- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
28th Aug 2021
100 DAYS ‘SUJALAM’ CAMPAIGN BEGINS
Recently, the Ministry of Jal Shakti has flagged off ‘SUJALAM’ Campaign.
SUJALAM Campaign





- It is a‘100 days campaign’ as part of the ‘Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav’ celebrations.
- It aims to create more and more ODF Plus villagesby undertaking waste water management at village level particularly through creation of 1 million Soak-pits.
- The effort of campaign would be directed towards achieving the ODF plus status for villagesacross the country in an accelerated manner in a short time.
- The key activities that will be organised in the villages under this campaign include:
- Organizing Community consultations, Khuli Baithaks and Gram Sabha meetings to analyze the current situation
- Pass resolution to maintain ODF sustainability and achieve needed number of soak pits to manage the grey water
- Develop a 100 days’ plan to undertake sustainability and soak pit construction related activities
- Construct requisite number of soak pits
- Retrofit toilets where needed through IEC and community mobilization and
- Ensure all newly emerging Households in the village have access to toilets.
- It will enable building of desired infrastructure soak pit for management of greywater in villages.
- It will aid in sustainable management of waterbodies.
- It will help in management of the wastewater and in turn will help to revive the waterbodies.
- It would boost the momentum of Swachh Bharat Mission-Gramin (SBMG) phase II activities through community participation.
- It will use the platform of awareness and behaviour change achieved during the first phase of the SBMG.
- It will provide focus for sustaining the same along with achieving the visual cleanliness by the way of SLW Management.

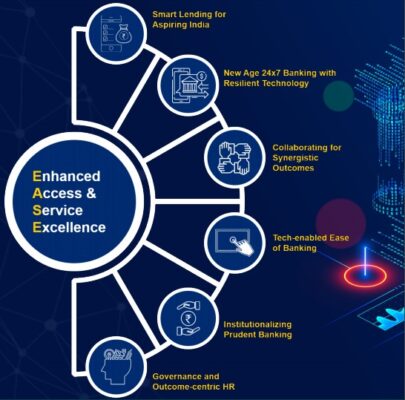
- The PSB reforms agenda - EASE was launched based on the recommendations made by PSB Whole Time Directors (WTDs) and senior executives in PSB Manthan in 2017.
- It encapsulates a synergistic approach to ensure prudent and clean lending, better customer service, simplified and enhanced credit, and robust governance and HR practices.
- The Reforms Agenda is pursued through a unique Reforms Index that enabled objective assessment of progress on all key areas in PSBs.
- The first edition of the EASE program pertaining to FY19 aimed at laying the foundation for themes such as Customer Responsiveness.
- The second edition of the EASE program for CLEAN and SMART banking was launched for FY20 to further build on the foundation of EASE 1.0.
- The third edition of the EASE reforms (EASE 3.0) was launched in FY21 to help catalyze accelerated adoption of customer-centric digital transformation initiatives across PSBs.
- Public Sector Banks have reported healthy profits and have accelerated on technology-driven reforms.
- These banks have reported a profit of Rs. 31,817 crore in FY21 as compared to a loss of Rs. 26,016 crore in FY20.
- It is the first year when PSBs have reported profit after five years of losses.
- The total gross non-performing assets stood at Rs. 6.16 lakh crore as of March 2021 i.e. a reduction of Rs. 62,000 crore from March 2020 levels.
- The EASE 4.0 aims to further the agenda of customer-centric digital transformation and deeply embed digital and data into PSBs’ ways of working.
- The two new theme shave been introduced to deliver on these objectives:
- New Age 24x7 banking with resilient technology has been introduced to ensure uninterrupted availability of banking services by ensuring 24X7 availability of select banking channels.
- Collaborative banking for synergistic outcomes aims to maximise synergies through collaboration between PSBs and with broader financial services ecosystem such as NBFCs for the coordinated handling of co-originated loans.

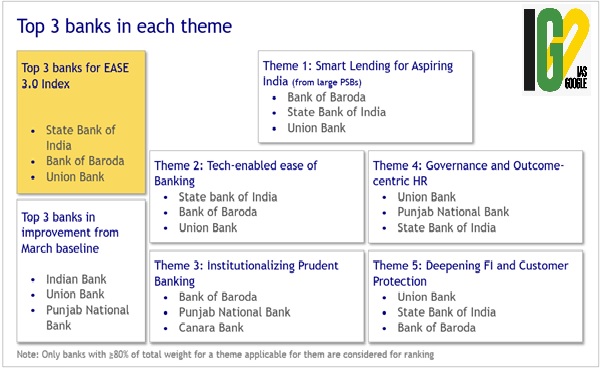
- State Bank of India, Bank of Baroda and Union Bank of India have won the awards for best performing banks for PSB Reforms EASE 3.0 based on the EASE index.
- Indian Bank won the award for the best improvement from the baseline performance.
- SBI, BoB, Union Bank of India, Punjab National Bank and Canara Bank won the top awards in different themes of the PSB Reforms Agenda EASE 3.0.
- Losses in Rural Branches: Most of the rural branches are running at a loss because of high overheads and prevalence of the barter system in most parts of rural India.
- Large Over-Dues: The small branches of commercial banks are now faced with a new problem—a large amount of overdue advances to farmers.
- Non-Performing Assets: The commercial banks at present do not have any machinery to ensure that their loans and advances are, in fact, going into productive use in the larger public interest.
- Advance to Priority Sector: The slow progress is partly attributable to the fact that the bank officials from top to bottom could not accept nationalisation gracefully, i.e. diversion of a certain portion of resources to the top priority and hitherto neglected sectors.
- Gap between Promise and Performance: One major weakness of the nationalised banking system in India is its failure to sustain the desired credit pattern and fill in credit gaps in different sectors.
- The agenda of the workshop was to review State SVEEP Plans & conduct extensive deliberations on the important aspects of SVEEP for a comprehensive strategy for the forthcoming elections.
- The Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) observed that each voter interacts with the election machinery at two critical stages namely enrollment and polling day.
- The workshop stressed that the field teams should ensure that the enrolment process is seamless and polling experience remains pleasant and hassle free for the voters.
- The workshop elaborated on the importance of content strategy and distribution channels as part of the holistic communication plan.
- The seed of SVEEP was born in 2009, out of managerial underlining of the gaps in the registration of citizens as voters and the more glaring gap in turnout from election to election.
- In India, the turnout had historically stagnated around 55-60 percent, thus leaving out the choices of millions of eligible citizens.
- It began with the introduction of planned IEC (Information, Education, and Communication) interventions in the Jharkhand elections of end-2009.

- It is the flagship program of the Election Commission of India for voter education & awareness, spreading voter awareness and promoting voter literacy in India.
- Its primary goal is to build an inclusive & participative democracy by encouraging all eligible citizens to vote and make an informed decision & ethical choice.
- It is designed according to the socio-economic, cultural and demographic profile of the state as well as the history of electoral participation in previous rounds of elections.
- The objectives of SVEEP are:
- Educating civilians about the importance of voting
- Increase participation of people in elections
- Increase participation in registration and turnout
- A person can enroll as a Voter if he/she:
- is an Indian citizen.
- has attained the age of 18 years on the qualifying date i.e. 1st of January of the year of revision of electoral roll.
- is ordinarily resident of the part/polling area of the constituency where you want to be enrolled.
- is not disqualified to be enrolled as an elector.
- TheIndia SARS-CoV-2 Genome (INSACOG) consortium, which tracks emerging variants, has said that some cases of the Delta variant are being “reclassified” to another sub-lineage i.e. AY.12.
- As the virus spreads through the body, it makes copies of itself, which often have small mistakes and changes.
- The Delta variant (B.1.617.2) has given birth to several sub-lineages called‘Delta Plus’ variants that bear most of its characteristic mutations but are different in other ways.
- One of these sub-lineages, AY.12, has all the characteristic Delta mutations except one.
- The reclassification is primarily to assist micro-epidemiology and is not based on acquisition of significant mutations.
- According to INSACOG, it is not known yet whether 12 is clinically different from Delta or B.1.617.2.
- 12 has lost some of the mutations seen in the Delta lineage, such as G142D in spike protein.
- No new mutations of concern are noted in the spike protein of this variant.
- 12, a reassigned sub-lineage of Delta is being seen in many states, but the numbers need closer examination.
- The Delta plus cases, in which12 is included, only number 67, though this is expected to swell after the reclassification.
- It comprises of 10 labs namely DBT-NIBMG Kalyani, DBT-ILS Bhubaneswar, ICMR-NIV Pune, DBT-NCCS Pune, CSIR-CCMB Hyderabad, DBT-CDFD Hyderabad, DBT-InSTEM/ NCBS Bengaluru, NIMHANS Bengaluru, CSIR-IGIB Delhi, and NCDC Delhi.
- The aim of the Indian SARS-CoV-2 Genomics Consortium is to monitor the genomic variations in the SARS-CoV-2 on a regular basis through a multi-laboratory network.
- The consortium will ascertain the status of new variant of SARS-CoV-2in the country.
- It will also establish sentinel surveillance for early detection of genomic variants with public health implication, and determine the genomic variants in the unusual events/trends.
- The INSACOG will have a high level Inter-Ministerial Steering Committee which will provide guidance and oversight to the consortium especially for policy matters.
- The INSACOG will monitor the genomic variations on a regular basis through the multi-laboratory network.
- The DBT-NIBMG as the Coordinating Unit of Genome Sequencing Consortium and will closely work with a Nodal Unit of National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) on activities like SOPs, data annotation, data analysis, data release etc.

- It is an initiative of Ministry of Agriculture & Famers’ Welfare with a special focus on farmers.
- It is organized by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR).
- Under the campaign, the farmers associated with KVK should motivate other farmers for improved farming.
- It will ensure participation of all farmers in various schemes including FPO, Agri Infra Fund, increasing the area of organic farming under traditional farming.
- It is the responsibility of the farmers along with the government to ensure that our products should be of better quality, meet global standards.
- It is important that farmers should be attracted towards costly crops, educated youth should be attracted towards agriculture while being environment-friendly.
- It is Government of India’s flagship programme to improve nutritional outcomes for children, pregnant women and lactating mothers.
- It was launched by the Prime Minister on the occasion of the International Women’s Day on 8 March, 2018from Jhunjhunu in Rajasthan.
- For implementation of POSHAN Abhiyaan the four point strategy/pillarsof the mission are:
- Inter-sectoral convergence for better service delivery
- Use of technology (ICT) for real time growth monitoring and tracking of women and children
- Intensified health and nutrition services for the first 1000
-
- Jan Andolan
- The task of implementation of POSHAN Abhiyaan is to be carried out through the Technical Support Unit (TSU) established at NITI Aayog.
- The companies will now be allowed to provide share-based employee benefits to employees, who are exclusively working for such a company or any of its group companies including a subsidiary or an associate.
- Under the earlier regulations, only permanent employees of the company and its holding and subsidiary companies were eligible for share-based benefits.
- The new regulations broaden this by deleting the word “permanent” and also permitting employees of group/associate companies.
- The experts have said that this will help companies to better use share-based employee benefits for retaining employees for longer period.
- It will imbibe a sense of responsibility and ownership in the employee that will push him/her to work for the growth of the company.
- The new rules will be applicable only to listed companies as these have been framed by SEBI, which only regulates listed companies.
- For unlisted companies, any change needed will have to be brought into the Companies Act 2013, by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs.
- The regulations have dispensed with the requirement of a minimum vesting period and lock-in period (minimum 1 year) for all share benefit schemes.
- It aims to provide immediate relief to an employee or his/her family in instances of permanent incapacity or death.
- The experts feel this will allow companies to provide instant relief to bereaved family members who otherwise would have had to wait.
- The new regulations have extended the time period for appropriating the unappropriated inventory of shares held by the trust from the existing one year to two years, subject to the approval of the Compensation Committee/ Nomination and Remuneration Committee.
- It is expected to provide relief to companies that could not grant or dispose of such excess inventory due to adverse market conditions.
- The regulations now permit companies to transfer excess shares or monies held by a trust upon its winding up, to other share-based employee benefit schemes, subject to approval of the shareholders for such transfer.
- It will give more clarity to companies to manage their assets and financial resources of the trust in a more efficient and organised manner.
- The regulations will now provide companies with flexibility in switching administration of their schemes from the trust route to the direct route, or vice versa, with the approval of the shareholders.
- The companies that opted for any of these routes had tocarry on with that route until the conclusion of the scheme.
- Sweat equity shares will be allowed to be issued for providing the know-how or making available rightsin the nature of intellectual property rights or value additions.
- As per Section 2(88) of the Companies Act, 2013“sweat equity shares” means such equity shares as are issued by a company to its directors or employees at a discount or for consideration, other than cash, for providing their know-how or making available rights in the nature of intellectual property rights or value additions, by whatever name called.
- The regulations have aligned the pricing and the lock-in requirements of the sweat equity shares with the preferential issue norms as provided in the SEBI (Issue of Capital and Disclosure Requirements) Regulations, 2018.
- The maximum yearly limit of sweat equity shares that can be issued by a company listed on the main board has been prescribed at 15% of the existing paid-up equity share capital within the overall limit, not exceeding 25% of the paid-up capital at any time.
- In case of companies listed on the Innovators Growth Platform (IGP), the yearly limit will be 15% and overall limit will be 50% of the paid-up capital at any time.
- It enhanced overall limit for IGP will be applicable for 10 years from the date of the company’s incorporation.
- It will benefit all new start-up companies seeking listing on the IGP platform.

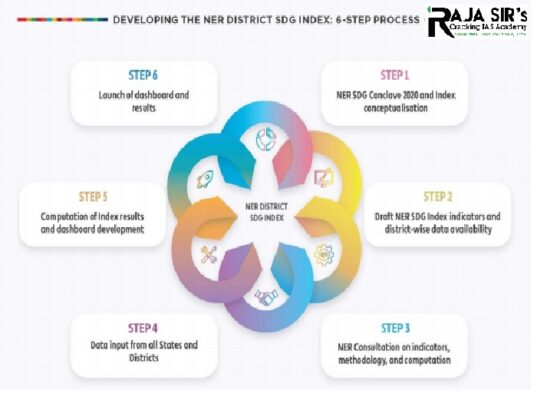
- It is the first edition of SDG Index for the North East Region districts.
- It is developed by NITI Aayog and Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region (MDoNER).
- The technical support is provided by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP).
- It is the first of its kind in the country as it focuses on the North Eastern Region, which is of critical significance to the country’s development trajectory.
- It measures the performance of the districts of the eight States of Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim and Tripura on the Sustainable Development Goals.
- It is based on NITI Aayog’s SDG India Index the principal and official tool for monitoring progress on the SDGs at the national and State/ Union Territory levels.
- It aims at delineating progress at the district level on a basket of indicators and enhancing analytical understanding of sectoral issues as well as data gaps.
- Districts have been classified based on their NER District SDG Index score:
- Aspirant: 0–49
- Performer: 50–64
- Front-Runner: 65–99
- Achiever: 100

- It offers insights into the social, economic, and environmental status of the region and its districts in their march towards achieving the SDGs.
- It is a unique policy tool which has immense potential to measure district level progress, highlight critical gaps, and facilitate resource allocation.
- It will be a handy tool for policy makers in the eight North Eastern States, Ministry of DoNER and other Union Ministries.
- It will help in evidence-based planning, resource allocation, both financial as well as others, and effective supervision and monitoring of the developmental efforts for focused and balanced regional development.
- It will contribute immensely to providing reliable and high-quality data to design initiatives to address inter-State and intra-State disparities and accelerate SDG achievements in the region.
- Out of the 103 districts considered for ranking, 64 districts belonged to the Front Runner category while 39 districts were in the Performer category in the composite score and ranking of districts.
- All districts in Sikkim and Tripura fall in the Front Runner category and there areno districts in the Aspirant or Achiever categories.
- East Sikkim (Score 75.87) ranks first in the region followed by districts Gomati and North Tripura (Score 75.73) in the second position.
- The score for the 103 districts ranges from 00 in Kiphire (NL)to 75.87 in East Sikkim (SK).









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies