- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
Tardigrades
Researchers in China identified a new tardigrade species, Hypsibius henanensis, from moss samples collected in Funiu Mountain, Henan province with the ability to withstand Radiation.
Key highlights of the study
- Genome Sequencing: Scientists sequenced the genome of Hypsibius henanensis, revealing 14,701 genes, with around 30% unique to tardigrades.
- Radiation Exposure: The team subjected this tardigrade species to high doses of gamma radiation, far exceeding human survivability limits, to study its response.
Tardigrades’ radiation resistance reasons
- Genetic Adaptation: The researchers have identified the genetic mechanisms that help a newly discovered species of tardigrades (Hypsibius henanensis) withstand high levels of radiation.
- DNA Repair Genes: They identified 2,801 genes involved in DNA repair processes. Key elements include:
- TRID1 Protein: Aids in rapid repair of DNA double-strand breaks resulting from radiation.
- Mitochondrial Proteins: Two proteins, generated from a radiation-activated gene, are crucial for mitochondrial synthesis and DNA repair.
- Betalain Pigments: These antioxidant pigments help neutralise reactive chemicals caused by radiation exposure, protecting cellular structures.
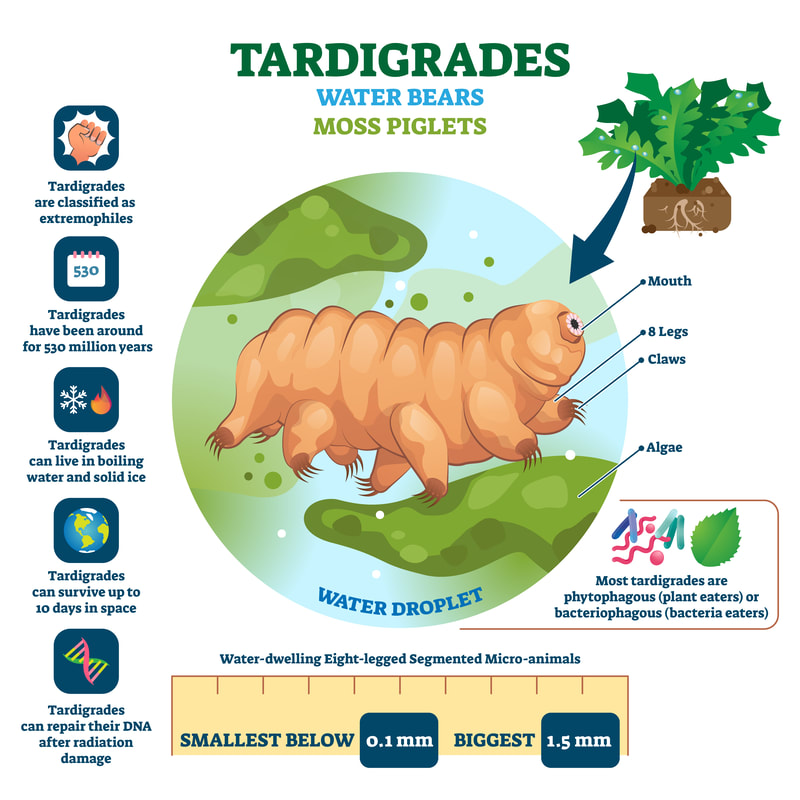 Tardigrades (Hypsibius henanensis)
Tardigrades (Hypsibius henanensis)
- Tardigrades are resilient Creatures also known as water bears or moss piglets.
- They are microscopic, eight-legged animals, typically about 1 mm (0.04 inch) or smaller.
- Classified as free-living invertebrates in the phylum Tardigrada.
- Their tiny, boneless bodies are supported by a hydrostatic skeleton filled with hemolymph (a fluid-filled compartment).
- Equipped with a specialised mouthpart called a buccal pharyngeal apparatus, enabling them to suck nutrients from plants and other microorganisms.
- Known as extremophiles, capable of surviving extreme environmental conditions.
- Require a thin layer of water around their bodies to prevent dehydration, making them effectively aquatic.
- Found globally across terrestrial, marine, and freshwater environments from the Arctic to the Antarctic, including high altitudes and deep-sea regions.
Potential Application of Tardigrades
- Space Exploration: Protecting astronauts from cosmic radiation.
- Nuclear Clean-up: Enhancing radiation tolerance for workers in radioactive environments.
- Cancer Treatment: Potentially improving radiation therapy for cancer patients by enhancing human cell stress resistance.
- Testing on Human Cells: Tardigrade-derived betalain pigments improved the survival rate of human cells exposed to radiation, suggesting promising applications for human health.
|
Researchers uncover remains of Ice Age mastodons in Peru The fossilized remains of three mastodons from the Ice Age have been uncovered in the Peruvian Andes, raising questions as to how the behemoths arrived in the area.
Excavations starting in 2019 uncovered the behemoths, believed to be between 11,000 and 12,000 years old, in the valley of the town of Chambara, about 300 km (186 miles) east of Lima. Mastodons were similar to the also-extinct mammoth, but had flatter heads and straighter tusks. Scientists now hope to find more fossils in the area, which could shed light on how and when the mastodons arrived. The mastodons likely migrated from North America down to South America in search of food and water as climate conditions changed, experts believe. Peru is a rich source of prehistoric remains. In April 2024, a team of paleontologists unveiled the fossilized skull of a river dolphin, the largest found to date, which had swam through the Peruvian Amazon some 16 million years ago.
|









 Latest News
Latest News

 General Studies
General Studies