- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
Dec 6, 2021
GOVT MAKES GOLD HALLMARKING MANDATORY: WHAT IT MEANS
Recently, The Government of India has made hallmarking of gold jewellery mandatory in the country. Bureau of Indian Standards

- Parent agency: Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food, and Public Distribution
- It is the National Standards Body of India under the Department of Consumer affairs.
- Headquarters: Delhi
- It is established by the Bureau of Indian Standards Act, 2016 which came into effect on 12 October 2017.
- Ex-officio President of the BIS: The Minister in charge of the Ministry or Department having administrative control of the BIS.
- Members: 25 members drawn from Central or State Governments, industry, scientific and research institutions, and consumer organizations.
- Aim:
- It is responsible for the harmonious development of the activities of standardization.
- It examines marking and quality certification of goods and for matters connected therewith or incidental thereto.
The activities of BIS can be broadly grouped under the following heads:
- Standards formulation
- BIS formulates Indian Standards in line with the national priorities for various sectors that have been grouped under 14 Departments like Chemicals, Food and Agriculture, Civil, Electro-technical, Electronics & Information Technology, Mechanical Engineering, Management & Systems, Metallurgical Engineering etc.
- International activities
- BIS is the National Enquiry Point for World Trade Organisation – Technical Barriers to Trade (WTO-TBT) Matters.
- Product Certification
- BIS operates a Product Certification scheme for ensuring compliance to Indian Standards.
- Presence of BIS standard mark (popularly known as ISI mark) on a product indicates conformity to the relevant Indian Standard.
- Hallmarking
- Hallmarking of Gold Jewellery was started by BIS in April 2000 to provide third party assurance to consumers on the purity of gold jewellery or its fineness.
- Laboratory services
- To cater to the needs of testing for certification activity, BIS has established eight laboratories in the country to discharge the work related to testing of products for conformity assessment.
- Training services - National Institute of Training for Standardisation
- Consumer Affairs and Publicity
RAJYA SABHA SPLIT OVER BILL ON CSR FUNDS FOR MONUMENTS’ UPKEEP
There was a split in Rajya Sabha over a Bill on mandating 25% of corporate social responsibility (CSR) funds used for restoration, management and maintenance of ancient monuments and archaeological sites. CSR Funds?
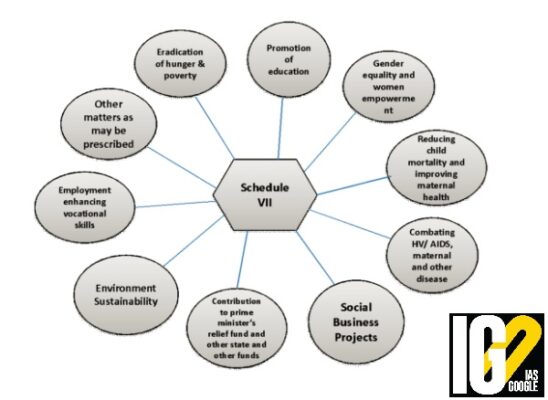
- Corporate Social Responsibility is a concept, whereby companies decide voluntarily to contribute to a better society and a cleaner environment.
- The companies integrate social and other useful concerns in their business operations for the betterment of the stakeholders.
- CSR motivates companies to contribute socially, economically and environmentally by engaging in acts like:
- Engaging members of local community
- By using Socially Responsible Investment (SRI)
- Develop an amicable relationship with employees and consumers
- Engage in actions which are protecting and sustaining the environment.
Need of CSR:
- CSR is responsible for generating goodwill to companies either directly or indirectly. These include
- Making employees more loyal and help companies retain them in the long run.
- Make companies more legitimate and help them in accessing a greater market share.
- Bolster the goodwill of companies amongst the general public and help in strengthening their brand value.
- Help in the stabilization of stock markets in both the short and long run.
Benefits of CSR: CSR helps companies and their shareholders to help in the development of a country’s economy on a macro-level.
- The Standard of living gets better with the introduction of more amenities.
- Companies engage in large-scale capacity building due to which the society becomes more prosperous and wealthier.
- Creates a more balanced world and healthier environmental systems.
CSR Laws in India:
- The Companies Act, 2013 made CSR a compulsory act.
- Under Section 135of the new act, CSR is compulsory for all companies- government or private or they meet any one or more of the following fiscal criterions:
- The net worth of the company should be Rupees 500 crores or more.
- The annual turnover of the company should be Rupees 1000 crores or more.
- Annual net profits of the company should be at least Rupees 5 crores.
List of Permitted Activities under the CSR is included in Schedule VII of the Companies Act, 2013 Features of CSR Laws:
- Money utilized for CSR purposes are to be included in the annual profit-loss report released by the company.
- The CSR rules will include subsidiary companies, holdings and other foreign corporate organizations, involved in business activities in India.
GIVE IMPETUS TO SET UP FORTIFIED RICE MANUFACTURING PLANTS IN PADDY PROCURING DISTRICTS OF MAHARASHTRA: GOVT
Recently, centre asked the rice manufacturing plants in Maharashtra to give impetus to set up fortified rice manufacturing plants. Suggestions made by the Centre to state:
- Improve the infrastructure at the procurement centres.
- Interact with the farmers encouraging them to avail the benefits of various schemes of the Centre.
- Promote diversification of crops towards corn to encourage grain-based distilleries for ethanol production.
- Emphasized the strengthening of solvent extraction plants to manufacture rice bran oil in the purchasing areas.
- Emphasised to give impetus on setting up fortified rice manufacturing plants especially in and around paddy procuring districts.
- It has set out a plan for issuing fortified rice through public distribution system (PDS) in future.
Food Fortification
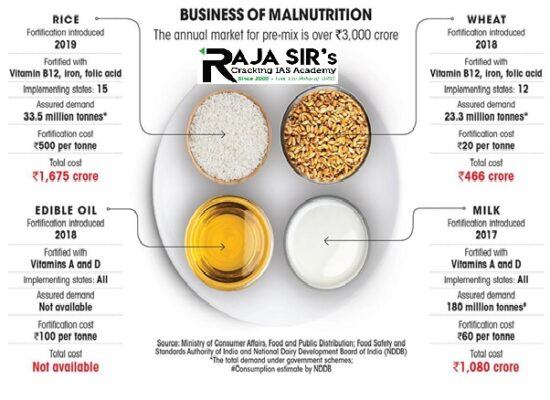
- Food fortification is defined as the practice of adding vitamins and minerals to increase their nutritional value.
- It is a proven, safe and cost-effective strategy for improving diets and for the prevention and control of micronutrient deficiencies.
- It is done by the addition of key vitamins and minerals such as iron, iodine, zinc, vitamins A and D to staple food items such as rice, wheat, oil, milk, and salt, during the processing.
- The addition of the vital nutrients is done to staple food items so that it can reach a larger population.
Need of food fortification:
- 70% of people in India do not consume enough micronutrients such as vitamins and minerals.
- 70 % of pre-school children suffer from anaemia caused by Iron Deficiency and 57 percent of preschool children have sub–clinical Vitamin A deficiency.
- Neural Tube Defects (NTDs)are the most common congenital malformation with an incidence that varies between 0.5-8/1000 births.
- Malnutrition is the primary reason behind 69 % of deaths of children below the age of five in India.
- It is estimated that 50-70% of these birth defects are preventable.
- One of the major causes is deficiency of Folic Acid.
- Deficiency of micronutrients or micronutrient malnutrition, also known as “hidden hunger”, is a serious health risk.
Advantages of Food Fortification
- The nutrients are added to staple foods that are widely consumed reach a large section of people.
- Fortification is a safe method of improving nutrition among people.
- The addition of micronutrients to food does not pose a health risk to people.
- The quantity added is so small and so well regulated as per prescribed standards that likelihood of an overdose of nutrients is unlikely.
- It does not require any changes in food habits and patterns of people.
- It is a socio-culturally acceptable way to deliver nutrients to people.
- It does not alter the characteristics of the food—the taste, the feel, the look.
- It can be implemented quickly as well as show results in improvement of health in a relatively short period of time.
- This method is cost-effective especially if advantage is taken of the existing technology and delivery platforms.
- Fortified foods will maintain body stores of nutrients more efficiently and more effectively than other supplements.
Disadvantages of Food Fortification
- They are not a substitute for a good quality diet that supplies adequate amounts of energy, protein, essential fats and other food constituents required for optimal health.
- It might not benefit infants as a child will get nutrition only if the lactating mother will be healthy and consumes adequate nutrition.
- Restricted access to fortified foods in the open markets due to low purchasing power and an underdeveloped distribution channel.
- It is not a long-term solution to malnutrition.
- For long term sustainability, dietary diversity is the key to address micronutrient malnutrition.
- It can have detrimental effects as excess dosages of vitamins and minerals in some cases can have harmful effects.
SRI LANKA’S MALAIYAHA TAMILS LIVING IN INHUMANE, DEGRADING CONDITIONS: U.N. EXPERT
According to UN, Sri Lanka’s Malaiyaha Tamil workers are living in inhumane and degrading conditions.
- Malaiyaha Tamils–They were brought from India to work in the plantation sector.
- They continue to face multiple forms of discrimination based on their origin.
What is the Issue?
- The Malaiyaha Tamil communityhas been historically neglected and marginalised.
- Roughly 1.5 lakh people from the community are engaged in direct labour in the estates, and most of them are women.
- Their daily wage is about ₹373 for plucking 18-22 kgs tea leaves every day.
- Up to 10 people live in a 10x12 space with poor sanitation facilities.
- India has committed to building 14,000 houses in Sri Lanka.
India and Sri Lanka Relations:

- India and Sri Lanka have a legacy of intellectual, cultural, religious and linguistic interaction.
Commercial Relations
- The entry into force of the India-Sri Lanka Free Trade Agreement (ISFTA) contributed towards the expansion of trade between the two countries.
- Sri Lanka remains among the largest trade partners of India in the SAARC.
- In 2020, India was Sri Lanka’s 2nd largest trading partner with the bilateral merchandise trade amounting to about USD $ 3.6 billion.
- India is one of the largest contributors to Foreign Direct Investment in Sri Lanka.
- FDI from India amounted to about US$ 1.7 billion during the period 2005 to 2019.
Development Cooperation
- Grant projects cut across sectors such as education, health, livelihood, housing, industrial development.
- The Indian Housing Project, aims to build 50,000 houses in war affected areas and estate workers in the plantation areas is a flagship grant project in Sri Lanka.
- The country-wide 1990 Emergency Ambulance Service is another flagship project.
India-Sri Lanka Foundation
- The India-Sri Lanka Foundation was set up in December 1998 as an intergovernmental initiative.
- Aim: To enhance scientific, technical, educational and cultural cooperation through civil society exchanges and enhancing contact between the younger generations of the two countries.
Tourism:
- Government of India formally launched the e-Tourist Visa scheme for Sri Lankan tourists on in 2015.
- In 2019, Sri Lanka included India in the free visa on arrival scheme.
Human resource development
- India now offers about 710 scholarship slots annually to Sri Lankan students.
- Indian institutes under ‘Study in India’ Program provide technical expertise across a diverse range of courses.
LONGEST IN-COUNTRY MIGRATION ROUTE OF LESSER FLORICAN FROM RAJASTHAN TRACKED
Recently, the longest in-country migration route of lesser floricans has been tracked for the first time from Rajasthan to Maharashtra’s Ahmednagar district. Highlights of the study:
- The telemetry exercise was undertaken in the Shokaliya landscape of Ajmer district to trace the journey of lesser floricans from their breeding grounds to their places of origin.
- The scientific experiment has succeeded in locating a bird which travelled a distance of 1,000 km after breeding during the monsoon.
Lesser Florican

- Lesser florican is a small and slender bird species belonging to the bustard group.
- It comes from the taxonomic family of bustards, the Otididae.
- It is the only member of its genus,
Physical Features:
- Male is striking: Black with pale wings and a filamentous crest.
- The female is light brown but her size and shape set her apart from other similar species.
Distribution
- Lesser Floricans are observed in Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat.
- The population is concentrated in the north-west of India.
Habitat And Ecology
- They inhabit grasslands and open fields, particularly un-grazed areas with grass ~1 metre high.
- It occurs in scattered bushes, shrub, and in agricultural fields of millet, cotton, and some cereal crops.
Breeding
- They have a lekking mating system, where males perform unique aerial displays.
- A lek is an aggregation of male animals gathered to engage in competitive displays and courtship rituals, known as lekking.
- A lesser florican can jump up to 2-3 metres while performing its courtship display.
- They have separate breeding and wintering sites.
- Rainfall and land-use is intrinsically linked to the sprightly florican’s breeding habits.
- Sufficient grass cover is particularly important during the breeding season.
- Diet: They are omnivores, feeding on insects, frogs, small lizards, leaves, crop shoots, herbs and berries.
- Threat:
- Habitat destruction caused by natural and man-made reasons.
- Changing agricultural patterns is a very prominent reason
- Human Intervention
- Conservation status:
- IUCN Red List: Endangered
- Its population has been identified as “decreasing”.
MAHAPARINIRVAN DIWAS WAS CELEBRATED BY PAYING TRIBUTE TO DR. BR AMBEDKAR
Recently, India observed December 6 as Mahaparinirvan Divas to mark the death anniversary of Dr. Bhimrao Ramji Ambedkar. B.R. Ambedkar

- He was an Indian jurist, economist, and social reformer who fought economic and social discrimination against the untouchables (now Dalits) in India's Hindu society.
- Born on: 14 April 1891 in Mhow, Madhya Pradesh.
- In 1955, Ambedkar converted to Buddhism, together with about 200,000 fellow Dalits, at a ceremony in Nagpur.
- The credit of giving place to "Ashok Chakra" in the Indian Tricolour also goes to Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar. Although the National flag was designed by Pingali Venkayya.
- Died on:6th December 1956 in Delhi
- Academic Achievement:
- He was the first Indian to get a Doctorate (Ph.D.) degree in Economics from abroad.
- He is the only Indian whose statue is attached to Karl Marx in the London Museum.
- He was a master in 64 subjects.
- He knew 9 languages like Hindi, Pali, Sanskrit, English, French, German, Marathi, Persian, and Gujarati.
- He studied at universities in the US, Britain, and Germany. After obtaining a degree in economics and political science from Bombay University.
- Political Contribution:
- In 1936, Ambedkar wrote his magnum opus ‘Annihilation of Caste’, a fiery critique of the caste system.
- As a law minister, he took a leading part in framing the Constitution. He also played a critical role in forming the Reserve Bank of India.
- He became the chairman of the committee for drafting the constitution
AN INNOVATION THAT CAN BETTER PROTECT POWER GRIDS
Researchers from Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Kanpur have come up with an innovation to protect power grids. Need of new technology:
- Power grids need protection from sudden surges in the current (fault current).
- Surge in current can arise due to short-circuits, sudden overdrawing of power or excess power generated due to a falling demand.
- These surges cause heating of the wires and melting and fire accidents.
- Earlier this used to be controlled by using circuit breakers, which would cut off the current in the event of a surge.
- These suffered from the limitation that if the response time to the current surge was too large, they would fail to be effective.
- Also, once the circuit was broken to avert the accident, the switch had to be manually turned on once again, and this could lead to longer power cuts.
Superconducting fault current limiters (SFCL):

- This device uses a superconductor, which allows a dissipation less passage of current under normal circumstances.
- However, if the current flowing through it increases beyond a threshold value, as during a fault, its resistance increases sharply.
Features:
- The operation of a SFCL is very rapid and automatic.
- Once the fault current reduces and the current flow returns to below the threshold value, the resistance of the SFCL also automatically goes down to zero.
- It is cost effective compared to the imported counterparts.
- It can operate at higher currents.
Significance:
- It shields the grid from large current surges and consequent fire accidents.
- It can also sensewhen the current surges will happen and warn the system about it.
- This can help the detection of a fault situation even while it is developing
Superconductors:
- Superconductivity is a set of physical properties observed in certain materials where electrical resistance is near zero.
- Superconductivity is a phenomenon which can only be explained by quantum mechanics.
Characteristics:
- It has a characteristic critical temperature below which the resistance drops abruptly to zero.
- An electric current through a loop of superconducting wire can persist indefinitely with no power source due to zero resistance.
- Superconducting magnets are some of the most powerful electromagnets
Applications:
- In mass spectrometers, the beam-steering magnets used in particle accelerators and plasma confining magnets in some tokamaks.
- For magnetic separation, where weakly magnetic particles are extracted from a background of less or non-magnetic particles, as in the pigment industries.
- In large wind turbines to overcome the restrictions imposed by high electrical currents.
- Earlier, superconductors were used to build experimental digital computers using cryotron switches.
- More recently, superconductors have been used to make digital circuits based on rapid single flux quantum technology and RF and microwave filters for mobile phone base stations.
| LANDSLIDE EARLY WARNING SYSTEM – LEWS |
|
| PRESIDENT’s STANDARD |
|
| SEMERU VOLCANO | Recently, the Semeru volcano on the tallest mountain on Java Island erupted, spewing towers of ash and hot clouds.
Mount Semeru:
|
| SUMMARY EXECUTION |
|
| EXERCISE EKUVERIN |
|









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies