- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
September 25, 2024 Current Affairs
CPENGRAMS brings Financial Empowerment for Family Pensioners and Super-Senior Pensioners
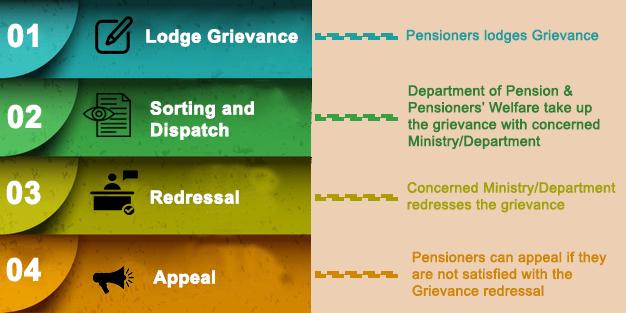
- The Department of Pension and Pensioners’ Welfare (DoPPW) is committed towards effective and expeditious redressal of grievances through Centralized Pension Grievance Redress and Monitoring System (CPENGRAMS), an online portal.
- To ensure this, the grievances are monitored in terms of pace and quality of the redressal by conducting Inter-Ministerial Review Meetings (IMRMs), both in physical and virtual mode.
- The resolution of these cases including those of Family Pensioners and Super-senior Pensioners has brought financial stability and social empowerment in the life of pensioners.
- CPENGRAMS
- CPENGRAMS is an online web-enabled systemfor speedy redressal of grievances related to pension by various Central Government Ministries/ Departments/Organizations.
- This system, besides providing a faster access to pensioners, offers the following online facilities:
- Registration of pension grievances online
- Forwarding of reminderson line
- Query on the statusof any of the registered grievances
- Available (24*7) basis for submission of grievance online
- It has been developed with the objective of speedy redress and effective monitoring of the grievances besides providing fast access to pensioners.
- Pensioners can also appeal if they are not satisfied with the redressal of their grievance.
Swachh Vayu Diwas: India’s Commitment to Clean Air
International Day of Clean Air for Blue Skies
Establishment: Designated by the United Nations General Assembly in 2019 to raise awareness about air quality and its impact on health and climate.
- Theme for 2024: "Invest in #CleanAirNow" emphasizes the urgency of investment in measures that ensure clean air.
- Significance: Highlights the global commitment to combat air pollution, urging nations to prioritize air quality management for better health outcomes.
Swachh Vayu Divas 2024
- Key Outcomes:
- National Clean Air Programme (NCAP): Focused actions have led to significant reductions in air pollution across 95 cities.

Impressive Statistics:
- 51 cities reported PM10 reductions of over 20%.
- 21 cities achieved reductions exceeding 40% compared to the baseline year of 2017-18.
- Recognition: The event featured the Swachh Vayu Survekshan Awards, rewarding cities for outstanding efforts in improving air quality.
National Clean Air Programme (NCAP)
- Launch Year: 2019.
- Objective: Aims to reduce PM10 concentrations by 20-30% by 2024-25 (revised to 40% by 2025-26).
- Coverage: Targets 131 cities across 24 states, recognizing the urgent need for cleaner air due to rapid urbanization and industrialization.
- Financial Commitment: ₹19,614.44 crores allocated for air quality initiatives from FY 2019-20 to FY 2025-26, with ₹11,211.13 crores already released for implementing City Action Plans (CAPs).
- Air Quality Monitoring: The initiative includes 1510 monitoring stations across 543 cities to track ambient air quality.
Implementation Strategies
- City Action Plans (CAPs): Developed for all 131 cities, these plans address specific pollution sources such as:
- Dust from Construction and Demolition: Implementing dust control measures.
- Vehicular Emissions: Promoting cleaner fuels and electric vehicles.
- Waste Management: Reducing open burning of waste and enhancing solid waste management practices.
- Public Engagement: Establishment of Public Grievance Redressal Portals to handle citizen complaints regarding air pollution.
- Emergency Response Systems: Developed for rapid action during air quality crises, ensuring timely interventions based on air quality alerts.
Supporting Initiatives
- Nagar Van Yojana: Launched in 2020, this initiative aims to create urban forests (Nagar Vans) to enhance green cover, improve air quality, and provide recreational spaces for residents.
- Ek Ped Maa Ke Naam: Encourages tree planting by citizens to foster community involvement and environmental stewardship.
- Air Quality Index (AQI): Communicates air quality levels in a simplified manner, categorizing conditions from "Good" to "Severe" based on pollutant concentrations and their health impacts.
- Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) Programme: Promotes the use of ethanol in fuel to reduce vehicular emissions and reliance on fossil fuels.
- Air Quality Early Warning System: Implemented in cities like Delhi, Kanpur, and Lucknow to provide timely alerts about deteriorating air quality, enabling preemptive action.
Raksha Mantri Shri Rajnath Singh inaugurates 41st Indian Coast Guard Commanders’ Conference in New Delhi
Key Highlights
- Focus: Strategic, operational, and administrative discussions on maritime security.
- Role of ICG: Ensures the security of India’s coastline and Exclusive Economic Zone; prevents terrorism, arms, and drug trafficking.
- Technological Shift: Emphasis on transitioning to a technology-oriented force, incorporating AI, drones, and modern tech.
- Government Commitment:
- 31 ships worth over ₹4,000 crore being built by Indian shipyards.
- Procurement of advanced equipment like Multi-Mission Maritime Aircraft and Fast Patrol Vessels.
- Collaboration: Interaction with Chief of Defence Staff and Navy Chief to enhance maritime security cooperation.
- Evaluation: Commanders to assess operational initiatives and ongoing projects related to ''Make in India'' and ''Aatmanirbhar Bharat''.
Indian Coast Guard:
- It is an armed force that protects India''s maritime interests and enforces maritime law, with jurisdiction over the territorial waters of India, including its contiguous zone and exclusive economic zone.
- History: it was formally established in 1978 by the Coast Guard Act, 1978 as an independent Armed force of India.
- Parent ministry: It operates under the Ministry of Defence.
- Administration: The organization is headed by the Director General Indian Coast Guard (DGICG).
- HQ: Coast Guard Headquarters (CGHQ) is located at New Delhi.
Functions:
- Preventing Smuggling: One of the primary duties of the ICG is prevention of smuggling through maritime routes.
- Aid to Civil Authority: It has also rescued approximately 13,000 personnel till date during various ‘Aid to Civil Authority’ operations viz. assistance provided to civil authorities during floods, cyclones and other natural calamities; most recently during the recent floods in Maharashtra, Karnataka and Goa.
- Maritime Security:It is also collaborating with littoral countries to combat transnational maritime crimes and enhance maritime safety in its area of responsibility and in the Indian Ocean Region.
- Under SAGAR'' - Security and Growth for all in the Region & ''Neighbourhood First'' policy, the ICG has nurtured professional relationships across oceans and established ties with countries in the Indian Ocean Region for Ocean Peacekeeping.
- Role in Disaster Management: The ICG has successfully averted major ecological disasters and emerged as the‘First Responder’ in the region.
Expanding Horizons in Space Sector: From Lunar Exploration to a National Space Station
India’s Space Exploration Initiatives
- India is embarking on a significant expansion of its space program, with several visionary missions approved by the Union Cabinet under the leadership of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
- These initiatives reflect India''s commitment to becoming a key player in global space exploration, technological innovation, and industry collaboration.
Key Missions and Projects
- Chandrayaan-4 Mission
- Objective: The primary aim of the Chandrayaan-4 mission is to develop and demonstrate the technologies required for safely returning lunar samples to Earth. This mission is a crucial step toward establishing capabilities for future manned missions to the Moon, planned for 2040.
- Focus Areas:
- Advanced technologies for docking and undocking.
- Safe landing on the lunar surface.
- Lunar sample collection and analysis back on Earth.
- Timeline: The mission is expected to be completed within 36 months following its approval.
- Budget: ₹2,104.06 crore, which covers spacecraft development, two launches using the LVM3 vehicle, deep space network support, and special design validation tests.
- Impact: This mission is anticipated to boost India’s self-reliance in space technologies, create employment opportunities, and foster collaboration with Indian industries and academia through workshops and knowledge-sharing initiatives.
- Venus Orbiter Mission (VOM)
- Objective: The VOM aims to place a scientific spacecraft in orbit around Venus to study its surface, atmospheric processes, and the influence of the Sun on its environment. Understanding Venus''s transformation from a potentially habitable planet to its current state will provide insights into planetary evolution.
- Launch Date: The mission is scheduled for March 2028.
- Budget: ₹1,236 crore, with ₹824 crore allocated for spacecraft development, including its payloads and technology elements.
- Significance: This mission will enhance India’s capabilities in planetary exploration and involve significant collaboration with Indian industries. It also offers opportunities for academic institutions to train students in relevant areas of space technology.
- Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS)
- Objective: The establishment of the first module of the BAS represents a major expansion of the Gaganyaan program, focusing on the technologies necessary for building and operating an Indian space station.
- Timeline: The operational goal for BAS is set for 2035, with the program including an Indian crewed mission to the Moon by 2040.
- Funding: The revised Gaganyaan program now has a total budget of ₹20,193 crore, with an additional ₹11,170 crore approved for new initiatives.
- Impact: The program is expected to significantly enhance microgravity research and technology development while creating employment in high-tech sectors. The missions will include four launches by 2026 and four additional missions focused on technology demonstration by 2028.
Union Budget 2024-25
- Venture Capital Fund: A ₹1,000 crore fund has been established to support space startups, aimed at catalyzing growth in the space sector and positioning India as a key player in the global space economy.
Union MoS for Health and Family Welfare, Shri Prataprao Jadhav Launches Tobacco Free Youth Campaign 2.0 to Protect the Health and Well-Being of India’s Youth
Key Highlights of Tobacco Free Youth Campaign 2.0
- Objective: To protect young people''s health from tobacco''s harmful effects and encourage a tobacco-free lifestyle.
- Statistics: Approximately 1.3 million deaths annually in India attributed to tobacco use.
Campaign Focus (60 Days):
- Public Awareness: Educate about tobacco dangers, especially targeting youth and rural communities.
- Tobacco-Free Educational Institutions (ToFEI): Ensure compliance to keep schools and colleges tobacco-free.
- Law Enforcement: Strengthen enforcement of COTPA 2003 and PECA 2019 to restrict youth access to tobacco.
- Tobacco-Free Villages: Encourage community efforts to eliminate tobacco.
- Social Media Outreach: Utilize digital platforms to spread anti-tobacco messages among youth.
Pledges and Participation:
- Participants took the ‘Say No To Tobacco’ pledge.
- Involvement of celebrities and influencers to amplify the campaign’s message.
Educational Initiatives:
- Launch of WHO educational video for schools on the effects of tobacco.
- Release of three important guidelines:
- Health Workers Guide
- SOPs for Tobacco-Free Villages
- Guidelines for Law Enforcement (2024)
About tobacco cultivation:
- Tobacco cultivation in India was introduced by the Portuguese in 1605.
Area and production:
- In India tobacco is predominantly cultivated in Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Karnataka, UP and Bihar.
- Gujarat accounts for 45 per cent of the area (0.13 M ha) and 30 percent of production (0.16 M t). Productivity is also highest (1700 kg ha-1) in Gujarat followed by AP.
Types of tobacco:
- Anand area of Gujarat grows wholly bidi tobacco.
- Nipani area of Karnataka grows bidi tobacco.
- North Bihar and Bengal area has both tabacum and rustica types used in the manufacture of hookah and to a limited extent chewing and snuff types.
- Madurai and Coimbatore area of Tamil Nadu grow cigars, filter, binder and chewing tobacco.
Climate and soil:
- Tobacco is grown when the mean temperature is 20° to 27°C.
- When grown as a rainfed crop, it requires at least about 500 mmof well distributed rainfall during crop growing season.
- It is not usually grown where rainfall exceeds 1200 mm during the season.
Govt Schemes and initiatives for Tobacco Control in India
- Cigarettes Act 1975- The Act is largely limited to statutory warnings like ‘Cigarette Smoking is Injurious to Health’ to be displayed on cigarette packs and advertisements. However, it did not include non-cigarettes.
- The Cigarettes and Other Tobacco Products (Prohibition of Advertisement and Regulation of Trade and Commerce, Production, Supply, and Distribution) Act (COTPA) 2003- The act contains 33 sections governing the production, advertisement, distribution, and consumption of tobacco in India.
- WHO’s framework convention on Tobacco Control- India is one of the 168 signatories of the WHO’s Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (FCTC). It was launched in 2005. It aims to reduce tobacco usage worldwide by helping countries develop demand and supply reduction strategies.
- Food Safety and Standards Act 2006- Government of India has issued regulations under the Food Safety and Standards Act 2006 which lay down that tobacco or nicotine cannot be used as ingredients in food products.
- Cable Television Networks Amendment Act of 2000- It prohibited the transmission of advertisements on tobacco and liquor in India.
- Prevention and Control of Pollution Act of 1981- The Act recognized smoking as an air pollutant.
- The Motor Vehicles Act 1988- It made smoking illegal in public vehicle.
- National Tobacco Control Programme (NTCP), 2008- The objective of the programme was to control tobacco consumption and minimize tobacco consumption related deaths. The activities include- training and capacity building, information, education, and communication (IEC) activities; reporting survey and surveillance and tobacco cessation.
- Tobacco Cessation- The program provides targeted support to help people overcome the personal challenge of maintaining efforts to quit tobacco use. Tobacco cessation clinics have been set up across the country as part of the program.
- Tobacco Taxation- According to WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic 2017, cigarette taxes in India are amongst the highest in the world. Cigarettes are subjected to high and discriminatory rates of taxation, as compared to other tobacco products. As of 2014-15 Government collected 87% of its total tobacco revenue from legal cigarettes









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies