- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
OCTOBER 18, 2025
FSSAI Bans Misuse of ‘ORS’ Label
- The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) directed that no product can use the ‘Oral Rehydration Salts (ORS)’ tag unless approved by the World Health Organisation (WHO).
- Violations will be considered misbranding and misleading advertisements and will be punishable under the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006.
- Rationale: Many beverage companies market sugary drinks with the ORS label; the regulation aims to prevent consumer deception and associated health risks.
|
FSSAI is a statutory body established by the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006. under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. It is the country’s apex food regulator. |
ORS
- Oral Rehydration Salts (ORS) are a scientifically formulated electrolyte-glucose solution used to treat dehydration caused by diarrhoea, vomiting, or heat stress.
- It is a highly effective treatment for childhood diarrhoea but should only be used under a prescription.
- The WHO offers a standard ORS formulation that includes sodium chloride, glucose, potassium chloride, and trisodium citrate in specific ratios.
- Mechanism: It works through glucose–sodium co-transport in the intestines, where glucose helps absorb electrolytes and water, effectively restoring hydration.
Inequality in Pre-Primary Education
- The NSS 80th Round (2025) reveals deep inequalities in India’s pre-primary education, showing how early schooling access and quality diverge sharply across rural–urban and income lines.
|
Key Findings of NSS 80th Round Survey
|
Challenges Faced in the Pre-Primary Education System
- Structural Inequity: Only 8% of rural households can afford private pre-primary education (NSS 2025).
- Privatisation Surge: Over 60% of urban pre-primary students in private unaided schools, and the government pre-primary enrolment share has declined by 12% since 2015 (NIEPA 2024).
- Quality Deficit: 1.3 million Anganwadis, but only 58% have dedicated learning spaces. Only 1 in 4 ECCE teachers receive formal pedagogical training (NCERT, 2023).
- Normative Conditioning: Social stratification begins by age 3–4, reducing intergenerational mobility (UNESCO GEM Report 2024).
Way Forward
- Universal ECCE Access: Expand Anganwadi–Pre-school Integration under Saksham Anganwadi & Poshan 2.0 for uniform quality. E.g. Tamil Nadu’s Anganwadi–Balwadi model.
- Equity-focused Funding: Implement NEP 2020’s 6% GDP target for education with dedicated pre-primary spending and use Samagra Shiksha 2.0 to bridge infrastructure gaps in rural areas.
- Regulate Private Pre-schools: Introduce a National Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) Regulatory Framework to standardise fees, curriculum, and quality.
- Capacity Building: Launch National Early Educator Fellowship for training ECCE teachers.
- Digital Inclusion: Develop a Unified ECCE Data Portal under the Ministry of Education for tracking enrolment, dropouts, and infrastructure. E.g. DIKSHA & PM eVidya platforms.
India and FAO Celebrate 80 Years of Partnership
- On World Food Day 2025, India and the Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO) celebrated 80 years of partnership.
India’s Achievements in Food Security
- Despite having less than 4% of the world’s agricultural land and freshwater, India maintains food self-sufficiency and price stability.
- Initiatives like Minimum Support Price (MSP) and public stockholding ensure food access to 800 million beneficiaries under the National Food Security Act (NFSA).
- Targeted interventions for small and marginal farmers, accounting for 146 million cultivators, are the backbone of Indian agriculture.
|
Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO)
|
India Sends Prussian Blue Capsules to Indonesia
- India sent Prussian Blue capsules to Indonesia to reduce health risks from Caesium-137 contamination, following an official request from Indonesia’s Ministry of Health.
|
Prussian Blue is an oral prescription drug used to treat internal contamination by radioactive and non-radioactive caesium and thallium. |
- India’s quick supply of medications highlights its role as a regional first responder for humanitarian and health emergencies.
Cesium-137 (Cs-137)
- Cs-137 is a radioactive isotope of caesium that does not occur naturally but is instead a byproduct of nuclear fission in reactors.
- It has a half-life of about 30 years, so it takes roughly three decades for its radioactivity to halve.
- It emits beta and gamma radiation, exposure to which can cause severe burns and radiation sickness, while ingestion leads to serious illness and raises the risk of cancer.
|
Caesium (Cs) is a highly reactive, soft, silvery-gold alkali metal with atomic number 55. It has only one stable naturally occurring isotope, Caesium-133, which is used in atomic clocks. |
MERCOSUR
- India and Brazil agreed to expand the 2004 Preferential Trade Agreement (PTA) with the Mercosur bloc to strengthen trade and economic cooperation.
- Mercosur, or the Southern Common Market, is a South American trade bloc created to promote free trade and economic integration.
- Framework: It was established under the Treaty of Asunción (1991). The Protocol of Ouro Preto (1994) granted it legal status and defined it as a customs union.
- Membership: The bloc includes five full members (Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay) and six associate members.
-
- Venezuela’s membership has been suspended indefinitely since 2016 due to non-compliance.
- Economic Significance: Mercosur contributes over 60% of South America’s GDP, making it among the largest trade blocs after the EU, USMCA, and ASEAN.
- Governance: The Common Market Council (CMC) is the highest decision-making body. It comprises foreign and economic ministers from each member state.
- The bloc’s presidency rotates every six months among full members.
- Trade Agreement: India signed a Preferential Trade Agreement with Mercosur in 2004 to expand market access, and it came into effect in 2009.
- India-Mercosur trade reached $17.9 billion in 2024-25, with Brazil accounting for $12.19 billion.
China’s WTO Complaint Against India
- China has filed a complaint at the WTO alleging that India’s EV and battery subsidies violate trade rules, claiming they discriminate against foreign manufacturers.
|
WTO’s Agreement on Subsidies and Countervailing Measures (ASCM) prohibits subsidies contingent on export performance or import substitution. |
Allegations by China
- National Treatment Violation: India’s subsidies and local-content rules allegedly favour domestic producers (Tata, Ola) over foreign firms (WTO Article III).
- Import-Substitution Subsidy: Claimed as a prohibited subsidy under ASCM Article 3, as benefits are tied to using domestic inputs.
- Market Access Barrier: 70–100 % import duty on fully built EVs deters Chinese automakers.
Consequences for India
- Trade Deficit Concern: India’s $99.2 billion trade deficit with China (2024-25) could widen.
- WTO Risk: May lead to a dispute panel and potential adverse ruling on India’s PLI scheme.
- Diplomatic Strain: Could undermine recent India–China thaw post-Ladakh standoff.
Way Forward
- Transparent Subsidy Design: Restructure EV incentives as R&D or green-tech support permissible under ASCM Article 8 (WTO Secretariat Guidelines 2024).
- Bilateral Consultation: Use the Dispute Settlement Article 4 consultation stage to negotiate a compromise before formal panel review.
- Strategic Alliances: Strengthen EV partnerships via the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF) Clean Economy Pillar and Global Biofuels Alliance to diversify sources.
- Technology Localisation: Encourage domestic innovation through Atmanirbhar EV Mission 2030 and public-private R&D grants instead of restrictive sourcing mandates.
|
India-Egypt Strategic Dialogue
- External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar co-chaired the inaugural India-Egypt Strategic Dialogue in New Delhi to promote collaboration in political, economic, defence, and counterterrorism.
India-Egypt Relations
- Diplomatic Evolution: India and Egypt established diplomatic relations in 1947, signed a Friendship Treaty in 1955, and elevated their relationship to a Strategic Partnership in 2023.
- Trade Targets: Both nations aim to increase bilateral trade to $12 billion by 2028, up from $5 billion in 2023-24. India’s exports make up nearly 75% of total trade (mainly petroleum products).
- Defence Collaboration: India and Egypt regularly hold joint military exercises like Bright Star, Exercise Cyclone, and Desert Warrior.
- Egypt has expressed interest in acquiring Indian defence systems like LCA Tejas and Akash missiles.
- Cultural Ties: The Maulana Azad Centre for Indian Culture in Cairo promotes cultural engagement through events like ‘India by the Nile’ and Hindi language courses.
- Strategic Importance: Egypt’s control of the Suez Canal remains critical for India’s maritime trade. Both nations collaborate on Red Sea anti-piracy and regional counterterrorism operations.
- Global South: India and Egypt collaborate through platforms like the UN, G20, and BRICS to amplify the voice of the Global South. Both were founding members of the Non-Aligned Movement.
- Emerging Threats: Instability in the Middle East, disruptions in the Suez Canal, global supply chain vulnerabilities, and China’s expanding influence pose challenges for India-Egypt relations.
Global Push for Fossil Fuels Phase-Out Treaty
- At the IUCN World Conservation Congress (Oct 2025), the IUCN adopted Motion 042, officially identifying fossil fuel production as a direct threat to nature and biodiversity.
|
The IUCN World Conservation Congress is a quadrennial (held every 4 years) global summit organised by the IUCN to set priorities for nature conservation and sustainable development. |
UNFCCC (United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change)
- Adopted: In 1992 at the Rio Earth Summit and entered into force in 1994.
- Headquarters / Secretariat: Located in Bonn, Germany.
- Objective: To stabilise greenhouse gas (GHG) concentrations in the atmosphere at a level that prevents dangerous human-induced interference with the Earth’s climate system.
- Conference of Parties: Supreme decision-making body; meets annually.
- COP28 (2023): Dubai, UAE │ COP29 (2024): Baku, Azerbaijan │ COP30 (2025): Belém, Brazil
IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature)
- Founded: In 1948; Headquarters located in Gland, Switzerland.
- Membership: Comprises 1,400+ members, including States, NGOs, and scientific organisations.
- Core Role: Serves as the global authority on the status of the natural world; maintains the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.
Global Fossil Fuel Production Data
- Top Oil Producers: U.S. (17%), Saudi Arabia (13%), Russia (12%).
- Top Coal Producers: China (51%), India (10%), Indonesia (8%).
- Top Gas Producers: U.S. (23%), Russia (17%), Iran (6%). (Source: IEA, 2024)
- Fossil Fuel Subsidies: $1.8 trillion globally in 2024 (IMF, 2024).
- Emission Share: Fossil fuels account ~75% of global GHGs and ~90% of CO₂ emissions (UNEP, 2024).
- Biodiversity Threat: Fossil fuel extraction is linked to >40% of terrestrial habitat degradation and is responsible for 80% of biodiversity loss in key hotspots such as the Amazon & Congo basins.
Evidence for Dark Matter
- Scientists are examining a diffuse glow of gamma-rays near the center of the Milky Way, which could potentially confirm the existence of dark matter.
- One hypothesis is that dark matter particles collide and annihilate near the galactic core, producing these gamma rays.
- The Cherenkov Telescope Array Observatory, the world’s most powerful ground-based gamma-ray telescope under construction in Chile, can test the theory.
Dark Matter
- Dark matter is an invisible, hypothetical form of matter forming ~85% of all matter and ~27% of the universe’s total mass-energy.
- It neither absorbs nor emits electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, making it undetectable with standard telescopes.
- Scientists infer its existence from gravitational effects unexplained by visible matter, like the high rotational speeds of galaxies, gravitational lensing, and cosmic structure formation.
|
Gravitational lensing is the phenomenon where the intense gravity of a massive object, like a galaxy cluster, bends and magnifies the light from distant objects; Albert Einstein’s theory of general relativity predicted it. |

Taftan Volcano
- An Iranian volcano appears to have woken up, 700,000 years after its last eruption.
- Location: Southeastern Iran, near the Pakistan border in Sistan-Baluchestan province.
- Type: Stratovolcano (composite volcano) built by successive layers of lava & ash.
- Elevation: Approximately 3,940 meters (12,927 feet) above sea level.
- Tectonic Setting: Part of the Makran volcanic arc, formed by subduction of the Arabian Plate beneath the Eurasian Plate, within the Alborz–Makran volcanic belt of southern Iran.
- Geological Features: Hosts an active hydrothermal system with fumaroles emitting sulphur gases.
- Last Known Eruption: ~710,000 years ago (Pleistocene epoch).
|
Stratovolcano (Composite Cone)
|
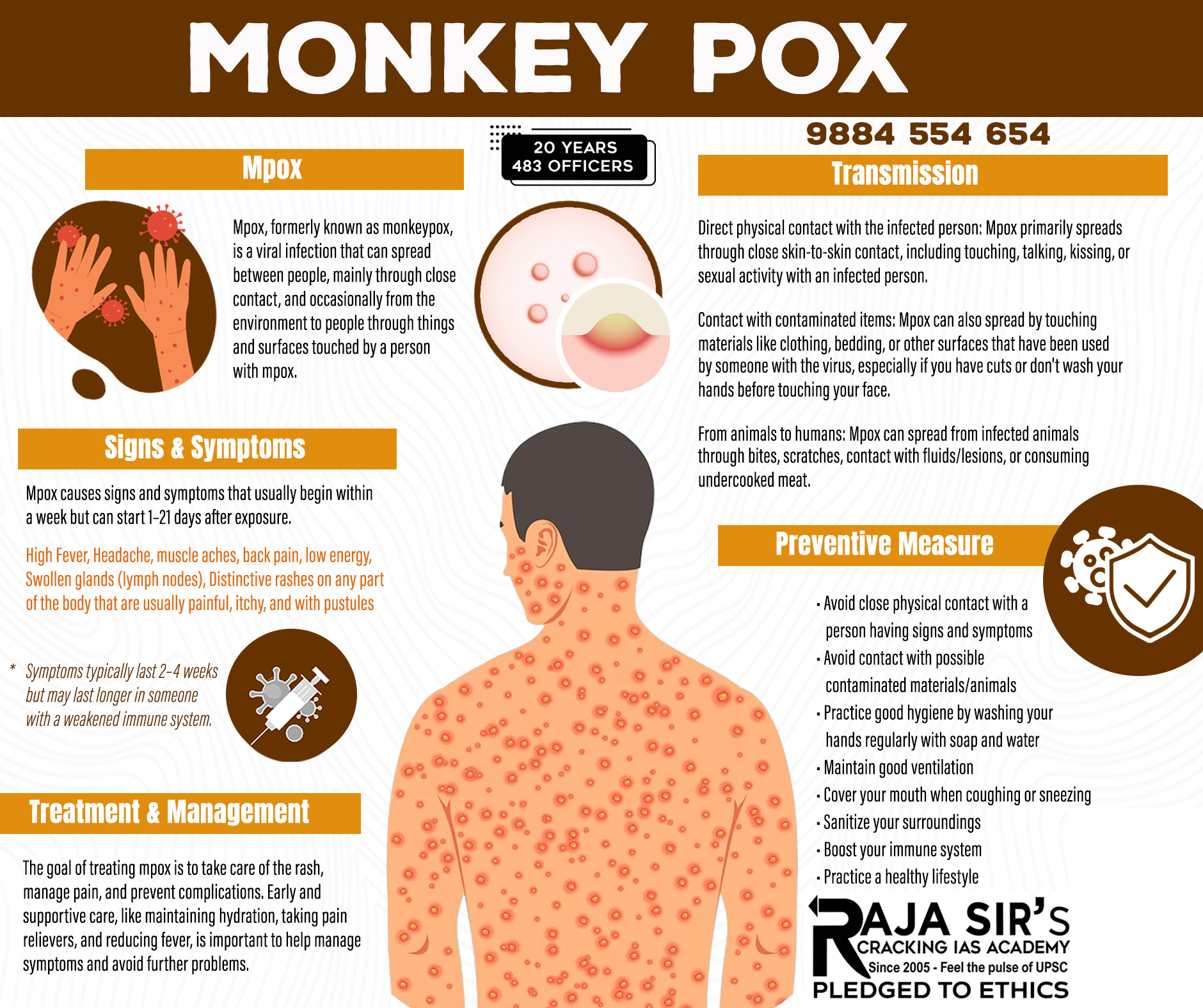
First Local Transmission of Mpox Strain in the US
- The U.S. has confirmed the first suspected local transmission of the Clade I mpox strain, with no identified travel links.
- Clade I is more severe than the clade that predominated in the 2022 outbreak (clade II). Estimates place clade I mortality between ~1% and 10%, versus under 1-4% for clade II.
Mpox Disease
- Mpox is a zoonotic viral disease caused by the Monkeypox virus (MPXV), an Orthopoxvirus closely related to smallpox.
- Symptoms: Fever, chills, body aches and painful skin lesions (face, hands, genital areas). Severe disease is more likely in children and immuno-compromised persons.
- Treatment: There is no specific cure, but antivirals such as Tecovirimat and Brincidofovir are used under emergency protocols for severe cases.
- Vaccine: The Jynneos vaccine (Bavarian Nordic) proved effective during the 2022 outbreak and remains the primary preventive tool for high-risk contacts and certain occupational groups.
- India reported 10 confirmed Clade 1b Mpox cases between December 2024 and March 2025, all linked to travel from the Gulf region, while there has been no domestic community transmission yet.
Expansion of LCA Tejas and HTT-40 Production Lines
- The Union Defence Minister has inaugurated Hindustan Aeronautics Limited’s (HAL) third LCA Tejas Mk1A and second HTT-40 production lines at Nashik, Maharashtra.
- The defence minister also flagged off the maiden flight of the first Tejas Mk1A aircraft produced in the new HAL facility.
- LCA Tejas: The Tejas Mk1A is a 4.5-generation, single-engine, delta-wing, multi-role light combat aircraft designed by the Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) and manufactured by HAL.
- HTT-40 Trainer: The Hindustan Turbo Trainer-40 (HTT-40) is an indigenous tandem-seat turboprop trainer aircraft developed by HAL for primary flight training of Indian Air Force cadets.
|
Hindustan Aeronautics Limited is a ‘Maharatna’ PSU headquartered in Bengaluru. It designs, develops, and manufactures aircraft, helicopters, engines, and avionics for India’s defence and aerospace sectors. |
IN-RoKN Exercise
- The Indian Naval Ship (INS) Sahyadri arrived at Busan Naval Harbour recently to take part in the inaugural India-Republic of Korea Navy (IN-RoKN) Bilateral Exercise.
- The exercise aims to enhance interoperability, coordination, and mutual understanding between the two navies, in line with India’s Act East Policy and Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI).
|
INS Sahyadri: A Shivalik-class guided missile stealth frigate, INS Sahyadri was indigenously designed and commissioned in 2012. |
Mongolian PM Resigned
- Mongolian Prime Minister Gombojav Zandanshatar has resigned after losing a confidence vote in parliament.
Kancha Sherpa
- Kancha Sherpa, the last surviving member of the 1953 British Mount Everest Expedition, recently passed away. The expedition resulted in the first successful ascent of Mount Everest by Edmund Hillary (New Zealand) and Tenzing Norgay (Nepali Sherpa).
World Menopause Day
- World Menopause Day is observed annually on October 18 to raise awareness about menopause. 2025 Theme: Lifestyle Medicine in Menopausal Health.
State Mining Readiness Index
- The Ministry of Mines has released the first-ever State Mining Readiness Index (SMRI) and corresponding state rankings to promote mining sector reforms across India.
Key Highlights
- The SMRI evaluates States on four criteria: auction performance, mine operationalisation, exploration efforts, and sustainable mining practices.
- The SMRI serves as a reform benchmarking tool promoting non-coal mineral development, investment-friendly policies, sustainable resource management, & cooperative federalism among States.
- Top Performers:
- Category A: Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Gujarat (Mineral-rich States).
- Category B: Goa, Uttar Pradesh, Assam (Moderate mineral endowment).
- Category C: Punjab, Uttarakhand, Tripura (Limited mineral endowment).









 Latest News
Latest News

 General Studies
General Studies