- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
NOVEMBER 4, 2025
National Geo-Spatial Platform
- The Survey of India (SoI) signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with C.E. Info Systems Pvt. Ltd. to develop a state-of-the-art National Geo-Spatial Platform.
|
Survey of India (SoI), established in 1767, is India’s oldest mapping agency, responsible for conducting foundational surveys and generating essential geospatial data for the country. |
- The National Geo-Platform will serve as a unified, scalable system to standardise and share accurate geospatial datasets among stakeholders.
- Objective: Promote data interoperability and collaboration to enhance governance, research, industry, and citizen-centric applications nationwide.
- Nodal Agency: The Department of Science & Technology (DST) acts as the main department, while the Survey of India (SoI) remains the primary data agency.
- Key Components: Includes a Geospatial Data Integration and Dissemination System, an Integrated Geospatial Application Interface (IGAI), and a Spatial Data Registry (SDR) for metadata management.
- Significance: The initiative strengthens India’s National Geospatial Ecosystem and advances the vision of the National Geospatial Policy, 2022.
|
National Geospatial Policy, 2022
|
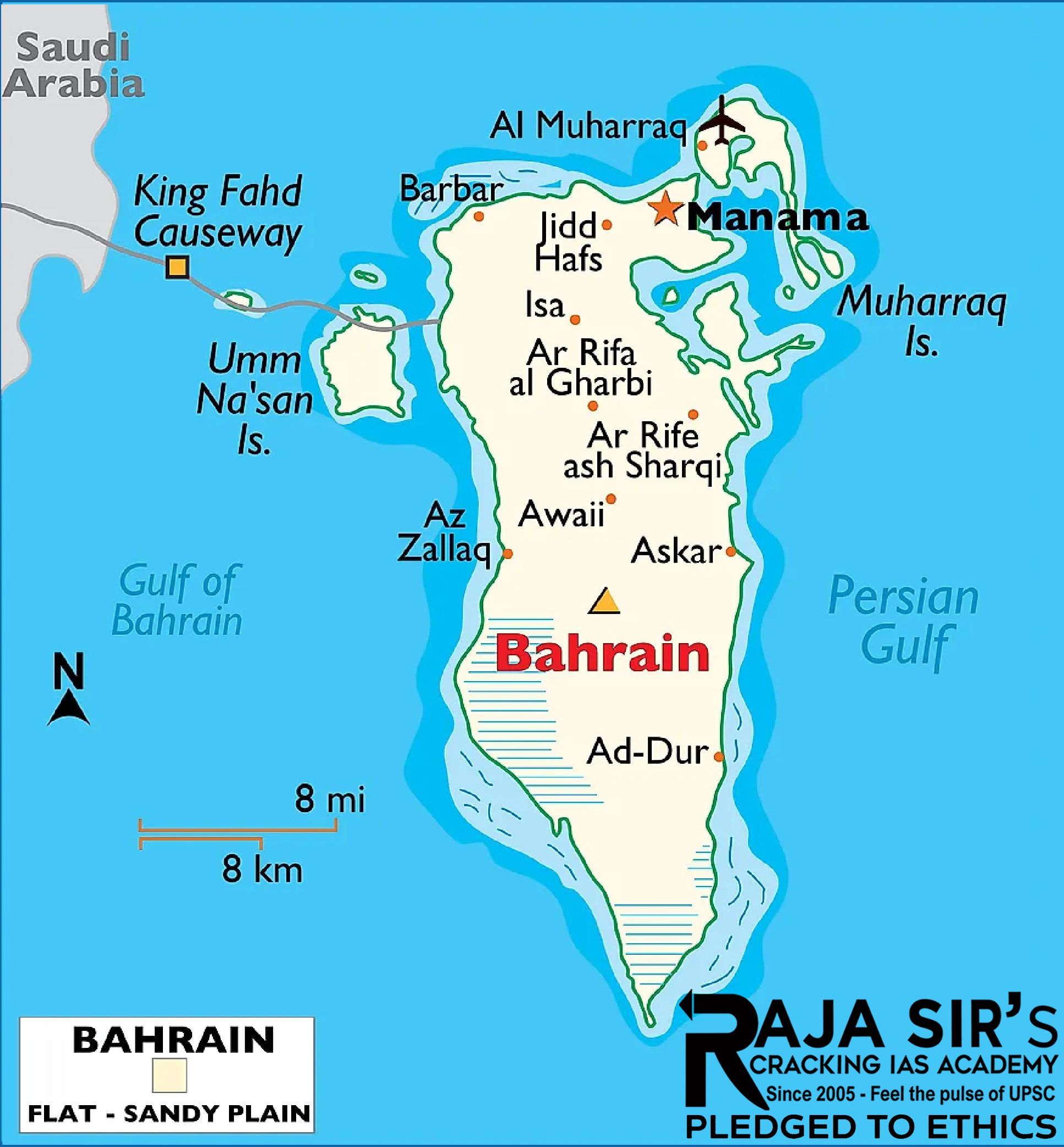
Bahrain (Capital: Manama)
 India and Bahrain hold talks on boosting defense and trade ties.
India and Bahrain hold talks on boosting defense and trade ties.
Political Features
- Bahrain is the third-smallest nation in Asia.
- Location: Lies in West Asia, in the Persian Gulf.
- Border: It is an archipelago of islands and has no land borders with other countries.
- Neighbouring Water Bodies: Persian Gulf.
Geographical Features
- Major physical region: Most of Bahrain is a desert with low-lying rocky and sandy plains.
- Highest point: Jabal ad Dukham.
- Umm er Radhuma- Dammam Aquifer System extends over Bahrain along with Qatar and Saudi Arabia.
Maldives Becomes First to Impose Generational Tobacco Ban
- Maldives became the world’s first country to enforce a nationwide generational tobacco ban under the global Tobacco Endgame framework.
- Ban Scope: The law applies to everyone born on or after January 1, 2007, covering all forms of tobacco for both residents and tourists.
- E-Cigarette Ban: It has also fully banned the import, sale, possession, and use of e-cigarettes and vaping products for all age groups.
- Policy Framework: The initiative is part of the Tobacco-Free Generation (TFG) model under the global Tobacco Endgame movement.
- Global Alignment: The policy aligns with the World Health Organization Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC).
|
Tobacco Endgame Movement
|
World Health Organization Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC)
- The WHO FCTC is a legally binding, evidence-based global treaty adopted to address the spread of the tobacco epidemic.
- Adoption: Adopted in 2003 and effective from 2005, it was WHO’s first international health treaty; India ratified it in 2004.
- Objective: To protect present and future generations from the health, social, environmental, and economic harms of tobacco.
- Supplementary Protocol: The 2012 Protocol to Eliminate Illicit Trade in Tobacco Products combats smuggling through global tracking and tracing mechanisms.
Key Provisions of the WHO FCTC
- Demand Reduction: Higher taxes and pricing policies (Article 6), large health warnings (Article 11), and a total ban on tobacco advertising and promotion (Article 13).
- Second-hand Smoke: Complete protection from second-hand smoke in all indoor public areas, workplaces, and public transport (Article 8).
- Trade Regulation: Eliminate illicit tobacco trade (Article 15) and prohibit tobacco sales to or by minors (Article 16).
- Policy Safeguards: Protect public health policies from tobacco industry influence (Article 5.3) and promote public awareness on tobacco harms (Article 12).
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) released The State of Food and Agriculture (SOFA) 2025 Report
SOFA 2025 provides the most comprehensive analysis of how human-driven land degradation impacts agricultural productivity, food security and ecosystem resilience.
Key Highlights of Report
- Land Degradation is defined as a long-term decline in the land’s ability to deliver essential ecosystem functions and services.
- It is driven by natural causes (soil erosion and salinization) and anthropogenic causes (deforestation, overgrazing, unsustainable cropping and irrigation practices etc.)
- Impact of Land Degradation
- Yield Loss: For about 1.7 billion people, crop yields are 10% lower because of human-induced degradation.
- Asian countries are the most affected - both because of their accumulated degradation debt and their high population densities.
- Productivity Loss: Total factor productivity growth, which reflects technological advancement and efficiency improvements, has declined since the 2000s, particularly in the Global South.
- Convergence with Food Security: Globally, 47 million children under five years of age suffer from stunting live in hotspots where stunting overlaps with significant yield losses.
- Ecosystem Impact: Degradation affects all agricultural systems, undermining livestock production in rangelands and – through forest loss driven by agricultural expansion – disrupting climate patterns and biodiversity.
|
Policy Options for Sustainable Land Use
|
International Migration Outlook 2025
Recently, the International Migration Outlook 2025 report has been released by the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
Major Findings
- In 2023, 225 000 Indian citizens acquired the nationality of an OECD country.
- China and India continued to account for a third of all international students in OECD countries.
India’s $30 Trillion Economy Projection
- According to the Commerce and Industry Minister, India is projected to become a $30 trillion economy within the next 20-25 years.
- India’s GDP for FY 2024 stood at $3.9 trillion, while the U.S. GDP was $29.2 trillion, roughly eight times.
- The size of an economy is measured by its Nominal Gross Domestic Product (GDP), the total market value of goods and services produced in a year, expressed in U.S. dollars for global comparison.
- Two key factors determine this figure:
- Nominal GDP growth in rupee terms (domestic economic expansion).
- Rupee-dollar exchange rate, which converts domestic value into global terms.
Historical Growth Patterns of India
- Over the past 25 years (2000-2024), India’s nominal GDP grew at a CAGR of 11.9%, and the rupee depreciated at a CAGR of 2.7%.
- Based on this trend, India could reach $30 trillion by 2048 within 25 years, consistent with the ministry’s forecast.
- However, in the past 11 years (2014-2025), Nominal GDP growth slowed to 10.3%, and rupee depreciation quickened to 3.1%.
- Under these conditions, India may reach $30 trillion only by 2055, nearly a decade later.
Factors Influencing the Projection
- Exchange Rate Volatility: A stronger rupee accelerates progress toward the $30 trillion mark while sustained depreciation delays it.
- Growth Moderation: As economies mature, growth rates tend to moderate. India, however, remains at a stage where higher growth is still feasible and necessary.
- Structural Reforms: It will be crucial to continue focusing on manufacturing, infrastructure, digital transformation, and ease of doing business.
- Inflation and Fiscal Health: Maintaining macroeconomic stability and low inflation is essential to sustain long-term growth.
- As the analysis highlights, each decade’s performance matters; even minor shifts in growth trajectory can lead to large divergences over time.
State Human Rights Commission (SHRC)
Chandigarh High Court reminds Punjab State Human Rights Commission (SHRC) that it can only recommend, not issue directions like court.
SHRC
- Statutory body formed under the Protection of Human Rights Act, 1993.
- Inquires into human rights violations under the State List and Concurrent List.
- Its recommendations are advisory, not legally binding.
- Composition: A Chairperson (retired Chief Justice or Judge of a High Court) and two members.
- Appointment of Chairpersons and Members: Appointed by the Governor on the recommendation of a committee.
- Members can be removed by the President of India.
Emerging Science & Technology Innovation Conclave
- PM Narendra Modi inaugurated the first Emerging Science, Technology and Innovation Conclave (ESTIC) 2025 at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi.
- The PM also launched the ₹1 lakh crore Research, Development, and Innovation (RDI) Scheme Fund.
ESTIC 2025
- The ESTIC has been established as an annual flagship government event in science and technology.
- Objective: It aims to foster collaboration among researchers, industry leaders, and young innovators to strengthen India’s research and innovation ecosystem.
- Participation: Over 3,000 delegates, including Nobel Laureates, eminent scientists, global policymakers, and representatives from academia, industry, and government, are participating.
- Focus Areas: The conclave emphasises 11 key areas, including Artificial Intelligence (AI), Quantum Science and Technology, Space Technologies, Bio-Manufacturing, and Semiconductor Design.
- Innovation Milestones: The PM highlighted that India’s R&D spending has doubled, and patent registrations have increased 17-fold over the past decade.
RDI Scheme Fund
- The RDI Scheme Fund is a program launched by the Indian government to encourage private sector investment in emerging and strategic sectors through R&D financing.
- It offers long-term low or zero-interest loans, startup equity investments, and a Deep-Tech Fund of Funds for advanced technology projects.
- Key Feature: It functions through a Special Purpose Fund (SPF) managed by the Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF), which directs resources to secondary fund managers for distribution.
Enshittification
- The digital spaces that once symbolised freedom, creativity, and connectivity are increasingly seen as exploitative ecosystems prioritising profit over user experience.
|
Understanding Enshittification
|
Symptoms of Enshittification
- Ad Saturation: Excessive unskippable ads and paywalls replacing once-free experiences. E.g. YouTube Premium and Netflix ad tiers (2024).
- Algorithmic Manipulation: Prioritising viral or paid content over authentic connections. E.g. Instagram’s algorithm now favours reels over user posts.
- Self-Preferencing: Tech giants promote their own content or products over competitors. E.g., Amazon’s sponsored results dominate search listings (FTC case, 2024).
- Data Exploitation: User data repurposed for micro-targeted advertising without transparency. E.g. Cambridge Analytica scandal (2018) exposed large-scale political profiling.
- Loss of Authenticity: Paid verifications and bots distort discourse and trust. E.g., X (Twitter) verification is now purchasable by anyone, including fake accounts.
Generational ban on tobacco
Maldives becomes thde first country to impose a generational ban on tobacco.
- Generational Tobacco Ban, or Lifetime Tobacco Ban, refers to a policy that permanently prohibits the sale of cigarettes or other tobacco products to anyone born after a specified date—meaning they can never legally purchase tobacco at any age.
- Other measures used for tobacco control: monitoring use, warning about harms, banning advertising, raising taxes, stopping illicit trade, and regulating new nicotine products.
Status of Tobacco consumption:
- Status: Around 80% of the world''s 1.3 billion tobacco users live in low- and middle-income countries.
- Forms of Tobacco Use includes cigarette smoking, waterpipe tobacco, cigars, heated tobacco, roll-your-own tobacco, pipe tobacco,smokeless tobacco products,etc.
- Steps Taken:
- WHO Member States adopted the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) in 2003. Currently 183 countries are Parties to this treaty.
Typhoon
Typhoon Kalmaegi made landfall in the central Philippines.
- Typhoons are essentially tropical cyclones that originate over Western Pacific Ocean.
- A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm that begins over tropical oceans, and they can vary in speed, size, and intensity.
- Favourable conditions for tropical cyclones include warm ocean waters, atmosphere cooling fast with height, relatively moist air, pre-existing near-surface disturbance etc.
- Other names for Tropical Cyclones include:
- Hurricane in Atlantic Ocean and Northeast and South Pacific Ocean.
- Cyclones in the Indian Ocean,
- Willy-willies in the Western Australia.
Alternative Investment Fund (AIF)
Real Estate is now the single largest recipient of AIF capital in India.
- AIF means any fund established or incorporated in India which is a privately pooled investment vehicle which collects funds from sophisticated investors, whether Indian or foreign, for investing it in accordance with a defined investment policy for the benefit of its investors.
- It can be set up in the form of a trust or a company or a limited liability partnership or a body corporate
- Regulated by: Securities and Exchange Board of India
- Types:
- Category I - Investments in Startups & Social Ventures.
- E.g: Venture Capital Funds (VCFs), SME Funds, Social Venture Funds, Infrastructure Funds
- Category II - which do not fall in Category I and III and which do not undertake leverage or borrowing other than to meet day-to-day operational requirements
- E.g: Real Estate, Private Equity Funds, funds for distressed assets
- Category III - employ diverse or complex trading strategies and may employ leverage including through investment in listed or unlisted derivatives
- E.g: Hedge Funds, Private Investment in Public Equity (PIPE) Funds
Note: AIF does not include funds covered under the SEBI (Mutual Funds) Regulations, 1996, SEBI (Collective Investment Schemes) Regulations, 1999 or any other regulations of the Board to regulate fund management activities.
3I/ATLAS
Comet 3I/ATLAS has been found to contain water, marking a significant discovery in understanding cometary evolution.
- Comet 3I/ATLAS is the third known object from outside our solar system to be discovered passing through our celestial neighborhood.
- Other two are 1I/ʻOumuamua seen in 2017 and 2I/Borisov seen in 2019.
- Astronomers have categorized this object as interstellar because of the hyperbolic shape of its orbital path. (It does not follow a closed orbital path about the Sun.)
- It was first spotted by NASA-funded Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS) telescope in Río Hurtado, Chile.
Research, Development, and Innovation (RDI) Scheme gets approval from Cabinet
The scheme aims to strengthen India’s capabilities in strategic technologies and promote technological self-reliance, aligning with the nation’s long-term innovation and Atmanirbhar Bharat vision.
Funding Mechanism
- Corpus: ₹1 lakh crore / Rs. One lakh Crore
- Two-tiered funding mechanism.
- Level 1 (Custodian): Special Purpose Fund (SPF) established within the ANRF.
- Level 2 (Disbursement): Funds allocated to a variety of Second-Level Fund Managers
- Mode of Funding: Long-term concessional loans (at low or nil interest rates), Equity infusion (especially for startups), Contributions to Deep-Tech Fund of Funds (FoF)
Key Objectives
- Encourage private sector to scale up RDI in sunrise domains and sectors relevant for economic security, strategic purpose, and self-reliance
- Finance transformative projects at higher Technology Readiness Levels
- Support acquisition of critical technologies or those of high strategic importance
- Facilitate establishment of a dedicated Deep-Tech Fund of Funds
Targeted Sectors:
- Sunrise Sectors: Energy Security, Deep Technology(includes quantum computing, robotics & space), Artificial Intelligence, Biotechnology & Health, Digital Economy.
- Strategic Sectors: Technologies whose indigenization is necessary for strategic reasons, economic security, or Atmanirbharta.
- Public Sector: Any other sector or technology where it is deemed necessary in public interest.
Governance and Implementation Frameworks
- Nodal Department: Department of Science and Technology (DST).
- Strategic Direction: Provided by the Governing Board of ANRF chaired by the Prime Minister.
- Approval of Scheme Guidelines: Handled by the Executive Council (EC) of ANRF
- Changes in Schemes: Managed by an Empowered Group of Secretaries (EGoS) led by the Cabinet Secretary.
Vikram-3201 Microprocessor and India’s Semiconductor Ecosystem
- Debates have emerged over the selection of Assam and Gujarat for new semiconductor fabrication facilities following the launch of the Vikram 3201 microprocessor.
Vikram 3201
- Vikram 3201 is India’s first fully indigenous 32-bit, space-grade microprocessor built to operate in extreme environmental conditions.
- Development: It is designed by ISRO’s Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC) and fabricated at the Semiconductor Laboratory (SCL), Chandigarh.
- Purpose: Primarily used in avionics, navigation, and control systems of launch vehicles and satellites.
- Architecture: It features a general-purpose 32-bit architecture with 152 custom instructions and supports 64-bit floating-point operations. It operates at a frequency of 100 MHz.
- Advancement: Vikram 3201 represents an advancement over the 16-bit Vikram 1601 microprocessor, which has been deployed in ISRO’s launch vehicles since 2009.
- Durability: The processor can withstand extreme temperatures ranging from –55°C to +125°C, is radiation-hardened, and remains resilient under intense vibration and mechanical stress.
Semiconductor Landscape in India
- Market Size: India’s semiconductor market was valued at $52 billion in 2024-25 and is projected to exceed $100 billion by 2030.
- Project Status: Ten semiconductor projects worth ₹1.6 lakh crore have been approved under the India Semiconductor Mission (ISM) across six states.
- Import Dependence: India imports nearly 90-95% of its semiconductor chips, primarily from China, Taiwan, South Korea, and the United States.
- Global Dominance: Taiwan’s TSMC produces over 90% of advanced chips, and East Asia accounts for about three-fourths of global manufacturing capacity.
- Japan and the Netherlands remain leaders in semiconductor equipment production.
- Design Strength: Around 20% of semiconductor design talent is based in India, supported by major chip design and R&D centres of leading global firms.
- Strategic Focus: India prioritises manufacturing mature-node chips (28 nm+) used in automobiles, equipment, and power devices, instead of advanced-node chips (3–5 nm) for high-end computing.
Government Initiatives
- Semiconductor Integrated Circuits Layout-Design Act, 2000: Protects intellectual property rights for semiconductor circuit layouts and promotes innovation in chip design.
- Semicon India Programme (SIP): Allocates ₹76,000 crore with up to 50% fiscal support to attract investment in semiconductor and display manufacturing.
- India Semiconductor Mission (ISM): Serves as the nodal agency under MeitY to implement semiconductor schemes, assess proposals, and coordinate with industry stakeholders.
- Modified Scheme for Semiconductor Fabs: Offers 50% fiscal support for establishing silicon-based fabrication units targeting technologies of 28 nm or below.
- Modified Scheme for Compound Semiconductors: Provides 50% capital support for setting up facilities for compound semiconductors, silicon photonics, sensors, and ATMP/OSAT units.
- Design Linked Incentive (DLI) Scheme: Grants up to ₹15 crore per applicant and access to advanced design infrastructure for domestic semiconductor startups.
- SPECS Scheme (2020): Provides a 25% incentive on capital expenditure for producing electronic components and sub-assemblies.
- Chips to Startup (C2S) Programme: Aims to train 85,000 engineers in Very Large-Scale Integration (VLSI) and embedded design to strengthen India’s semiconductor workforce.
Typhoid Conjugate Vaccine
Bangladesh became the eighth country in the world to introduce the Typhoid Conjugate Vaccine (TCV).
- It is a single-dose, injectable vaccine that protects against typhoid fever by triggering the body to produce antibodies against the Salmonella Typhi bacterium.
- Eg- Typbar TCV (manufactured by Bharat Biotech).
Typhoid
- Caused by: Bacterium Salmonella Typhi.
- Spread through: Contaminated food or water.
- Symptoms include: prolonged high fever, fatigue, headache, nausea, abdominal pain, and constipation or diarrhoea.
Magnetic Waves Explaining the Sun’s Super-hot Atmosphere
- A new study offers insights into the cause of the large temperature gap between the Sun’s outer atmosphere (corona) and its surface.
|
The Sun’s surface (photosphere) is about 10,000°F (5,500°C), while its corona reaches 2 million°F (1.1 million°C). |
- Scientists examined magnetic waves in the Sun’s corona using the Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope (DKIST) in Hawaii, the world’s most powerful ground-based solar telescope.
- Wave Discovery: They observed Alfvén waves forming twisting patterns in the coronal magnetic field, confirming their widespread presence in the Sun’s outer atmosphere.
- Energy Transfer: The researchers also detected tiny, periodic Doppler shifts indicating that these waves carry substantial energy, which heats the corona to extremely high temperatures.
- Significance: The discovery provides direct evidence that magnetic waves heat the corona and strengthen models used for predicting space weather.
|
Alfvén Waves
|
Hurricane Melissa
- Hurricane Melissa recently caused devastating damage and multiple deaths across the Caribbean, especially in Jamaica, Haiti, and Cuba.
- It formed over the Caribbean Sea as a tropical cyclone and strengthened into a Category 5 hurricane.
- The hurricane sustained maximum winds of 185 mph (298 km/h) and had a minimum central pressure of 892 millibars—one of the lowest ever recorded in the Atlantic basin.
- Melissa became the strongest hurricane to make landfall in Jamaica, surpassing the destructive Hurricane Gilbert of 1988.
- The name “Melissa” was proposed by the United States and approved by the World Meteorological Organisation (WMO) hurricane naming panel.
|
NITI Aayog’s Frontier Tech Hub Unveils “Reimagining Agriculture: A Roadmap for Frontier Technology Led Transformation”
The report highlights the structural barriers slowing agricultural transformation and shows how frontier technologies can directly address these gaps to drive higher productivity, resilience, and farmer incomes.
Barriers affecting Agricultural Transformation
- Data: Siloed data, no single-source of truth, lack of localized, high-quality Al-ready datasets
- Limited Phygital Approach: Limited internet access, inadequate physical infrastructure, field force and touchpoints to integrate with digital solutions
- Fragmentation: Limited coordination and siloed functioning across industry, academia, policymakers & regulatory bodies
- Capital: Gap in funding for high-risk, slow-scaling AgTech innovations, constrained credit access for farmers
Role of Frontier Technologies in Agricultural Transformation
Frontier technologies include seed technologies, vertical farming, digital twins, precision tools and smart sensors, agentic AI, predictive analytics, and advanced mechanisation aimed at boosting productivity, sustainability, and farmer incomes.
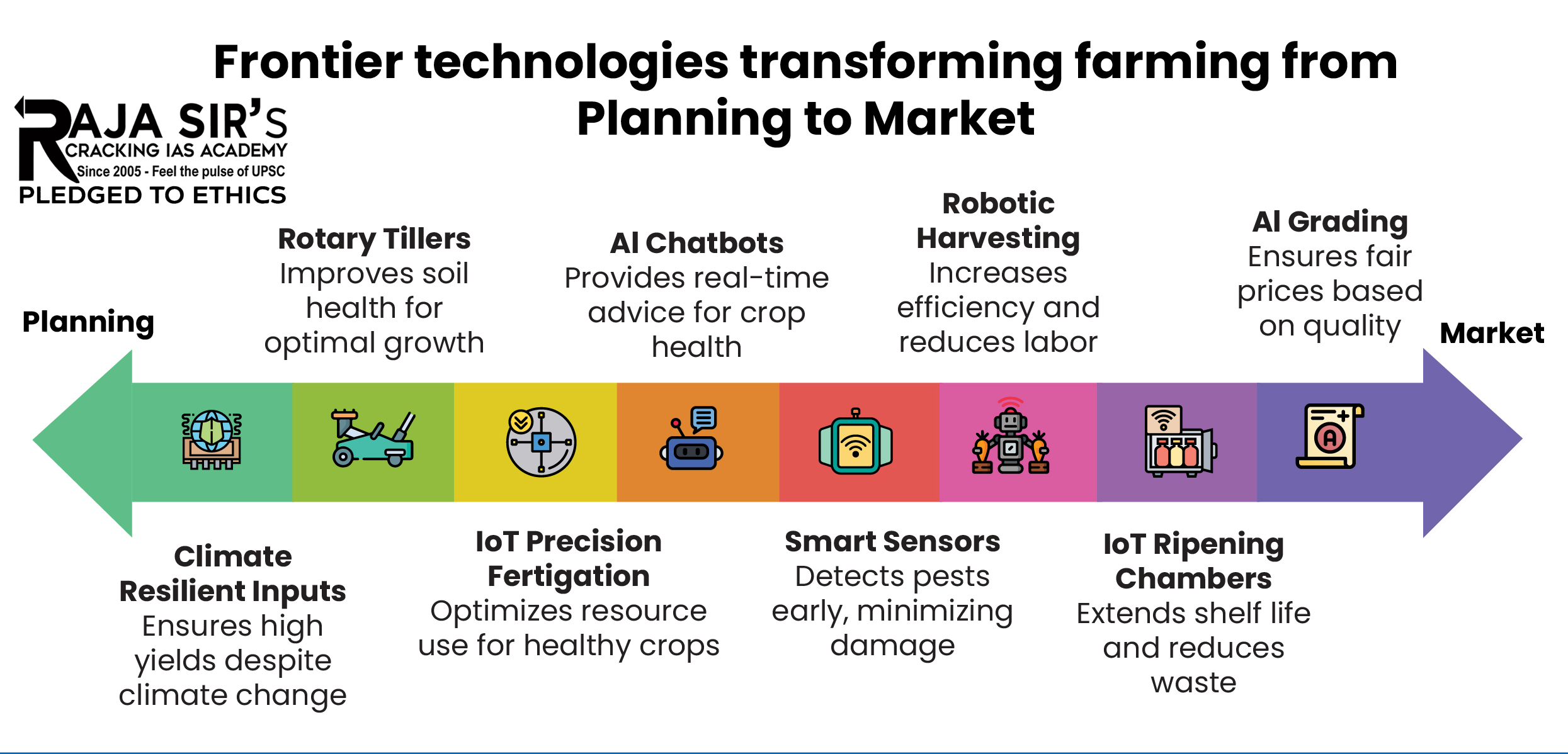
Path ahead for scaling up of frontier technologies
- A three-pillar framework for a Digital Agriculture Mission 2.0
- Enhance foundational systems to be frontier-tech ready: by 360-degree data ecosystem, digital enablement of the last-mile interventions and upgrading the AgriTech startup accelerator ecosystem.
- Reimagine Agri-Innovations & Agri-Talent Systems for Future-readiness: by globally competitive talent & innovation ecosystems, focusing on a shift to translational R&D, interdisciplinary industry-aligned talent and revamping the institutional architecture for innovation.
- Converge public-private efforts to accelerate agricultural transformation: by building instruments for public-private dialogue to align industry and government efforts for agile policy making.
Water Lettuce (Pistia stratiotes)
- Invasive aquatic species Water Lettuce (Pistia stratiotes) has overrun Lake Suchitlán in El Salvador, threatening local fisheries and livelihoods.
|
Lake Suchitlán is the largest artificial lake (135 sq. km) in El Salvador, created by the Cerrón Grande Hydroelectric Dam on the Lempa River. It is designated as a Ramsar site. |
Water Lettuce (Pistia stratiotes)
- Water lettuce, also called water or Nile cabbage, is a free-floating freshwater plant with leaves that resemble a head of lettuce.
- It is a popular ornamental plant but is also considered an invasive weed.
- Habitat Preference: It thrives in still or slow-moving freshwater environments (i.e., ponds, lakes, and reservoirs), mainly in tropical and subtropical regions.
- Physical Traits: The plant has soft green leaves with fine white hairs that trap air bubbles, and unbranched roots with a hair-like appearance.
- Invasive Nature: Its fast growth and mat formation block sunlight, deplete oxygen, and disrupt local aquatic biodiversity.
- Ecological Role: Despite being invasive, it provides temporary refuge for fish and helps suppress algal blooms by absorbing excess nutrients.
- Human Use: It is unsafe for human consumption due to high concentrations of calcium oxalate crystals that irritate mucous membranes.
- Phytoremediation: Its hyperaccumulation ability makes it useful for phytoremediation, wastewater treatment, and oil-spill cleanup.
- Conservation Status: IUCN: Least Concerned
Exercise Poorvi Prachand Prahar
- The Indian Armed Forces conducted Exercise Poorvi Prachand Prahar in Mechuka Valley, Arunachal Pradesh.
- Exercise Nature: Poorvi Prachand Prahar is a multi-domain tri-service military drill involving coordinated high-altitude combat operations.
- Objective: It aims to improve operational synergy, interoperability, and combat readiness for potential multi-front conflicts.
- Assets and Technology: The drill combines Special Forces, drones, precision-strike systems, and networked command centres for real-time coordination.
- Series Linkage: The exercise continues India’s progressive series of joint military drills, following ‘Bhala Prahar‘ (2023) and ‘Poorvi Prahar‘ (2024).
Ramnami Tribe
- PM Modi Honours Ramnami Tribe During Chhattisgarh Foundation Day.
- The Ramnami Samaj originated in the 19th-century Chhattisgarh as a peaceful resistance movement against the caste system, which barred lower-caste devotees from temple entry.
- Members are often called the “living embodiment of faith” as they tattoo ‘Ram’ on their bodies.
- For the Ramnamis, ‘Ramnam’ (chanting the name) is religion, and ‘Rambhakti’ (devotion) is action.
- They uphold gender equality and adorn themselves with ghungroos (ankle bells) and a peacock feather crown, which are significant in their devotional performances and Bhajans.
- The community’s attire, white garments inscribed with “Ram”, and their musical devotion are integral to Chhattisgarh’s folk heritage.
India’s Information Technology Industry is undergoing a transformation
The Indian IT industry is undergoing major transformation due to automation, shifting global trends, steepest workforce layoffs, and evolving skill needs.
Indian IT Industry
- Contributes about 12% to total services GVA and nearly 7% to India’s GDP, adding over $280 billion to the economy.
- Employs around 1% of the workforce, with nearly 6 million people working in the sector.
- Women form about 36% of the total workforce, reflecting growing gender inclusion.
- Industry has positioned India as a global hub for software services and digital innovation while providing upward mobility for youth, especially from smaller towns.
Transformations in the IT Industry
- Technology transformation: AI-driven automation is disrupting the sector by automating routine work like reporting, basic coding, and coordination.
- It is drastically improving developer productivity, and shifting the industry’s focus towards high-value, AI-driven digital transformation.
- Global Realignments: Restrictive U.S. immigration policies with hike in H-1B visa fees and tariff threats are prompting Indian IT firms to localise their overseas workforce.
- Outdated outsourcing model: Mass hiring and cost-based services are giving way to solution-driven demand powered by specialised expertise and AI fluency.
- Skill gap: Many professionals lack expertise in evolving fields of AI, cloud, and cybersecurity.
|
Way Forward
|
Mussels
Mussels reveal growing microplastic pollution in Greece’s seas.
- Mussels are bivalve mollusks characterized by a blue–black shell that lives attached to surfaces in marine environments.
- The molluscs include many familiar animals, including clams, snails, slugs, squid, tusk shells and chitons.
- These are filter-feeding organisms that absorb a range of contaminants into their tissue, including invisible microplastics.
- They are known for their efficient feeding, higher protein content compared to oysters.
- They have been used globally for decades as a barometer of marine pollution.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies