- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
OCTOBER 21, 2025
International Telecommunication Union (ITU)
ITU’s World Telecommunication Standardization Assembly (WTSA) 2024 held in New Delhi.
- WTSA is the governing conference for the standardization work of the ITU, organized every four years.
- It is for the first time that the ITU-WTSA is being hosted in India and the Asia-Pacific.
ITU
- Genesis: In 1865, the first International Telegraph Convention signed in Paris established International Telegraph Union (the first incarnation of ITU).
- Role:
- UN’s specialized agency for digital technology
- Harnessing innovation and connecting everyone to ensure a better future for all
- Members: 193 Member States (including India)
- Headquarters: Geneva (Switzerland)
At Food and Agriculture Organization’s World Food Forum (WFF) Global Family Farming Forum (GFFF) was launched
GFFF celebrates essential role of family farmers in building sustainable agrifood systems and tackling the impacts of the climate crisis.
- GFFF also marked the halfway completion of the United Nations Decade of Family Farming 2019-28 (UNDFF).
- UNDFF was declared by United Nations General Assembly and it serves as a framework for countries to develop public policies and investments to support family farming.
- Family Farming: Is a means of organizing agricultural, forestry, fisheries, pastoral and aquaculture production that is managed and operated by a family, and is predominantly reliant on the family labour of both women and men.
- Significance of Family farming
- Food security: With over 550 million farms worldwide, it is the backbone of food production.
- It produces 70 to 80%of the world’s food in value terms.
- Nutritional diversity: Family farming, in low- and middle-income countries, grow diverse, nutritious food and support cropbiodiversity.
- Sustainable stewardship: Family farmers use traditional methods, minimal external inputs to maintain soil health and build climate resilience naturally.
- Challenges faced by Family farming: Financial barriers, limited access to assistance, genetics and knowledge., fragmentation of land, market access difficulties, climate threats, lack of generational succession support, etc.
|
Trojan asteroids
Discovery of a Trojan asteroid (2019 UO14) for Saturn establishes the presence of celestial bodies alongside all giant planets (Jupiter, Neptune & Uranus).
- They occupy a stable Lagrange Point (Usually L4 and L5) in a planet’s orbit around the sun.
- Lagrange Point is a position in space where objects stay in a relatively stable position without drifting away.
- Significance: As they remain gravitationally stable for long period of time, studying them can provide useful insights into the evolution of the solar system.
- Mission Lucy (launched in 2021): The first mission to explore the Jupiter Trojan asteroids.

MHA issues advisory to states & UTs to implement Section 479 BNSS for relief of Undertrial Prisoners
The advisory from the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA), raising the issue of long detention of undertrial prisoners, highlights the recent Supreme Court of India’s order.
- The order legally mandates the state that Section 479 of Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita (BNSS) applies to all undertrials, irrespective of whether the case was registered before 1st July 2024'' (BNSS came into effect).
Bail Provisions under BNSS for the detainees
- Regular Cases: Undertrial to be released if detention period reaches half of maximum specified imprisonment.
- First-Time Offenders: To be released if detention reaches 1/3rd of maximum imprisonment. Not applicable for offenses with death/life imprisonment.
Undertrials in India
- As per National Crime Records Bureau, India’s prisons (It’s a state subject as per the 7th Schedule of the constitution) have a 131.4% occupancy. Around 75% are undertrials (2022).
- An undertrial prisoner is in prison or judicial custody while the charges against them are tried in court.
Reasons for high number of Undertrial prisoners in India
Indiscriminate arrests by police, ignorance of legal rights, delay in trial, reluctance of the courts to grant bail, inability to provide surety.
|
Measures taken to alleviate hardships faced by the Undertrials
|
‘eShram-One Stop Solution’
Ministry of Labour & Employment is set to launch the ‘eShram-One Stop Solution’
- Aim: To integrate information on beneficiaries of all social security and welfare schemes for Unorganised Workers (UW) on a single platform.
- Significance: Making UW aware of schemes meant for them and ensuring easy access to these programs
eShram portal is a centralized database (seeded with Aadhaar) of all UWs including Gig and Platform workers. Since its launch in 2021, over 30 crore UWs are enrolled on it.
UV Photodetectors
Memorandum of understanding (MoU) signed with IIT-Delhi for the development of diamond-based deep ultraviolet (UV) photodetectors for the first time in India.
- It’s an optoelectronic device that converts light or other electromagnetic radiation into an electrical signal.
- It generates a small current or voltage, which can be measured.
Diamond-based UV Photodetector
- Specifically detects deep UV light due to diamond''s high UV photon sensitivity.
- Durable in harsh conditions (resistant to radiation and heat damage).
- Exhibit high efficiency at room and higher temperatures
- Applications: UV imaging, secure communications, biological and military detection, etc.
Global Multidimensional Poverty Index 2024
2024 Global MPI was on the theme “Poverty Amid Conflict.” It is published annually by the UN Development Programme (UNDP), Oxford Poverty and Human Development Initiative.
- Uses ten indicators across three dimensions: health, education, and living standards.
- Households are “multidimensionally poor” if they are deprived in at least one-third of these indicators.
Key Findings
- Across 112 countries,18.3 percent live in acute multidimensional poverty. Nearly 40% of the 1.1 billion people living in poverty, approximately 455 million, are situated in countries experiencing conflict.
- The five countries with the largest number of people living in poverty are India (234 million), Pakistan (93 million), Ethiopia (86 million), Nigeria (74 million), and the Democratic Republic of the Congo (66 million). These five countries account for nearly half (48.1%) of the 1.1 billion poor people.
- Around 584 million people under the age of 18 are living in extreme poverty, making up 27.9% of all children globally, compared to 13.5 % of adults. Most poor people (83.7 %) reside in rural areas.
- It noted that 2023 witnessed more conflicts than ever since WWII, displacing over 117 million people.
Factors Contributing to India’s Poverty
- Geographical Inequalities: Rural poverty rates remain high due to inadequate infrastructure, poor service delivery, and limited economic opportunities outside agriculture.
- Educational Standards: The quality of education in many government-run schools is poor, leading to insufficient learning outcomes.
- Hygiene and Sanitation: Poor access to safe drinking water and inadequate sanitation, particularly in rural areas, continues to push many households into multidimensional poverty.
- Malnutrition Issues: India struggles with severe malnutrition, particularly among children.
- Economic Challenges: The COVID-19 pandemic severely disrupted India’s economy, leading to job losses, reduced incomes, and increased vulnerabilities for millions of households.
India’s Government Steps for Poverty Alleviation
- National Food Security Act (NFSA), 2013
- National Nutrition Mission (POSHAN Abhiyaan)
- Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY)
- Ayushman Bharat scheme
- Right to Education Act (RTE)
- Swachh Bharat Mission
African Baobab
New research by South African ecologists disproves claims that African Baobab trees are dying due to climate change, noting they have survived past extreme climate fluctuations.
- ‘Tree of Life’: Vital to dry African savanna, helping keep soil humid, recycling nutrients, and reducing erosion.
- Trunk: As a succulent, the tree absorbs and stores water from the rainy season in its massive trunk.
- False cavities: The bark regenerates in the space between these stems, called false cavities.
- Flowers: Large and whitish flowers open at night and fall within 24 hours.
- Fruit: Contains tartaric acid and Vitamin C, serving as a vital nutrient and food source for many species.
Bipolar World and India
- India’s diplomatic engagement with China is tense following the 2020 Galwan Valley clash, while relations with the U.S. are strengthening amid escalating Sino-American rivalry.
- Indian National Security Adviser Ajit Doval met Chinese Foreign Minister Wang Yi at the BRICS National Security Advisers’ meeting in St. Petersburg, indicating a potential thaw in diplomatic relations.
Reason for a Bipolar World
- China’s rapid economic rise as the world’s second-largest economy, with a GDP of approximately $18 trillion in 2023, competing with the U.S.’s GDP of about $26 trillion.
- China has modernised its military about 350 battle-force ships, surpassing the U.S.’s 293 as of 2024. Rising tensions in the South China Sea and issues regarding Taiwan further exacerbate this.
- U.S’s democracy and China’s authoritarianism: As of 2023, only 20% of the global population lives in free countries, while authoritarian regimes govern around 30%.
- Shift in global power dynamics: U.S. unilateralism has declined, reducing its share of global GDP from 40% in 1990 to 24% in 2024. This shift allows China to challenge U.S. dominance.
- Technological Competition: China aims to lead in AI by 2030, with the sector projected at $1 trillion. It also controls about 70% of the global 5G market as of 2024.
- Cold War-like containment strategies of USA through alliances such as the Quad, enhancing security in the Indo-Pacific. The 2024 military budget includes $9 billion for initiatives countering China.
India’s Stand in a Bipolar World
- Non-Alignment and Strategic Autonomy allowing engagement with both the U.S. and China.
- Balancing Relationships with major powers by engaging with the U.S. through partnerships like the Quad while managing over $117 billion in trade with China despite ongoing border tensions.
- As a leader in the Indo-Pacific India promotes stability through initiatives like the Act East Policy and strengthened ties with Southeast Asia by hosting the India-ASEAN summit in 2023.
- Economic Engagement: India aims to diversify its economic relationships. The “Make in India“ initiative seeks to enhance local manufacturing and reduce import dependence.
- Enhancing military through collaborations with the U.S., such as the Defense Technology and Trade Initiative (DTTI). In 2024, India’s defense budget is approximately $73 billion, focusing on modernisation.
- Technological Development: India is investing in information technology, AI, and space technology, with the Indian space sector projected to grow to $13 billion by 2025.
- India advocates for a multipolar world and seeks reforms in global governance institutions, including the UNSC. Its G20 presidency in 2023 underscores its influence on global decision-making.
- Diplomatic Engagement: India manages tensions through dialogue with China, including 2023 talks to de-escalate border issues and participation in multilateral forums like BRICS and SCO.
Challenges of India in a Bipolar World
- Sovereignty and Security: India must protect its sovereignty amid U.S.-China tensions and threats from China’s assertive foreign policy, as seen in the 2020 Galwan Valley clash.
- Strategic Autonomy: India should avoid becoming a pawn in geopolitical contests, exemplified by its participation in the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) to maintain independent strategies.
- Economic Dependence: Engaging with the U.S. and China risks economic dependence. In 2022, India’s trade with China reached $117 billion, highlighting the need for a balanced economic approach.
- Regional Stability: U.S.-China tensions may destabilise the Indo-Pacific, impacting India’s national security, as demonstrated by 2022 naval encounters in the South China Sea.
- Military Modernization: India must modernise its military in response to China’s expansion, which includes about 350 battle-force ships compared to India’s 130, requiring significant defence investment.
- Technological Competition: India needs to enhance its technological capabilities. In 2024, China controlled 70% of the global 5G market, risking India’s marginalisation in tech innovation.
- Global Governance: India must assert influence in global governance shaped by U.S.-China rivalry, as seen during its G20 presidency in 2023, advocating for a multipolar world.
- Geopolitical Alliances: India should carefully choose alliances to avoid alienating the U.S. or China, balancing its partnership with the Quad and maintaining dialogue with China for autonomy.
Way Forward for India in a Bipolar World
- Enhancing Regional Alliances: Expand ties with Southeast Asia through the Act East Policy. The 2023 India-ASEAN summit aimed to counter China’s 25% share of ASEAN trade in 2021.
- Diversifying Economic Engagement: Reduce dependence on China, with 2022 trade at $117 billion, by promoting “Make in India” and targeting a $500 billion manufacturing output by 2025.
- Investing in Defense Modernisation: Increase the defence budget of around $73 billion to modernise military capabilities, including acquisitions like Rafale jets, against China’s 350 battle-force ships.
- Promoting Technological Advancement: Invest in AI and space sectors, projected to reach $13 billion by 2025, to enhance global competitiveness through initiatives like the National AI Mission.
- Advocating for Reforms in Global Governance: Push for a permanent UN Security Council seat, leveraging its 2023 G20 presidency to influence global discussions on sustainability.
- Enhancing Diplomatic Engagement: Engage in constructive dialogue with China to address border tensions, exemplified by the 2023 Eastern Ladakh talks, while participating in multilateral forums like BRICS.
- Fostering Public Diplomacy: Educate the public on foreign policy through initiatives like the International Day of Yoga, celebrated in over 180 countries, to enhance India’s soft power globally.
European Sky Shield Initiative (ESSI)
Switzerland joins European Sky Shield Initiative (ESSI).
- Genesis: Founded in 2022 after Russia invaded Ukraine
- It is a German led European Iron Dome-style defence system.
- Aim: Bolstering Europe’s defence against air strikes as it will strengthen NATO’s integrated air and missile defence.
- Members: 21 member states, including the UK
- At the heart of this initiative is the Arrow 3, an Israeli-American missile defence system that can intercept long-range ballistic missiles.
Lighthouse Tourism
2nd National Lighthouse Festival with first of its kind ‘Lighthouse Tourism Conclave 2024’ began in Puri, Odisha.
- It is an initiative of Ministry of Ports, Shipping, and Waterways that aims to explore the vast potential of lighthouse tourism.
- Leveraging India’s maritime heritage: Lighthouses have played a crucial role in guiding ships safely through treacherous waters for centuries.
- Align with Maritime India Vision 2030: Strives to repurpose lighthouses into multifunctional facilities, including maritime museums and cultural centers.
- Current Status: 75 iconic lighthouses across 10 coastal states and union territory have been developed.
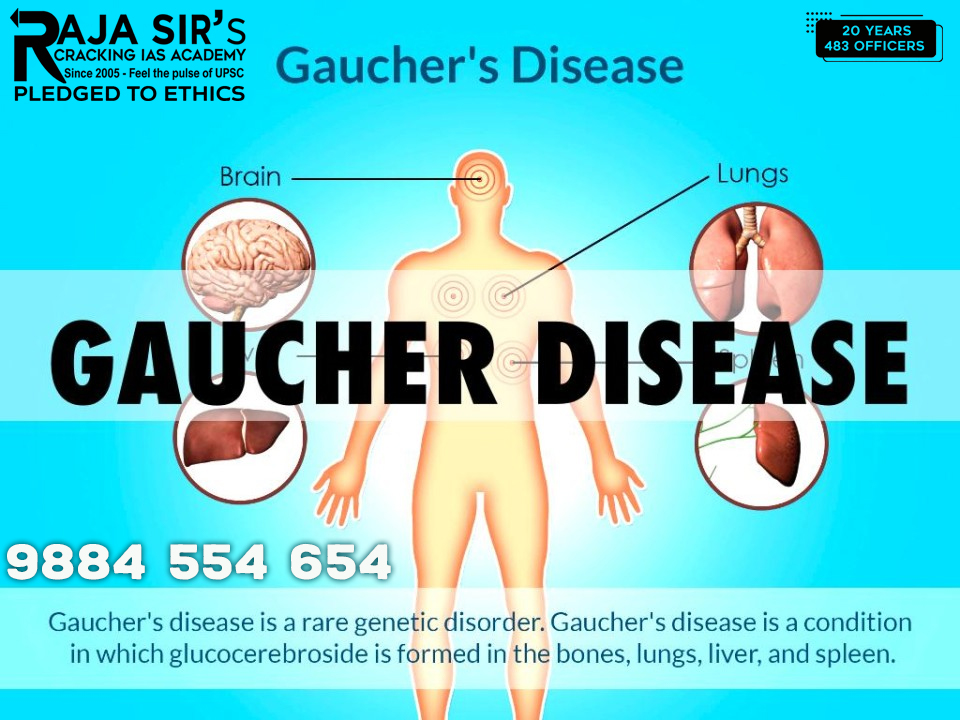
Gaucher Disease
- Petition seeking sustainable treatment support for Gaucher disease was submitted
- It is an inherited lysosomal storage disorder (LSD) that leads to the accumulation of fatty substances, known as sphingolipids, in organs like the bone marrow, liver, and spleen.
- It can cause the weakening of bones and enlargement of the affected organs. Common symptoms include an enlarged spleen and liver, eye movement disorders, and yellow eye spots.
India’s $1 Trillion “Just Energy” Coal Transition
- India, the second-largest coal producer globally, faces a significant challenge in transitioning away from coal, which will remain central to its energy mix for at least another decade.
- A study by the International Forum for Environment, Sustainability and Technology (iForest) estimates that a just transition away from coal will require over $1 trillion over the next 30 years.
What is a ‘Just’ Energy Transition?
- A just energy transition refers to an equitable and inclusive shift towards a low-carbon economy that considers the interests of fossil-fuel-dependent workers and communities.
Costs Associated with a Just Transition
- Mine Closures and Repurposing: Costs associated with closing coal mines and repurposing the sites.
- Retirement of Coal Plants: Costs of retiring coal plants and converting the sites for clean energy.
- Labour Skilling: Training coal workers for green jobs.
- Economic Diversification: Developing new businesses to replace coal-based industries.
- Community Support: Providing support to communities affected by the transition.
- Green Energy Investments: Building new energy infrastructure to replace coal mines & coal-fired plants.
- Revenue Substitution: Compensating states for the loss of revenue from coal.
- Planning Costs: Costs associated with planning and managing the transition.
Funding the Transition
- Public Funding: Grants and subsidies for non-energy costs like community support & worker retraining.
- Private Investments: Investments in green energy plants and infrastructure.
- District Mineral Foundations Funds: Nearly $4 billion is available from funds collected from miners, which can be used to support new businesses and communities in coal districts.
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): Additional support for new businesses & community resilience.
International Approaches to a Just Transition
- South Africa: Just Energy Transition Investment Plans will require $98 billion over the next two decades, with $8.5 billion to be provided from various countries in 2023-2027.
- Germany: Enacted laws to phase out coal power by 2038, with an outlay of over $55 billion to close coal mines and coal-powered plants and support coal-dependent regions.
Indian Railway and its Challenges
- Mysuru-Darbanga Express collision and the challenges that Indian Railways faces in safety and operational efficiency.
Challenges of Indian Railways
- Frequent Train Accidents like Balasore (2023) and Kavaraipettai (2024) reveal safety gaps, primarily due to staff errors (55.8%) and signaling failures.
- Limited Implementation of ‘Kavach: Kavach, a collision prevention system, covers only 2% of the network due to high costs (₹50 lakh per km), and slowing rollout.
- High Operating Ratio: An OR of 98.2 (2024-25) signals high costs, limiting capital investment and increasing reliance on government support, with dues rising from 10% to 17% of revenue since 2015-16.
- Freight Congestion: Freight, which contributes 65% of revenue, faces network congestion, reducing the average speed to 26 km/h. Delays in Dedicated Freight Corridors exacerbate the issue.
- Over-Reliance on Coal: Heavy reliance on coal freight risks long-term revenue sustainability while the government pushes for renewable energy.
- Track and Maintenance Deficiencies: Capital allocation for track renewal fell to 7.2% in 2023-24, reducing maintenance and equipment upgrades.
- Passenger Service Losses: Passenger services operate at a loss, with ₹68,269 crore in losses (2021-22), despite increased revenue in 2024-25.
- Capacity Constraints: 30% of the network operates beyond 100% capacity, causing delays and inefficiencies and impacting technologies like Kavach.
- Wage and Operational Costs: Rising wage, pension, and fuel costs, along with stressful working conditions for pilots, add to financial and operational pressures.
Government Initiatives to Strengthen Indian Railways
- Kavach Safety System provides real-time alerts and automatic braking to prevent accidents.
- Track Development: In 2022-23, 5,243 km of new tracks were laid, averaging 14.4 km per day. This reduces congestion and enhances network efficiency.
- Gauge Conversions: Between 2014-2022, 1,544 km of gauge conversions and new lines were completed, improving regional connectivity.
- High-Speed Rail Project: The $14.27 billion Mumbai-Ahmedabad high-speed rail project is being constructed to offer faster train services.
- Gati Shakti National Master Plan to enhance multimodal connectivity, improves freight and passenger logistics by streamlining operations and reducing bottlenecks across various transportation modes.
- Dedicated Freight Corridors: The Eastern DFC from Ludhiana to Dankuni for freight movement in key industrial area and The Western DFC from Dadri to Jawaharlal Nehru Port for improving overall efficiency.
- Integration with Union Budget: Since 2016-17, merging the railway budget with the general budget has increased flexibility in accessing gross budgetary support and reduced reliance on internal revenues.
- Railway Electrification: Aiming for 100% electrification by 2024, 61,813 km of broad-gauge track was electrified by 2023, saving $1.55 billion annually.
- Automatic Block Signaling (ABS) implemented over 3,946 route km to improve operational safety.
- Technological and Green Initiatives: By 2024, Wi-Fi will be installed at 6,089 railway stations to enhance passenger connectivity, and over 1,000 stations solarised to promote sustainable energy use.
- Freight Optimization: Record freight loading of 1,512 MT in 2022-23, with a 2024 target of 2,024 MT. Freight revenue constitutes 65% of internal earnings, largely from coal.
- FDI in Railways: 100% FDI is allowed in railway infrastructure to modernise stations, introduce high-speed corridors, and upgrade technology.
- 400 Vande Bharat Trains planned for faster, more efficient travel across key routes.
Way Forward for Indian Railways
- Deploy the Kavach system across the network, as the Kakodkar Committee (2012) recommended.
- Dedicated Freight Corridors (DFCs) could increase freight capacity by 70%, with the Eastern DFC cutting transit time from Ludhiana to Kolkata from 60 to 24 hours.
- Diversifying Revenue Streams: Public-private partnerships (PPPs) could attract ₹20,000 crores by 2024 and reduce dependence on ticket sales.
- 100% Electrification by 2024: At 85%, this goal will be supported by renewable energy initiatives like solar installations, which are projected to generate 20 GW.
- Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS): Implement real-time traffic management and automated train control systems. Over 100 trains use GPS tracking and digitise 70% of ticket sales by 2025.
- Fast-track high-speed rail projects starting with Mumbai-Ahmedabad route, which will cut travel time.
- Infrastructure upgrades and optimised train schedules are essential to address the 8% annual passenger growth rate contributing to congestion.
- Staff Training: Enhance railway personnel skills, as the Rakesh Mohan Committee emphasises. Improving working conditions for locomotive pilots could increase their efficiency by up to 30%.
- Enhancing Passenger Amenities: Upgrade station facilities and onboard services. A survey revealed that 78% of passengers want better sanitation.
- Establishing Robust Frameworks as the Bibek Debroy Committee recommended setting key performance indicators, aiming for a 20% improvement in service delivery.
Azores Island
- Azores island created the largest marine protected area in the North Atlantic.
- The Autonomous Region of the Azores is a Portuguese archipelago of volcanic origin made up of nine islands in the North Atlantic Ocean.
- It is located at the seismically active Azores Triple Junction plate boundary where the North American Plate, Eurasian Plate and African Plate meet.
- The archipelago, alongside Madeira, Cape Verde, and the Canary Islands, is part of Macaronesia.
- The islands lie in a northwest-southeast direction and are divided into three groups: northwest, central and eastern. Mount Pico, located on Pico Island, is the highest point on the archipelago
Naseem Al Bahr
- Indo-Oman bilateral naval exercise held on the coast of Goa, demonstrating India’s commitment to collaboration with Oman and regional security in the Indian Ocean Region
Other Bilateral Exercises with Oman
- Al Najah is a bilateral military exercise between the Indian Army and the Royal Army of Oman focused on counter-terrorism in desert environments.
- Eastern Bridge is a bilateral air exercise between the Indian Air Force and the Royal Air Force of Oman.
Vitiligo
- A recent Kannada film draws attention to vitiligo.
- Vitiligo is a long-term skin disorder that results in the loss of pigment in patches, causing white areas to appear on the skin. It is not contagious. Affects between 0.5 – 2% of the global population.
- Cause: It arises due to the malfunction or destruction of melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin, the pigment that gives skin its colour.
- It could result from autoimmune responses, genetic predispositions, and environmental factors (UV radiation, chemical exposure, etc). It results in depigmented patches that may occur anywhere on the body, including the skin, hair, and even the lining of the mouth.
- Does not have a permanent cure. Treatments aim to manage symptoms and restore skin pigmentation.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies