- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
OCTOBER 14, 2025
Experts Call for National Strategy on Alzheimer’s & Ageing Health
- Health experts have urged the need for a National Strategy on Ageing and Mental Health to address the rising burden of Alzheimer’s disease and dementia in India.
|
Key Recommendations from Experts
- National Dementia Strategy: Experts urged the government to adopt a comprehensive national plan integrating dementia care into India’s broader ageing and mental health policy.
- The plan should align with the WHO Global Action Plan on Dementia (2017-2025).
- Community-Level Screening: Incorporate cognitive health screening within Ayushman Arogya Mandirs (expanded Health and Wellness Centres).
- Care Platforms: Expand the use of memory clinics and telemedicine platforms like eSanjeevani.
- Infrastructure Support: To address the social and economic impact of dementia, strengthen caregiver support systems, long-term care infrastructure, and research on risk factors.
|
Recent Initiatives for Elderly Mental Health Care
|
Satark Nagrik Report Flags Gaps in RTI
- The Satark Nagrik Sangathan’s 2025 report highlights significant gaps in India’s Information Commissions as the Right to Information (RTI) Act, 2005, approaches its 20th anniversary.
|
Information Commissions of India
|
Key Findings of the Report
- Non-Functionality: Several Information Commissions are non-functional due to unfilled posts, with the CIC operating at minimal capacity and lacking a Chief Information Commissioner.
- Severe Backlogs: Over 2.4 lakh appeals and complaints remained pending across the country in 2024, with some commissions expected to take decades to clear their current caseloads.
- Transparency Deficits: Twenty of the twenty-nine commissions failed to publish their 2023–24 annual reports, despite the legal mandate of the RTI Act.
- Weak Enforcement: Penalties on Public Information Officers (PIOs) were applied in only about 2% of eligible cases, which weakens accountability and raises non-compliance.
RTI Act, 2005
- The RTI Act, 2005, grants citizens the right to access information from public authorities, promoting transparency, accountability, and integrity in governance.
- Constitutional Basis: The Act is rooted in Article 19(1)(a) of the Constitution, which guarantees the right to freedom of speech and expression.
- Nodal Agency: The Department of Personnel and Training (DoPT) under the Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions.
- Operational Framework: The Act mandates public authorities to appoint a PIO to provide information within 30 days.
- Applicants may initially appeal to the First Appellate Authority (FAA) in case of denial or delay, and if unresolved, they can submit a final appeal to the Information Commissions.
Govt Panel Proposes Reforms to Boost Nuclear Energy
- A panel under the Ministry of Power has proposed reforms to accelerate India’s nuclear programme & achieve the 100 GW capacity target by 2047, up from the current 8.88 GW.
Key Recommendations of the Panel
- Faster Approvals: The panel has called for reducing the average 11-12-year timeline from site approval to reactor commissioning through streamlined land acquisition and regulatory clearances.
- Site Optimisation: It is recommended to use existing nuclear sites and retired thermal power plant locations for upcoming projects.
- Fuel Security: The panel urged boosting domestic uranium mining, acquiring overseas uranium assets, and allowing private participation in uranium sourcing and fuel fabrication.
- It also advised maintaining a strategic fuel reserve sufficient for reactor lifespans of up to 60 years.
- Fuel Reprocessing: Supported continuation of spent fuel reprocessing, to be managed by a government entity, ensuring sustainability in the nuclear fuel cycle.
- Insurance Framework: Suggested restructuring the nuclear insurance pool to provide ₹15 billion coverage per incident per operator, replacing the existing annual liability cap across installations.
India-AI Impact Summit 2026
- The Government has announced applications for three flagship Global Impact Challenges under the upcoming India-AI Impact Summit 2026.
India-AI Impact Summit 2026
- The India-AI Impact Summit 2026 is a global platform to highlight the transformative role of Artificial Intelligence in fostering inclusive development and sustainability.
- It will be held in New Delhi by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology.
- Objective: Promote a global vision for ethical and inclusive AI and focus on achieving real-world impact through AI solutions.
- Guiding Sutras: The Summit is based on three principles — People for human dignity and inclusion, Planet for climate-resilient innovation, and Progress for equitable benefits.
- Significance: It is the first summit of its kind hosted by a Global South country, highlighting India’s leadership in AI governance.
Key Initiatives
- AI Pitch Fest (UDAAN): Showcases global AI startups and India’s Tier-2 and Tier-3 innovators.
- Global Impact Challenges: Includes AI for All to address global development issues, AI by HER to empower women-led innovation, and YUVAi to nurture youth-driven AI solutions for the public good.
- Symposium & Expo: Features a state-of-the-art AI research forum and an expo with over 300 exhibitors from more than 30 countries.
US Imposes 100% Additional Tariff on Chinese Imports
- US President Donald Trump announced a 100% additional tariff on Chinese imports effective November 1, 2025, as a countermeasure to China’s export controls on rare earth minerals.
- Tariff Scale: The decision raises cumulative tariffs on some Chinese goods to nearly 130%.
- Export Control: China recently increased export restrictions on five more rare earth elements, citing concerns over national security and the safeguarding of strategic resources.
- Beijing has also banned the export of several advanced refining and separation technologies
- Global Implication: These reciprocal actions intensify the US-China trade conflict, disrupting global supply chains and inflating the costs of critical minerals.
IUCN World Heritage Outlook Report
- The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) published its fourth edition of World Heritage Outlook at the World Conservation Congress in Abu Dhabi.
- First launched in 2014, the report assesses the conservation status of all Natural and Mixed UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
World Heritage Sites
- A World Heritage Site (WHS) is a location recognized by UNESCO under the 1972 World Heritage Convention for possessing “Outstanding Universal Value” for all of humanity.
- Global Count: As of 2025, there are 1,248 World Heritage Sites worldwide, including 44 in India (36 cultural, 7 natural, and 1 mixed).
- Governance: The UNESCO World Heritage Committee manages the listing process through multiple stages, starting with national Tentative Listing and concluding with final inscription after approval.
- Advisory Role: The IUCN serves as the official advisory body for natural and mixed sites to the UNESCO World Heritage Committee.
World Heritage Outlook Report
- The World Heritage Outlook is a periodic global assessment published every 3-5 years by the IUCN to evaluate the conservation prospects of Natural and Mixed WHS.
- Evaluation Criteria: Sites are evaluated based on three parameters: (a) the current condition of site values, (b) the severity of threats faced, and (c) the effectiveness of management.
- Rating System: Each site receives one of five ratings: (a) Good, (b) Good with Some Concerns, (c) Significant Concern, (d) Critical, or (e) Data Deficient.
- Purpose: It provides an evidence-based assessment of conservation progress and guides policy actions.
Key Findings of the World Heritage Outlook Report
- Declining Outlook: Sites rated ‘Good’ or ‘Good with Some Concerns’ fell from 62% (2020) to 57% (2025).
- Climate Threats: Climate change is now the most prevalent threat, affecting 43% of all-natural WHS.
- Invasive Species: Invasive Alien Species remain the second most common threat, affecting 30% of all assessed sites.
- Emerging Pathogens: Wildlife & plant diseases now threaten 9% of sites, compared to only 2% in 2020.
- Compounding Threats: Interlinked climate change, species invasion, and pathogen pressures are accelerating ecosystem degradation.
- Biodiversity Hotspots: Sites with rich biodiversity are facing disproportionately higher vulnerability.
- Protection Gaps: Only 50% of the assessed sites reported having adequate protection and management.
- Funding Risks: Around 15% of sites face severe financial shortages that weaken conservation outcomes.
- Positive Trends: 13 sites improved since 2020 due to targeted investment and community engagement.
India-Related Findings
- Sundarbans Decline: The Sundarbans National Park dropped from ‘Good with Some Concerns’ (2020) to ‘Significant Concern’ (2025) due to sea-level rise, increasing salinity, cyclones, & mangrove diseases.
- Persistent Concerns: Manas National Park and the Western Ghats remain under ‘Significant Concern’
- Positive Performer: Khangchendzonga National Park continues to be India’s only site rated as ‘Good,’
- Moderate Outlook: Great Himalayan, Kaziranga, Keoladeo, and Nanda Devi–Valley of Flowers are rated ‘Good with Some Concerns.’
- Cascading Threats: Glacial retreat and invasive alien species in Himalayan sites threaten hydrology and biodiversity in the Ganga River basin.
Green Sea Turtle (Chelonia mydas)
The IUCN has upgraded the conservation status of the Green Sea Turtle (Chelonia mydas) from Endangered to Least Concern, reflecting progress in global conservation efforts.
- Population Recovery: Global populations have risen by almost 28% since the 1970s, despite ongoing threats to some regional subpopulations.
- The Green Sea Turtle (Chelonia mydas) is the largest hard-shelled sea turtle and the only sea turtle with a strictly herbivorous adult diet.
- It gets its name from the green hue of its body fat and cartilage, not its outer shell.
- Diet: Hatchlings are omnivorous, while adults are herbivorous, using beak-like jaws adapted for grazing on seagrass and algae.
- Distribution: Found across tropical and subtropical oceans, including the Atlantic, Pacific, Indian Oceans, and the Mediterranean Sea.
- Indian Range: Occurs along India’s mainland coasts and islands, with key nesting sites in Saurashtra, Lakshadweep, and Andaman-Nicobar.
- Habitat Preference: Juveniles inhabit the open pelagic zone, while adults prefer shallow coastal areas like lagoons, reefs, and seagrass beds.
- Migration: Green Sea turtles are highly migratory and travel thousands of kilometres. They use Earth’s magnetic fields to locate natal nesting sites.
- Reproduction: Temperature-dependent sex determination produces more females in warmer nests and more males in cooler conditions.
- Keystone Role: Their grazing sustains seagrass ecosystems, improves carbon sequestration, and strengthens the resilience of marine biodiversity.
- Indicator Species: As long-lived (~80 years) marine organisms, their population patterns reveal the health and resilience of global ocean ecosystems.
- Major Threats: Overharvesting, hunting, entanglement in fishing nets, habitat destruction, and nesting disruptions caused by climate change.
- Conservation Status: IUCN: Least Concern; CITES: Appendix I; CMS: Appendix I & II; WPA: Schedule I.
Ozone Pollution in Indian Cities

- The National Green Tribunal (NGT) has taken suo motu cognisance of a report on the alarming rise of ground-level ozone pollution in major Indian cities.
- The tribunal linked high ozone to vehicular, industrial, and power-sector NOx emissions and sought a CPCB-led expert study to frame control measures.
|
Ozone Pollution
|
Scale of the Issue
- Ozone Exceedance: Highest in Delhi-NCR and Mumbai, often breaching safe limits (CPCB, 2025).
- Rising Trend: Urban ozone up >30% since 2018 from vehicles and power plants (MoEFCC, 2024).
- Health Impact: Causes respiratory diseases and ~70,000 premature deaths annually (WHO, 2024).
- Emission sources: Transport (~40%) and power generation (~30%) major NOx contributors.
- Environmental impact: Reduces crop yields by 5–20% and contributes to climate warming.
First-Ever Image of Two Orbiting Black Holes
- Astronomers have, for the first time, captured a radio image of two black holes orbiting each other in a distant galaxy called Quasar OJ287.
|
- The pair consists of a massive black hole of 18 billion solar masses and a smaller companion of 150 million solar masses, orbiting each other in a 12-year cycle.
- The smaller black hole emits a jet of high-energy particles that twists like a tail due to the immense gravitational pull of its larger companion.
- Imaging Method: The image was captured using a network of radio telescopes, including the RadioAstron satellite, which provided a much higher resolution than standard Earth-based optical telescopes.
|
Significance
- Scientific Milestone: This is the first visual confirmation of binary supermassive black holes, supporting predictions of Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity.
- Theory Validation: The observation confirms the long-standing theory that two orbiting black holes cause the 12-year light fluctuations observed in Quasar OJ287.
- Gravitational Insight: The binary system aids in studying gravitational waves, enhancing understanding of how massive bodies warp space-time.
- India’s Role: The research team included Indian scientists, highlighting India’s growing role in global astrophysics and space research.
Quantum Breakthrough in Digital Security
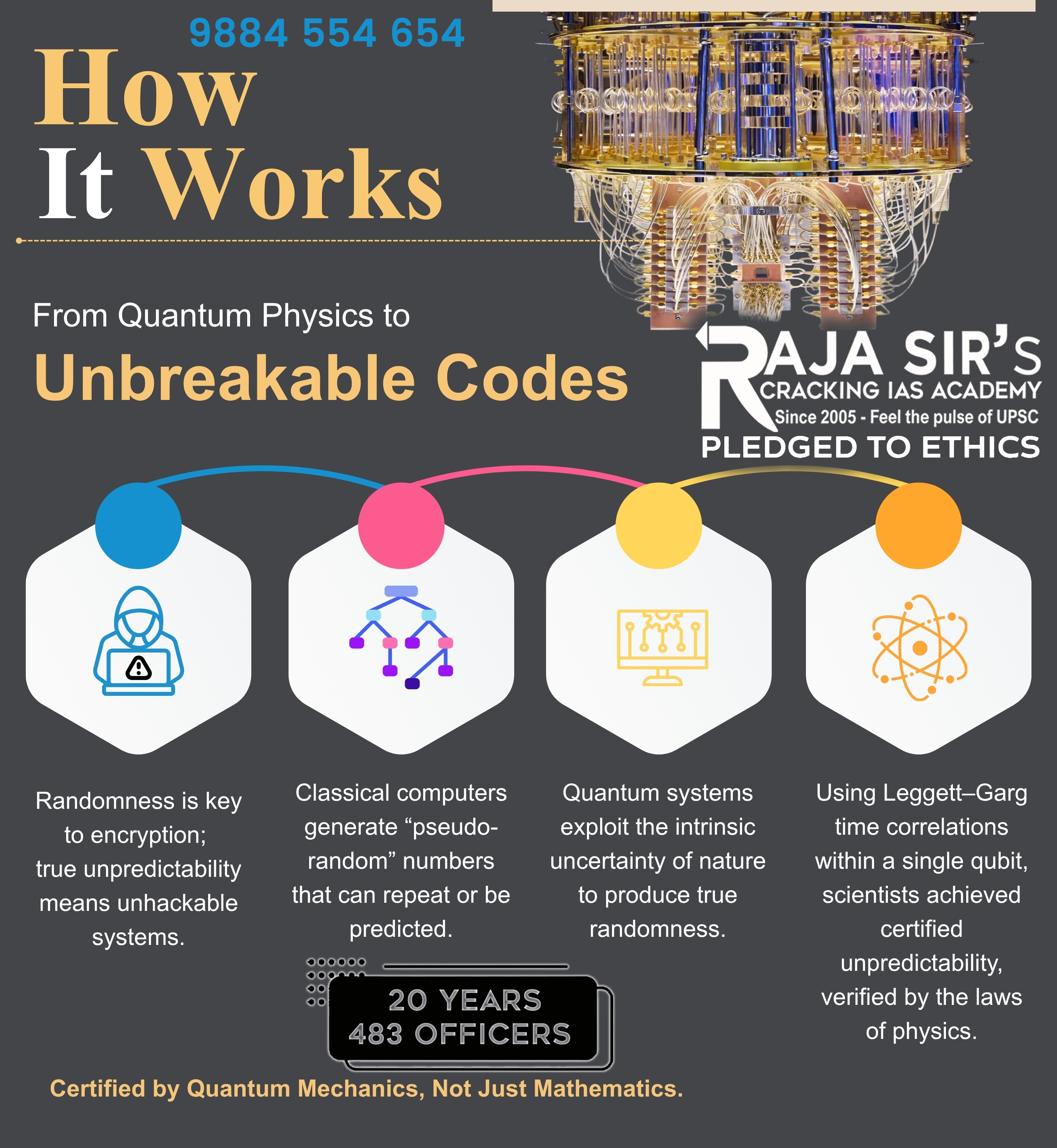
- Indian researchers at Raman Research Institute, Bengaluru, achieved a global first in certifying true random number generation using a commercial quantum computer.
- The discovery under the National Quantum Mission (NQM) marks a critical leap toward hack-proof digital security and quantum-safe encryption.
|
Need for True Randomness in Digital Security
|
How was the Breakthrough Achieved?
- Compact & Practical Setup: Used time separation in a single particle (Leggett–Garg principle) instead of two-particle systems, making the experiment smaller, cheaper, and real-world ready.
- Device-Independent Randomness: The randomness arises from pure quantum behaviour, not dependent on the machine itself, ensuring genuine, hacker-proof random numbers.
- Real-World Demonstration: Successfully tested on a commercial quantum computer, proving the technique’s robustness and readiness for deployment in banking, defence, and cybersecurity systems.
How does it impact India?
- Strategic Security: Enables quantum-proof encryption for defence, digital governance, and fintech.
- Technological Leadership: Positions India among the top five nations in quantum research.
- Data Sovereignty: Reduces dependence on imported cryptographic chips.
- Economic Potential: Opens up a $3 billion global QRNG market (Allied Market Research, 2025).
|
Fare Se Fursat Scheme
- The Ministry of Civil Aviation launched the ‘Fare Se Fursat’ scheme through the state-owned carrier Alliance Air to provide fixed airfares for passengers.
- The initiative replaces the conventional dynamic pricing system with fixed fares that stay the same.
- Implementation: Alliance Air, a regional airline connecting Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities, will implement the scheme on a pilot basis to evaluate its operational feasibility.
- Objective: To ease passengers’ worries about airfare fluctuations and make air travel more affordable.
- Significance: The scheme aligns with the objectives of the UDAN (Ude Desh ka Aam Nagrik) initiative and promotes last-mile air connectivity.
Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences 2025
- The Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences 2025 was awarded to Joel Mokyr, Philippe Aghion, and Peter Howitt for explaining how innovation shapes long-term prosperity.
Contribution of the Nobel Laureates
Joel Mokyr (Northwestern University, US)
- Historical Foundations: Mokyr highlighted how Europe’s Scientific Revolution fostered sustained economic growth by combining technological progress with intellectual development.
- Knowledge Fusion: He explained that blending practical “prescriptive” knowledge (knowing how) with theoretical “propositional” knowledge (knowing why) created a self-sustaining innovation ecosystem.
- Industrial Enlightenment: Mokyr coined the term (Industrial Enlightenment) to describe a period when openness to new ideas and scientific curiosity fuelled cycles of innovation and productivity.
Phillipe Aghion (Collège de France, INSEAD, and LSE) and Peter Howitt (Brown University, US)
- Model Development: Aghion and Howitt created mathematical models based on Joseph Schumpeter’s theory of “Creative Destruction.”
- Creative Destruction: Their model shows how new technologies, firms, and ideas replace outdated ones, keeping economies competitive and productive.
- Policy Implication: They emphasised that strong competition, education, & research investment are crucial for sustaining innovation-driven growth.
Bharat Taxi Initiative
- National e-Governance Division (NeGD) and Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology have partnered with Sahakar Taxi Cooperative Limited to launch Bharat Taxi Initiative.
Key Highlights of the Initiative
- It is a first-of-its-kind cooperative-driven, citizen-first national ride-hailing initiative.
- Cooperative Model: The platform is jointly promoted by major cooperatives and financial institutions such as NCDC, Indian Farmers Fertiliser Cooperative (IFFCO), KRIBHCO, NAFED, National Dairy Development Board (NDDB), AMUL, and NABARD.
- Technical Architecture: Integrating Bharat Taxi with key national digital platforms such as DigiLocker, UMANG, and API Setu facilitates secure digital identity verification and service delivery.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies