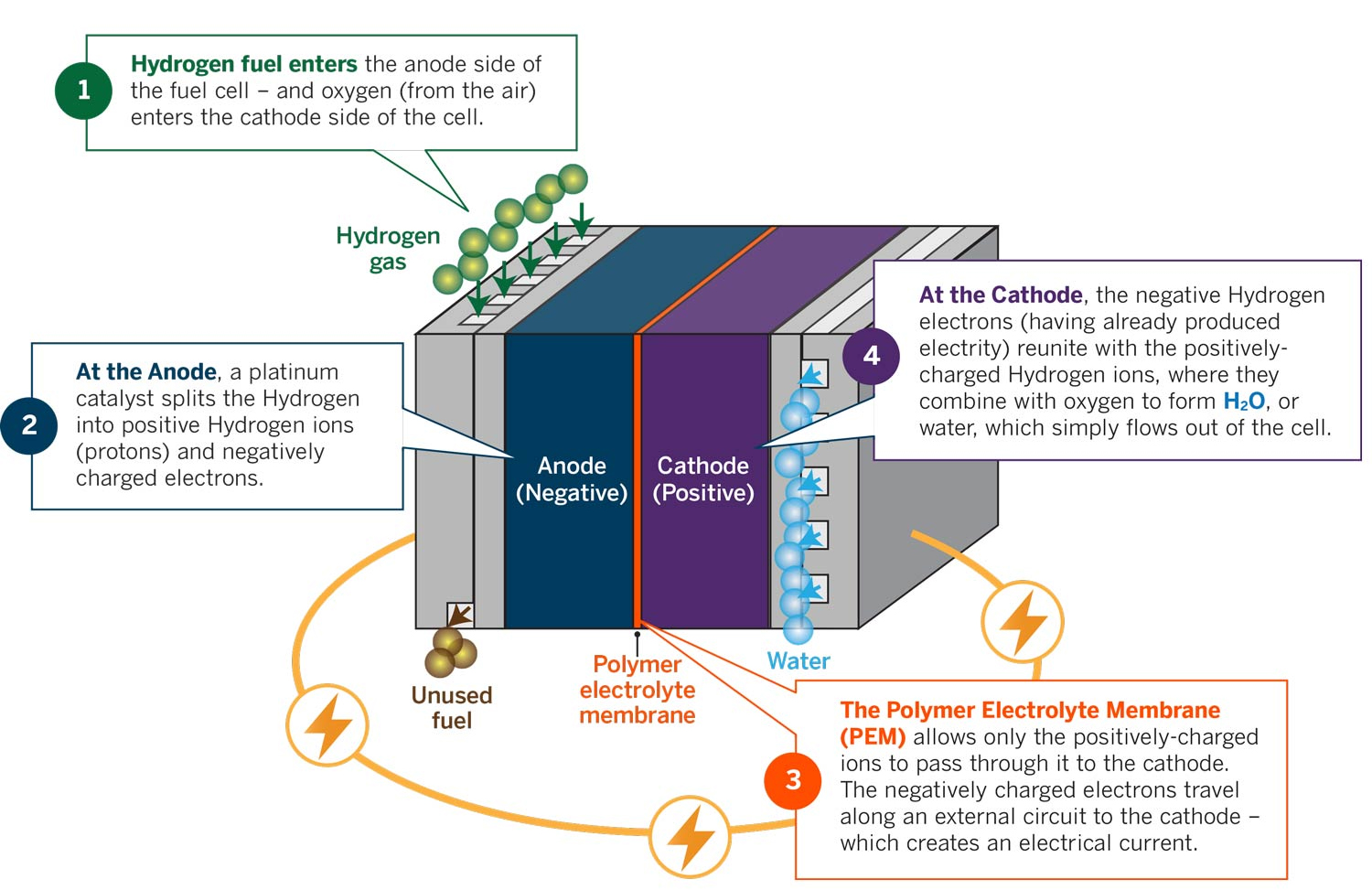
Hydrogen Fuel Cell
- Hydrogen fuel cells are a clean, reliable, quiet, and efficient source of high-quality electric power.
- They use hydrogen as a fuel to drive an electrochemical process that produces electricity, with water and heat as the only by-products.
- Hydrogen is one of the most abundant elements on earth for a cleaner alternative fuel option.
 Types of Hydrogen based on the process of its formation
Types of Hydrogen based on the process of its formation
- Green hydrogen is produced by electrolysis of water using renewable energy (like Solar, Wind) and has a lower carbon footprint.
- Electricity splits water into hydrogen and oxygen.
- By Products: Water, Water Vapor.
- Brown hydrogen is produced using coal where the emissions are released into the air.
- Grey hydrogen is produced from natural gas where the associated emissions are released into the air.
- Blue hydrogen is produced from natural gas, where the emissions are captured using carbon capture and storage.
- Significance:
- Best Zero Emission Solutions: It is one of the best Zero Emission solutions. It is completely environment friendly with no tailpipe emissions other than water.
- Tailpipe emissions: Emission of something such as gas or radiation into the atmosphere.
- Quiet operation: The fact that the fuel cells make little noise means that they can be used in challenging contexts, such as in hospital buildings.
- Easier scaling: Operation times of fuel cells are longer than those of batteries, with fuel cells, only the amount of fuel needs to be doubled to double the operation time, while batteries require the capacity of the components to be doubled to achieve the same.
- Issues:
- High Cost: Green hydrogen makes up only 0.03% of global hydrogen production and it is up to five times more expensive than ‘grey’ hydrogen produced from natural gas or worse, ‘brown’ hydrogen produced from coal.
- Hydrogen Storage: Storage and transportation of hydrogen is more complex than that required for fossil fuels. This implies additional costs to consider for hydrogen fuel cells as a source of energy.
- Hydrogen Extraction: Despite being the most abundant element in the Universe, hydrogen does not exist on its own so needs to be extracted from water via electrolysis or separated from carbon fossil fuels.
- Both of these processes require a significant amount of energy to achieve. This energy can be more than that gained from the hydrogen itself as well as being expensive.
- In addition, this extraction typically requires the use of fossil fuels, which in the absence of carbon capture and storage (CCS) undermines the green credentials of hydrogen.
Irrigation scheme unravels in Jharkhand: Aadhaar misused, funds claimed, farmers clueless
Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana
- It was launched in 2015 to improve farm productivity and ensure better utilization of the resources in the country.
- Objectives
- Convergence of investment in irrigation at the field level
- Expand cultivable area under irrigation
- Improve On-farm water use efficiency to reduce the wastage of water
- Enhance the adoption of being precise in irrigation and other water-saving technologies (more crop per drop)
- It consists of two major components namely,
- Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme (AIBP)
- Har Khet Ko Pani (HKKP): It consists of four sub-components, being Command Area Development & Water Management (CAD&WM), Surface Minor Irrigation (SMI), Repair, Renovation and Restoration (RRR) of Water Bodies, and Ground Water (GW) Development component.
- In addition, PMKSY also consists of two components
- Per Drop More Crop (PDMC) component is being implemented by the Department of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- The Watershed Development component (WDC) is being implemented by the Department of Land Resources
''Agni Prime'' ballistic missile successfully flight-tested by DRDO off Odisha coast
Agni Prime Missile
- It is a short-range ballistic missile that will have a range of 1000 km to 1500 km.
- It is a surface to a surface missile that can carry a payload of around 1,000 Kg or a nuclear warhead.
- It incorporates new propulsion systems and composite rocket motorcasings as well as advanced navigation and guidance systems.
Ballistic missile
- Ballistic Missiles are launched directly into the upper layers of the earth’s atmosphere.
- They travel outside the atmosphere, where the warhead detaches from the missile and falls towards a predetermined target.
- They are rocket-propelled self-guided weapons systems which can carry conventional or nuclear munitions. They can be launched from aircraft, ships and submarines, and land.
Union Cabinet approves continuation of Central Sector Scheme of ‘Exploration of Coal and Lignite Scheme’
Exploration of Coal and Lignite Scheme
- The period for the extension is from 2021-22 to 2025-26.
- Under this scheme, exploration for coal and lignite is conducted in two broad stages: (i) Promotional (Regional) Exploration and (ii) Detailed Exploration in non-Coal India Limited blocks.
- Benefits of the scheme
- This scheme is required to prove and estimate coal resources available in the country, which helps in preparing detailed project reports to start coal mining.
- The geological reports prepared through these explorations are used for auctioning new coal blocks, and the cost is thereafter recovered from successful allocatee.
Types of Coal
- Anthracite: It contains the highest amount of carbon out of all coal ranks (86%-97%) and it is used mostly in industrial settings and the metals industry due to its high heat value.
- Lignite: it is lighter in colour than the higher ranks of coal. It has the lowest carbon content out of all the coal ranks (25%-35%) and it has a high moisture content and crumbly texture.
- Bituminous: It has slightly lower carbon content than anthracite (45%-86%)1. The wide range of carbon content in bituminous coal warrants uses for both electricity and steel production.
- Peat: It is the starting stage of a coal formation which has low calorific value and low carbon content.
Kaziranga mahouts caught for consuming rare turtles
Kaziranga National Park
- It is located in the state of Assam.
- It is also a UNESCO World Heritage Site and houses two-thirds of the total world population of greater one-horned rhinoceros.
- Flora:
- It is a mix of eastern wet alluvial grasslands, semi-evergreen forests and tropical moist deciduous forests.
- It is primarily famous for its dense and tall elephant grassesintermixed with small swamplands.
- It also includes an abundant cover of water lilies, water hyacinths and lotus.
- Fauna:
- It is home to the One-horned rhinoceros, Leopard, Fishing Cat, other Lesser cats, royal Bengal tiger, Large Indian Civet, Small Indian Civet, Sambar, Barking deer, Hog deer, Gaur, Hog Badger, Capped Langur, etc.
- It is also one of the last remaining homes of the endangered and endemic western hoolock gibbon, the only species of apes found in India.
- It is one of the last homes of the critically endangered Bengal florican.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies