- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
27th Aug 2021
PM CHAIRS 37TH PRAGATI - PRO ACTIVE GOVERNANCE AND TIMELY IMPLEMENTATION
Recently, the Prime Minister has chaired the 37th Pro Active Governance and Timely Implementation (PRAGATI) meeting.
PRAGATI Platform



- It is a multi-purpose and multi-modal platform that is aimed at addressing common man’s grievances, and simultaneously monitoring and reviewing important programmes and projects of the Government.
- It was launched in
- It is a three-tier system(PMO, Union Government Secretaries, and Chief Secretaries of the States).
- The Prime Minister will hold a monthly programme where he will interact with the Government of India Secretaries, and Chief Secretaries through Video-conferencing enabled by data and geo-informatics visuals.
- It is aimed at starting a culture of Pro-Active Governance and Timely Implementation.
- It is a robust system for bringing e-transparency and e-accountability with real-time presence and exchange among the key stakeholders.
- It uniquely bundles three latest technologies: Digital data management, video-conferencing and geo-spatial technology.
- It offers a unique combination in the direction of cooperative federalism since it brings on one stage the Secretaries of Government of India and the Chief Secretaries of the States.
- Endemic is derived from Greek en meaning in and demos meaning people.
- It is used to describe a disease that is present at an approximately constant level within a society or country.
- According to the US Centers of Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), endemic refers to the “constant presence and/or usual prevalence of a disease or infectious agent in a population within a geographic area”.
- The experts have written that when epidemics become endemic, they become “increasingly tolerated” and the responsibility of protecting against it shifts from the government to the individual.
- An epidemic, on the other hand, refers to a scenario when the number of cases of the disease increases, often suddenly, which means the cases are more than the expected levels.
- It refers to that a disease reaches an endemic stage when a population learns to live with the conditions.
- It means its spread is limited to a particular area and its rate is predictable.
- Unlike an epidemic, it does not overwhelm a population.
- Every disease pathogen that has affected people over the last several decades stayed in some form or other as it is impossible to fully eradicate them.
- Pathogens like malaria that are as old as humanity still exert a heavy disease burden and so are epidemics like tuberculosis, measles, leprosy, and younger pathogens like Ebola virus, MERS, SARS, and recent SARS-CoV-2.
- Even Plagues returned every decade, each time hitting vulnerable societies and taking its toll during at least six centuries.
- The only disease that has been eradicated through relentless mass vaccination campaigns is Smallpox.
- It would help in establishing mutual cooperation in the areas of Professional Accountancy Training, Professional Ethics, Technical Research, Advancement of Accounting Knowledge, Professional and Intellectual Development.
- It aims to strengthen cooperation in matters of accountancy profession through exchange of views and information.
- It is also intended to promote mutual cooperation through seminars, conferences and joint activities mutually beneficial to both the parties.
- It provide updates on the development of the accountancy profession in India and Russia to promote the profession in the world.
- The parties will also create a linkage to each other's websites as a means of information support.
- It is expected to provide an additional impetus to prospects of the ICAI Members to get professional opportunities in Russia in short to long term future.
- The aim of MoU is to work together to develop a mutually beneficial relationship for the best interest of ICAI members and the two respective organizations.
- With MoU, ICAI would be able to help strengthen the partnership with Russia by providing the Export of Services in Accountancy profession.
- ICAI members are holding middle to top level positions in various organisations across the countries and can influence the decision/policy making strategies of respective organisations of a country.
- ICAI through its vast network of Chapters and Representative Offices is committed to play an important role by sharing the prevalent practices in their respective countries.
- It will enable Government of India to adopt the best practices being followed by ICAI to attract foreign investment and to encourage them to establish their setup in India.
- The MoU will benefit Ministry of Corporate Affairs, Institute of Chartered Accountants of India and Institute of Professional Accountants of Russia.
- It is a statutory body established by an Act of Parliament i.e. The Chartered Accountants Act, 1949.
- It was established for regulating the profession of Chartered Accountancy in the country.
- It functions under the administrative control of the Ministry of Corporate Affairs.
- It is the second largest professional body of Chartered Accountants in the world, with a strong tradition of service to the Indian economy in public interest.
- The affairs of the ICAI are managed by a Council in accordance with the provisions of the Chartered Accountants Act, 1949 and the Chartered Accountants Regulations, 1988.
- Out of 40 members of the institute, 8 are nominated by the Central Government generally representing the Comptroller and Auditor General of India, Securities and Exchange Board of India, Ministry of Corporate Affairs, Ministry of Finance and other stakeholders.
- Cushman & Wakefield’s Manufacturing Risk Index report ranks countries based on a range of factors including:
- Risk and cost factors
- Political and economic risk
- Market conditions and labor costs
- Market Access
- It is based on the most favorable locations for international manufacturing.
- The index ranks 47 countries across Europe, the Americas, and the Asia Pacific.

- China has retained its top position and continues to diversify its manufacturing base.
- The report stated that even with the Biden administration’s concerns about trade, China continues to diversify its base to move up the value chain to focus on telecom, high-tech, and computers.
- Guangdong and Jiangsu regions are spearheading its electronic components and automotive manufacturing, while Zhejiang and Liaoning focus on chemicals and natural resources.
- The US is a desirable hub as it offers a large consumer market as well as incentives at both state and federal levels.
- In the category of the cost scenario, India and Vietnam were overtaken by Indonesia, while China retained its lead position.
- India slipped to the third rank, while Indonesia moved to the second from the fifth spot.
- The report stated that Jakarta’s dipping rents have a part to play in cost effectiveness that pushed Indonesia up by three spots.
- In the category of the risk scenario that takes into account lower levels of economic and political risks, India is nowhere near the top.
- India has been clubbed in the third quartile of the rankings along with Malaysia, Belgium, Indonesia, Bulgaria, Romania, Thailand, Hungary, Colombia, Italy, Peru and Vietnam.
- On top of the first quartile is China, followed by Canada, US, Finland, Czech Republic.
- The second quartile has countries like Lithuania, France, Netherlands, Spain, Poland, Japan, UK etc.
- In the category of the bounce back rating that takes into account a country’s ability to restart its manufacturing sector, India is in the fourth quartile with Sri Lanka, Mexico, Vietnam, Indonesia, Bulgaria, Thailand, Tunisia, Peru, Philippines and Venezuela.
- India has been ranked as the second-most sought-after manufacturing destination in the world.
- It is second only to China and has surpassed the US to bag the second ranking.
- India slipped a rank in the cost scenario and was overtaken by Indonesia.
- India could benefit from relocations from China to other parts of Asia, as it already has an established base in pharmaceuticals, chemicals and engineering sectors.
- The index stated that reforms in land and labour laws are critical to ensure India’s success as a global manufacturing hub.
- Benefits of having a manufacturing set-up in India: Manufacturing set-up requires favorable business conditions, policies along various intricate details, for business to thrive.
- As a manufacturing hub, India provides various advantages for companies worldwide.
- India has relatively cheap land and labor, ever-improving infrastructure, and policies that go in favor of a thriving business.
- Boosting India as a Manufacturing Destination: With the ambition to boost domestic manufacturing in the nation, the government introduced various financial incentives for companies to produce IT hardware.
- The government of India is actively bringing reforms to boost the Indian economy and some of the efforts taken include:
- Accounting as the lowest in Southeast Asia, India has reduced corporate tax from 30% to 25%.
- Government introduced initiatives like ‘Make in India’ and ‘Skill India’ that have achieved a feat in creating job opportunities in the manufacturing sector.
- These initiatives have also enhanced skill development to create a large pool of skilled human resources.
- It is a joint initiative of Bureau of Police Research and Development (BPR&D) and All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE).
- It is a unique national initiative to identify innovative concepts and technology solutions for addressing the security challenges of the 21st century faced by our intelligence agencies.
- The prize money for the winning teams will be Rs. 40 Lakh.
- It will be conducted in two phases:
- In the first phase, participants are expected to submit their concepts against the problem statements which they wish to solve on the portal.
- In the Grand Finale, selected participants are expected to build the solution to demonstrate their concepts and prove to the juries that their ideas are technically feasible and more importantly implementable.
- The participants are expected to develop digital solutions under 6 themes for 20 different challenge statements using new technologies like Artificial Intelligence, Deep Learning, Augmented reality, Machine Learning, etc.
- It is basically focused on following categories:
- Image and Video Analytics
- Sentiment Analysis
- Natural Lang. Processing
- Image & Video Analytics
- Data Analytics
- Fake Content Detection
- Under MANTHAN-2021, the selected youths from education institutions across the country and registered start-ups will participate to offer strong, safe and effective technology solutions using their technical expertise and innovative skills.
- It covers all area that needs reformation from young Innovative minds that will help nation to build systems more secure and scalable without opting foreign tools.
- It was formally established in 1970.
- It was formed with the primary objectives of:
- To take direct and active interest in the issues
- To promote a speedy and systematic study of the police problems
- To apply science and technology in the methods and techniques used by police
- It is working with its 4 divisions of Research, Development, Training and Correctional Administration.
- It is under the administrative control of Ministry of Home Affairs
- It was set up in November 1945 as a national-level apex advisory body to conduct a survey on the facilities available for technical education.
- It aims to promote development in the country in a coordinated and integrated manner.
- As stipulated in the National Policy of Education (1986), AICTE was vested with:
- Statutory authority for planning, formulation, and maintenance of norms & standards
- Quality assurance through accreditation
- Funding in priority areas, monitoring, and evaluation
- Maintaining parity of certification & awards
- The management of technical education in the country
- It was constituted to provide for the establishment of an All India Council for Technical Education with a view to proper planning and co-ordinated development of a technical education system.
- India has achieved emission reduction of 28% over 2005 levels, against the target of 35% by 2030committed in its NDC (Nationally determined contributions).
- It makes India among one of the few countries globally which has kept to its Paris Climate Change (COP21) commitments along with an exponential increase in renewable energy capacity.
- The Indian Power Sector has achieved the coveted milestone of 100 GW of installed Renewable Energy Capacity.
- While 100 GW of capacity has been installed and operationalized, 50 GW of additional capacity is under installation and another 27 GW is under tendering process.
- 5% of India’s installed power generation capacity is based on clean renewable energy sources and with this pace we will reach the target of 40% by 2023.
- India stands at 4th position in the world in terms of installed RE capacity 5th in Solar and4th in Wind energy capacity.
- India plans to continue its momentum in the clean energy sector by systematically scaling up its targets to install 450 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2030from its existing target of 175 GW by 2022.
- The NDCs are at the heart of the Paris Agreement and the achievement of these long-term goals.
- The NDCs embody efforts by each country to reduce national emissions and adapt to the impacts of climate change.
- The Paris Agreement (Article 4, paragraph 2) requires each Party to prepare, communicate and maintain successive nationally determined contributions (NDCs) that it intends to achieve.
- It represent pledges on climate action that seek to limit global warming to well below 2°C, preferably to 1.5 °C, over pre-industrial levels.
- To put forward and further propagate a healthy and sustainable way of living based on traditions and values of conservation and moderation.
- To adopt a climate-friendly and a cleaner path than the one followed hitherto by others at corresponding level of economic development.
- To reduce the emissions intensity of its GDP by 33 to 35 per cent by 2030 from 2005 level.
- To achieve about 40 per cent cumulative electric power installed capacity from non-fossil fuel based energy resources by 2030, with the help of transfer of technology and low cost international finance, including from Green Climate Fund.
- To create an additional carbon sink of 2.5 to 3 billion tonnes of CO2 equivalent through additional forest and tree cover by 2030.
- To better adapt to climate change by enhancing investments in development programmes in sectors vulnerable to climate change, particularly agriculture, water resources, Himalayan region, coastal regions, health and disaster management.
- To mobilize domestic and new and additional funds from developed countries to implement the above mitigation and adaptation actions in view of the resource required and the resource gap.
- To build capacities, create domestic framework and international architecture for quick diffusion of cutting edge climate technology in India and for joint collaborative R&D for such future technologies.

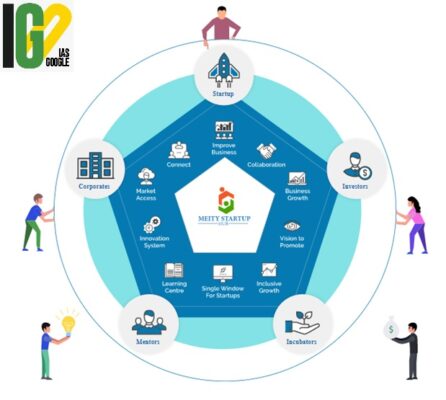
- It is Start-up Accelerators of MeitY for pRoduct Innovation, Development and growth programme of MeitY.
- It is being implemented by MeitY Start-up Hub (MSH).
- It has been developed on the lines of Silicon Valley based accelerator YCombinator.
- It will focus on accelerating the 300 start-ups by providing customer connect, investor connect, and international immersion in next three years.
- An investment of up to ₹ 40 lakh to the start-up based on current valuation and growth stage of the Start-Up will be provided through selected accelerators.
- It will facilitate equal matching investment by the accelerator / investor.
- Only accelerators that have been in the incubation business for at least three years and supported more than 50 startups, with at least 10 having a non-public business will be able to apply for the scheme.
- They must also have operations in India and the necessary space and infrastructure to be eligible.
- It aims to create a conducive platform to Indian Software Product star-ups to enhance their products and securing investments for scaling their business.
- It will provide the funding support to the startups and help in bringing skill sets together which will help them to become successful.
- It will pick up startups that are ready for acceleration stage and will provide them with funding support, mentorship and a lot of other support that is required by startups at this stage.
- It aims to further the Indian start-up growth which has seen the emergence of 63 Unicorns is now the third largest Unicorn hub globally with a total valuation of 168 Bn USD.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies