- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
Structure and Functions of Liver
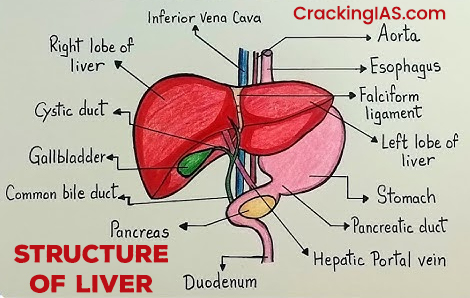
The liver is one of the most vital organs in the human body and plays an important role in various physiological processes. The liver in the human body is located on the right side of the upper abdominal portion near the stomach and intestines and beneath the diaphragm. It weighs approximately 1.5 kg in adults. The cells of the liver are called hepatocytes, and the study of the liver is known as hepatology.
- The Liver Anatomy starts with its division into two lobes, namely the right lop (larger) and the left lobe (smaller).
- The Liver consists of functional units called lobules, which are the basic structural or the building blocks of the liver.
- Each lobule consists of hepatocytes (liver cells) that are in plates radiating from a central vein.
- Sinusoids are capillaries within the liver lobules where blood flows and undergo filtration and exchange.
- The hepatic portal vein brings deoxygenated blood from the intestines, which contain nutrients and toxins, to be processed by the liver.
- The hepatic artery supplies pure/oxygenated blood to the liver.
- Bile ducts carry bile produced by hepatocytes to the gallbladder and small intestine.
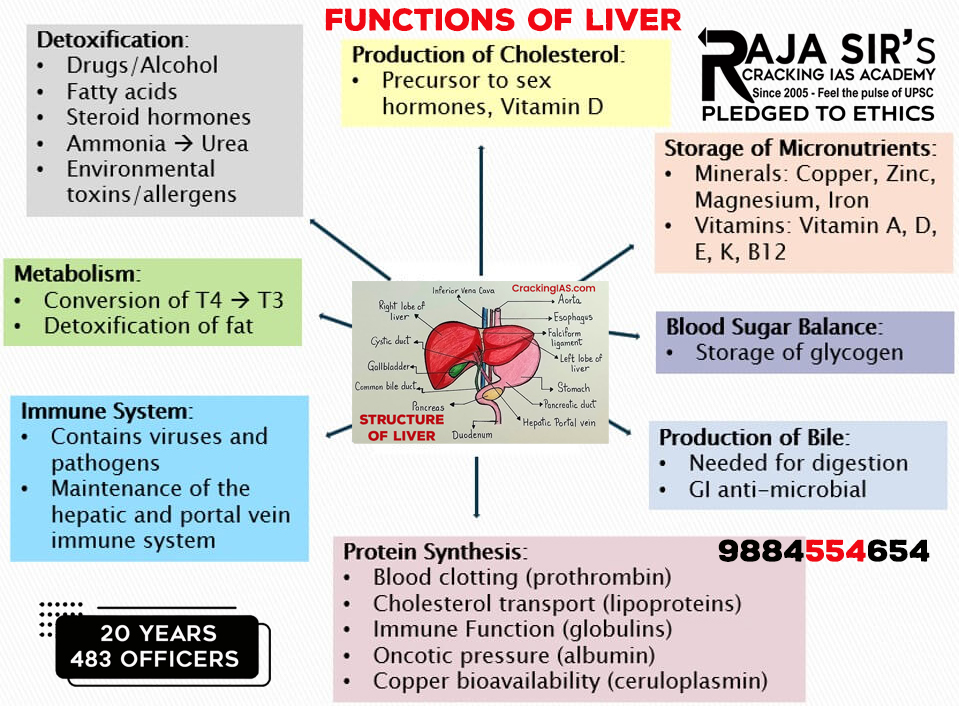
Functions of the Liver
- Metabolism of Nutrients: The liver helps in many metabolic activities that help in providing energy to the body. Some of them are:
- It converts and stores glucose into glycogen (glycogenesis).
- It may also convert glycogen back into glucose when the body needs energy.
- It helps in the metabolism of different macronutrients - fats, proteins, and carbohydrates - by secreting its juices (bile juice) into the digestive tract.
- Detoxification: The liver also works as a detoxifying organ. Detoxification is the breaking down and neutralisation of harmful substances like drugs, alcohol, and metabolic waste products, such as converting ammonia into urea, which is then excreted by the kidneys.
- Bile Production and Secretion: Bile juice is essential for digestion and absorption of fats in the digestive tract. It provides a basic pH for the acidic food coming from the stomach, which protects our intestines from the harmful effects of gastric acid. Bile juice is stored in the gallbladder and released into the small intestine when needed.
- Regulation of Blood Clotting: It manufactures blood clotting factors such as Prothrombin and fibrinogen, which are the main components for the clotting of blood, hence preventing excessive blood loss.
- Blood Circulation in the Liver: Hepatic Portal System
- As mentioned earlier, the liver processes the nutrients and also detoxifies harmful substances. But the question is: How do these substances reach the liver? The answer is the Hepatic Portal system. The system is the specialised network of veins that plays an important role in transporting blood from the digestive organs to the liver.
- The System carries blood from the intestines, spleen, and pancreas to the liver for processing, and after being processed, blood is transferred to the heart via the inferior Vena Cava.
 Liver Diseases
Liver Diseases
Liver conditions can vary from mild to injurious in terms of severity. These liver ailments can impair the liver’s function temporarily as well as permanently. Some of them are:
- Hepatitis: Inflammation of the liver is mostly caused by various viral infections like Hepatitis A, B, C, etc., alcohol, or toxins. Symptoms of hepatitis are fatigue, jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes), and abdominal pain.
|
The main types of hepatitis are Hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E, each caused by a different virus and differing in transmission, severity, and treatment. The Government of Tamil Nadu''s official health website also offers information on hepatitis, stating that Hepatitis A is a highly contagious liver infection caused by the Hepatitis A Virus (HAV). Other types include non-viral causes like alcoholic hepatitis, autoimmune hepatitis, and drug-induced liver injury. Types of Hepatitis
|
- Cirrhosis: Scarring of the liver tissue, mainly due to chronic alcohol abuse or viral hepatitis. It impairs liver function and can lead to liver failure.
- Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Accumulation of fat in the liver cells. Fatty liver symptoms often include obesity, diabetes, and excessive alcohol use. Fat liver disease causes tiredness, discomfort in the abdomen, and an enlarged liver.
- Liver Cancer: Known as hepatocellular carcinoma, cancer develops most frequently in individuals who suffer from chronic diseases such as cirrhosis and hepatitis.
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin & sclera (white part of the eyes) is caused due to excess bilirubin in the blood. It is a symptom of liver disease or bile duct obstruction.
- Liver Failure: when the liver loses its ability to function due to extensive damage. It can be acute (sudden) or chronic (long-term).
|
Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease Exercise is a cornerstone in managing metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), according to a study led by an Indian-origin researcher. Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD), previously known as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), is a chronic liver condition linked to fat accumulation in the liver. MASLD is a liver disease caused by excessive fat build-up in the liver, often linked to metabolic dysfunction. It can progress to inflammation (MASH) and severe complications like liver fibrosis or cirrhosis. Causes:
Symptoms:
Diseases Associated:
Treatment:
|
Liver Function Test (LFTs)
The liver function test (LFT), also known as the Hepatic panel or liver panel, is a series of tests of different enzymes and proteins that contribute to liver health. Any increase or decrease in these enzymes and proteins may lead to Liver dysfunction. Some Examples of LFT are:
- Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT): ALT is an enzyme mainly in the liver. High ALT levels in the blood indicate liver cell damage or inflammation that is commonly caused by diseases such as hepatitis or fatty liver. It is a sensitive marker of liver injury.
- Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST): AST is a type of enzyme that can be found in the liver, heart, and muscles. It is usually tested simultaneously with ALT. High levels of AST can suggest liver damage, but it could also point to heart or muscle conditions. The ratio of ALT to AST is often used to diagnose liver damage specifically.
- Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP): ALP is an enzyme present in the liver, bones, and bile ducts. Elevated levels are suggestive of liver or bile duct disease, such as cholestasis (obstruction of bile flow) or gallstones. It is often used to assess the health of the biliary system.
- Bilirubin (Total and Direct): Bilirubin is a product of hemolysis or the breaking down of red blood cells. An elevated level of bilirubin in the blood can cause jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes) that is associated with liver diseases, such as cirrhosis or bile duct obstruction. Bilirubin is reported as total and direct (conjugated) bilirubin.
- Albumin: Albumin is a protein produced by the liver, which helps in maintaining blood pressure and fluid balance. Low levels of albumin indicate liver disease, such as cirrhosis, where the ability of the liver to produce proteins is impaired.
Questions
|
1. |
Production of which one of the following is a function of the liver? I.A.S. (Pre) 2007 (a) Lipase (b) Urea (c) Mucus (d) Hydrochloric acid |
|
2. |
Extra glucose in body gets converted into glycogen and is stored in (a) Stomach (b) Liver (c) Pancreas (d) Bile |
|
3. |
Bile is produced in which part of the body? (a) Liver (b) Spleen (c) Gallbladder (d) Pancreas |
|
4. |
Which is the largest gland in the human body? (a) Liver (b) Pancreas (c) Thyroid gland (d) Stomach |
|
5. |
Digestion of Lipids takes place in the presence of some of the following: 1. Bile acids 2. Lipase 3. Pepsin Of these, (a) Only 1 is correct (b) Only 1 and 3 are correct (c) Only 1 and 2 are correct (d) 1, 2 and 3 are correct |
|
6. |
How is liver affected on fasting for more than 10 days? (a) Glucose level in liver diminished (b) Glucose level in liver increases (c) In liver triglycerides decrease (d) In liver triglycerides increase |
|
7. |
Energy is stored in liver and muscles in the form of: (a) Carbohydrate (b) Fat (c) Protein (d) Glycogen |
|
8. |
Assertion (A): In human body, the liver has an important role in fat digestion. Reason (R): Liver produces two important fat digesting enzymes. I.A.S. (Pre) 2008 Code: (a) Both (A) and (R) are individually true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). (b) Both (A) and (R) are individually true, but (R) is not a correct explanation of (A). (c) (A) is true, but (R) is false. (d) (A) is false, but (R) is true. |
|
9. |
Which one of the following statements is not correct? I.A.S. (Pre) 2019 (a) Hepatitis B virus is transmitted much like HIV. (b) Hepatitis B. unlike Hepatitis C, does not have a vaccine. (c) Globally, the number of people infected with Hepatitis B and C viruses arc several times more than those infected with HIV. (d) Some of those infected with Hepatitis B and C viruses do not show the symptoms for many years. |
|
10. |
Consider the following statements: 1. Hepatitis B is several times more infectious than HIV / AIDS. 2. Hepatitis B can cause liver cancer. Which of the statement given above is/are correct?. I.A.S. (Pre) 2010 (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 |









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies