- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
November 14, 2024 Current Affairs
|
Sudan extends opening of Adre border crossing for aid delivery
Sudan trapped in a ‘nightmare of violence’
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Cardiovascular Kidney Metabolic (CKM) syndrome
Health Burden & Statistics
Challenges in Healthcare Management
Globalization and Lifestyle Impact
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
India tops global diabetes list with 21.2 crore cases in 2022 • The number of adults living with diabetes worldwide has surpassed 80 crore, more than quadrupling since 1990, according to new data released in The Lancet on World Diabetes Day. • In 2022, an estimated 82.8 crore adults had diabetes, an increase of 63 crore from 1990. Of these, 42 crore were women and 40.8 crore were men. • Of the 82.8 crore, India’s share formed over a quarter (21.2 crore). Another 14.8 crore were in China, while 4.2 crore, 3.6 crore and 2.2 crore lived in the US, Pakistan and Brazil, respectively. • The analysis, conducted by the NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC) with support from the World Health Organisation (WHO), highlights the scale of the diabetes epidemic and an urgent need for stronger global action to address both rising disease rates and widening treatment gaps, particularly in low and middle-income countries (LMICs). World Diabetes Day • The United Nations observes November 14 as World Diabetes Day. • It provides an opportunity to raise awareness about diabetes as a critical global public health issue and emphasize the collective and individual actions needed to improve the prevention, diagnosis and management of the condition. • This year’s theme, “Breaking Barriers, Bridging Gaps,” underpins the commitment to reducing the risk of diabetes, and ensuring that all people who are diagnosed with diabetes have access to equitable, comprehensive, affordable and quality treatment and care. Some facts on diabetes: • Diabetes is a chronic disease, which occurs when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin, or when the body cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. This leads to an increased concentration of glucose in the blood (hyperglycaemia). • Type 1 diabetes (earlier known as insulin-dependent or childhood-onset diabetes) is characterised by a lack of insulin production. Type 1 diabetes is a chronic condition in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin by itself. • Type 2 diabetes (earlier known as non-insulin-dependent or adult-onset diabetes) is caused by the body''s ineffective use of insulin. It often results from excess body weight and physical inactivity. Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t make enough insulin. • Gestational diabetes is hyperglycaemia that is first recognised during pregnancy. It can lead to serious health risks for both the mother and child. • The rising prevalence of diabetes and other noncommunicable diseases is driven by a combination of factors — rapid urbanisation, sedentary lifestyles, unhealthy diets, tobacco use, and increasing life expectancy. • Obesity and overweight are the most important risk factors responsible for diabetes. Much of the diabetes burden can be prevented or delayed by behavioural changes favouring a healthy diet and regular physical activity. Key points of the Lancet report: • The study reports that global diabetes prevalence in adults rose from 7 per cent to 14 per cent between 1990 and 2022. • Low and middle-income countries experienced the largest increases, where diabetes rates have soared while treatment access remains persistently low. • In 2022, almost 45 crore adults aged 30 and older — about 59 per cent of all adults with diabetes — remained untreated, marking a 3.5-fold increase in untreated people since 1990. About 90 per cent of these untreated adults are living in low and middle-income countries. • In 2022, almost one third of the 44.5 crore adults (13.3 crore) with untreated diabetes lived in India. • Undiagnosed diabetes has been linked with complications such as diabetic retinopathy — when high levels of blood sugar damage the eye’s retina (which is sensitive to light) — which can potentially cause vision loss and blindness. • The study further reveals substantial global differences in diabetes rates, with the prevalence of diabetes among adults aged 18 and older around 20 per cent in the WHO South-East Asia and the Eastern Mediterranean Regions. These two regions, together with the African Region, have the lowest rates of diabetes treatment coverage, with fewer than four in 10 adults with diabetes taking glucose-lowering medication for their diabetes. • The study was conducted by the NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC), a worldwide network of over 1,500 researchers and practitioners, in collaboration with WHO. It is the first global analysis of trends in both diabetes rates and treatment coverage that is based on data from over 140 million people aged 18 years or older that were included in more than 1,000 studies covering populations in all countries. Countries must take action urgently • Diabetes increases the risk of debilitating complications such as amputation, vision loss, and renal failure, and is associated with cardiovascular disease, dementia, some cancers, and infections such as tuberculosis and severe COVID-19. Diabetes can be detected at the primary health-care level, and treatment with oral hypoglycaemic drugs or insulin, as well as newer injectable medicines, reduces the risk of, and slows progression to, complications and sequelae. • Failure to treat or delay in treatment increases the risk of complications and death. Therefore, diabetes prevalence and diabetes treatment coverage, and how they have changed, are important measures of population health and the performance of health systems. • In 2022, WHO established five global diabetes coverage targets to be achieved by 2030. One of these targets is to ensure that 80 per cent of people with diagnosed diabetes achieve good glycemic control. The latest report underlines the scale and urgency of action needed to advance efforts to close the gap. • To bring the global diabetes epidemic under control, countries must urgently take action. This starts with enacting policies that support healthy diets and physical activity, and, most importantly, health systems that provide prevention, early detection and treatment. Initiatives by Indian govt to support diabetes patients • The government of India has launched several proactive measures to tackle diabetes as part of the broader National Programme for Prevention and Control of Non-Communicable Diseases (NP-NCD) under the National Health Mission (NHM). • The government of India, under the NP-NCD, provides technical and financial assistance to states and Union Territories through the National Health Mission (NHM). • Support is allocated based on state and UT proposals with a focus on prevention and management of diabetes and other non-communicable diseases. • As many as 743 District NCD Clinics and 6,237 Community Health Center NCD Clinics have been established across India to ensure local-level care and accessible services. • Emphasis is on training healthcare personnel, strengthening healthcare infrastructure, and facilitating early diagnosis and referral. • Implemented a population-based initiative that offers screening and control for common NCDs like diabetes, hypertension, and certain cancers. • Targeting individuals over 30, screenings are a core part of the healthcare services provided at Ayushman Arogya Mandirs. • These centers promote preventive health practices, conduct screenings, and engage in community-based wellness initiatives. • Public awareness on diabetes is promoted through observance of national and international health days. • Healthy lifestyle promotion includes guidance from the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) on nutrition. • The Fit India Movement, led by the Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports, and yoga programs from the Ministry of AYUSH encourage active and healthy lifestyles. • Under NP-NCD, states receive financial support for diabetes awareness programs as per their programme implementation plans. • In addition to preventive measures, the NP-NCD also offers financial assistance for purchasing glucometers and diabetes medications, as requested by states and UTs. The NHM’s Free Drugs Service Initiative provides free essential medicines, including insulin, to economically vulnerable groups. • Through the Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Pariyojana (PMBJP), quality generic medications, including insulin, are made available at affordable prices with state collaboration to ensure wider accessibility. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Nasa is planning to lay down gas pipeline on Moon''s South Pole
Key features of the L-SPoP design include:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
NEW FINDINGS ON URANUS The In 1986, NASA’s Voyager 2 spacecraft flew close to Uranus to collect data. During its five-day visit, Voyager 2 sent back important information that shaped how we understand this distant planet.
Findings
Magnetosphere
Plasma
Voyager 2’s Mission
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Panje Wetland
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
RULES UNDER NEW WATER ACT NOTIFIED
Water Rules 2024
What changes were made to the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974, under the amendments in 2024?
Appointment of SPCB chairpersons under the new rule
Role of an adjudicating officer under the new rules
Violation of the Water Act 2024
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
SC slams ‘bulldozer justice’, calls it unconstitutional
Key points of the judgment:
Article 142 empowers the Supreme Court to pass any decree or order necessary for doing complete justice in any case or matter pending before it.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The Green transition India needs As COP29 negotiations unfold amidst global political uncertainties and regional conflicts, India faces the dual challenge of decarbonizing its economy while ensuring sustainable economic growth and attracting climate finance. The country must adopt seven critical shifts to build a green, resilient, and clean energy system that aligns with its growing power demands and emerging climate goals. Key Shifts in India''s Energy Transition
Strategic Approaches for Economic Integration
People-Centric Approach to the Energy Transition
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
West Bank The Israel’s far-right Finance Minister Bezalel Smotrich announced that 2025 would be the year when Israel will annex the occupied West Bank.
|









 Latest News
Latest News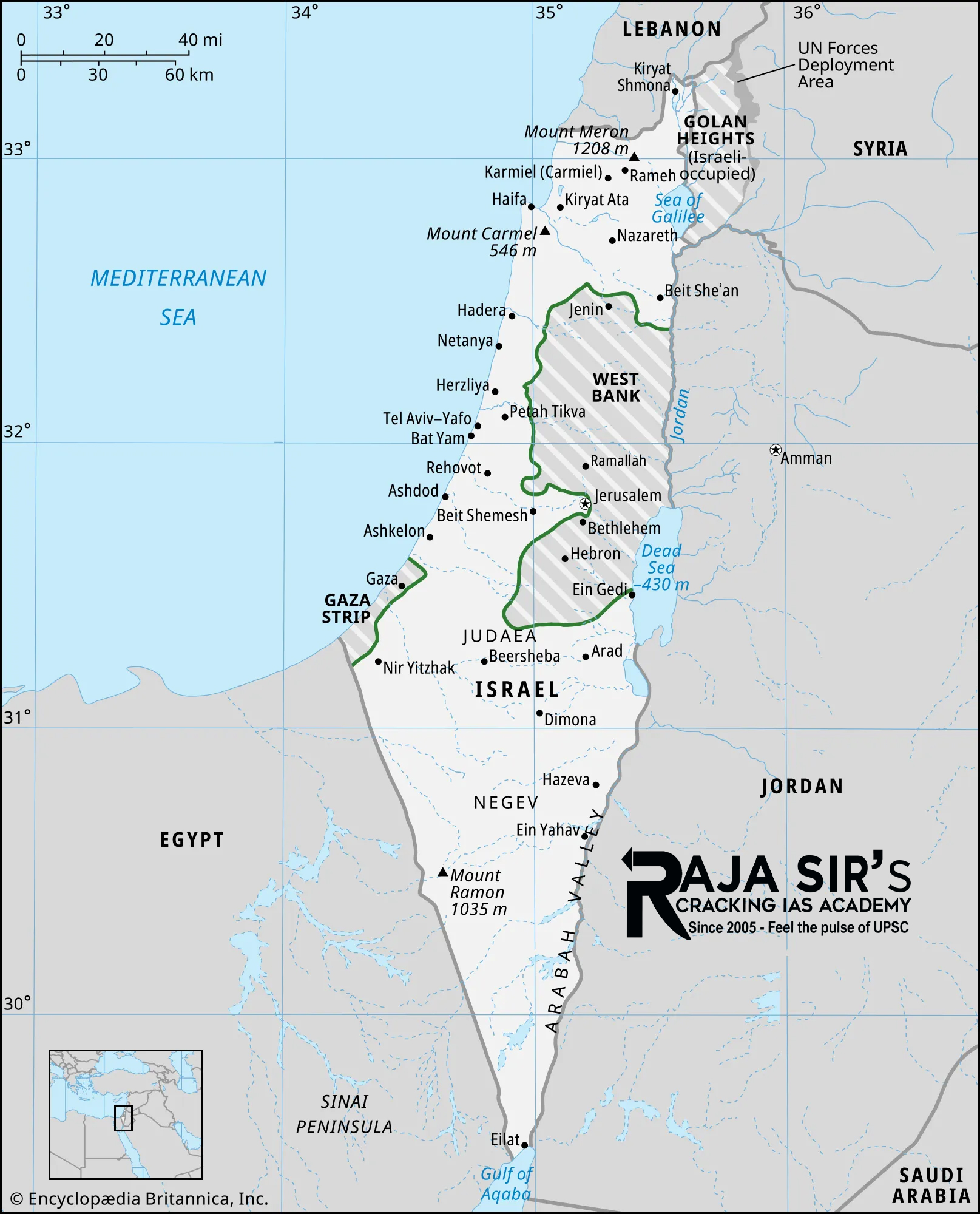
 General Studies
General Studies